All Refrigeration Systems Must Have Accumulators To Operate Safely
Breaking News Today
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
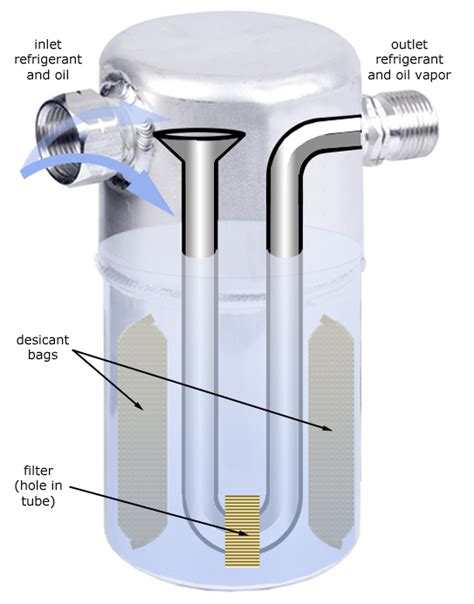
Table of Contents
All Refrigeration Systems Must Have Accumulators for Safe Operation: A Comprehensive Guide
Refrigeration systems are ubiquitous, silently working behind the scenes to keep our food fresh, our homes cool, and our industrial processes running smoothly. However, the complex interplay of pressures, temperatures, and refrigerants necessitates critical safety components. One such essential component is the accumulator. This article will delve into why all refrigeration systems must have accumulators to ensure safe and efficient operation. We'll explore the accumulator's function, various types, common applications, and the dire consequences of operating without one.
Understanding the Role of an Accumulator in a Refrigeration System
An accumulator, in the context of refrigeration, is a pressure vessel designed to store liquid refrigerant and separate liquid from vapor. This seemingly simple function is crucial for preventing several potentially catastrophic scenarios. Think of it as a safety net, safeguarding the compressor from liquid slugging and protecting the entire system from damage.
Liquid refrigerant entering a compressor can cause severe damage, including:
- Hydraulic lock: Liquid refrigerant is incompressible, meaning it can't be compressed by the compressor's pistons or vanes. This can lead to immediate and catastrophic compressor failure.
- Valve damage: The high pressure created by the incompressible liquid can damage compressor valves, requiring costly repairs or replacements.
- Bearing failure: The shockwaves generated by liquid slugging can damage the compressor's bearings, shortening its lifespan and potentially leading to complete system failure.
The accumulator prevents these problems by providing a reservoir for liquid refrigerant. As the refrigerant flows from the evaporator, the accumulator separates the liquid from the vapor phase. This ensures only superheated vapor enters the compressor, preventing liquid slugging and protecting the vital components.
Different Types of Accumulators and Their Applications
Accumulators aren't all created equal. They come in various designs, each suited to specific applications and system requirements. The most common types include:
1. Horizontal Accumulators: These are cylindrical vessels typically mounted horizontally. Their large surface area allows for efficient separation of liquid and vapor. They are commonly used in larger refrigeration systems.
2. Vertical Accumulators: As the name suggests, these are mounted vertically, often space-saving in applications where horizontal space is limited. They are frequently seen in smaller systems or where space optimization is a priority.
3. Suction Line Accumulators: These are installed directly in the suction line, providing a readily available reservoir of liquid refrigerant near the compressor. This design offers immediate protection against liquid slugging.
4. Liquid Line Accumulators: Less common than suction line accumulators, these are situated in the liquid line, primarily used for larger systems with significant liquid refrigerant flow. They help ensure steady refrigerant flow and prevent liquid hammer.
The choice of accumulator type depends on several factors, including:
- System size and capacity: Larger systems generally require larger capacity accumulators.
- Refrigerant type: The properties of the refrigerant can influence the design and size of the accumulator.
- System layout: The physical constraints of the system's layout will determine the orientation and placement of the accumulator.
- Operating conditions: Ambient temperature and system pressure variations influence the accumulator's design parameters.
Consequences of Operating a Refrigeration System Without an Accumulator
The absence of an accumulator is a recipe for disaster. Operating a refrigeration system without this crucial component exposes it to significant risks, resulting in:
-
Compressor failure: This is arguably the most significant consequence. The compressor, a major and expensive component, is extremely vulnerable to liquid slugging. Failure will likely result in costly repairs or replacement, significant downtime, and potential safety hazards related to refrigerant leaks.
-
System damage: The impact of liquid slugging isn't confined to the compressor. Other components like valves, expansion devices, and even the piping itself can suffer damage from the high pressures and shockwaves.
-
Refrigerant leaks: Damage to system components can easily lead to refrigerant leaks. Besides the financial cost of replacing refrigerant, these leaks present a serious environmental and safety hazard, as many refrigerants are harmful to the environment and pose health risks.
-
Reduced efficiency: Even if catastrophic failure is avoided, the absence of an accumulator can negatively impact system efficiency. Inefficient refrigerant flow and pressure fluctuations can reduce cooling capacity and increase energy consumption.
-
Safety hazards: Refrigerant leaks pose severe safety risks, ranging from mild discomfort to severe health problems and even death depending on the refrigerant used and the concentration of the leak. Furthermore, a system operating without an accumulator may experience unpredictable pressure surges and malfunctions, posing additional safety hazards for personnel nearby.
Accumulator Sizing and Selection – Crucial Considerations
Choosing the right accumulator is not simply a matter of picking the first one you find. Proper sizing and selection are crucial for ensuring optimal system performance and safety. Several factors must be taken into account:
-
Refrigerant Charge: The amount of refrigerant in the system directly impacts the required accumulator volume.
-
System Operating Conditions: Temperature variations and pressure fluctuations must be considered during sizing.
-
Safety Factor: A safety factor is always incorporated to provide additional margin for unexpected surges or fluctuations.
-
Accumulator Type: Different accumulator types have different design characteristics and sizing methodologies.
Improper sizing can lead to inadequate liquid storage, resulting in the very problems the accumulator is intended to prevent. An undersized accumulator will struggle to handle liquid slugs, while an oversized one might occupy valuable space unnecessarily.
Regular Maintenance and Inspection – Ensuring Long-Term Safety and Efficiency
While the accumulator itself is a relatively low-maintenance component, regular inspection and maintenance are essential to ensure it remains effective throughout the lifespan of the refrigeration system.
-
Visual Inspection: Regularly check for leaks, corrosion, or any physical damage.
-
Pressure Testing: Periodic pressure testing verifies the integrity of the vessel and its ability to withstand operating pressures.
-
Internal Cleaning: In certain cases, particularly in older systems, internal cleaning might be necessary to remove accumulated debris or contaminants.
Ignoring regular maintenance can compromise the accumulator's ability to perform its critical functions, ultimately jeopardizing the safety and efficiency of the entire refrigeration system.
Conclusion: The Indispensable Role of the Accumulator
The accumulator is not a luxury; it's a critical safety component for any refrigeration system. Its function of separating liquid and vapor refrigerant protects the compressor and other system components from damage, prevents refrigerant leaks, and ensures safe and efficient operation. Operating a refrigeration system without an accumulator is akin to driving a car without brakes – incredibly risky and potentially disastrous. Understanding the vital role of the accumulator, selecting the appropriate type and size, and implementing regular maintenance protocols are indispensable for ensuring the longevity, efficiency, and above all, safety of any refrigeration system. Ignoring these precautions not only risks significant financial losses but also poses serious environmental and safety hazards. Therefore, the unwavering inclusion of an accumulator remains paramount for responsible refrigeration system design and operation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Budget Should Be Based On A Persons Income
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is The Maximum Penalty For Habitual Willful Noncompliance
Mar 21, 2025
-
Creating As A Designer Is All About
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Is This An Autobiographical Piece Of Art
Mar 21, 2025
-
Unit 3 Progress Check Mcq Ap Chemistry Answers
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about All Refrigeration Systems Must Have Accumulators To Operate Safely . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
