Ap World History Unit 2 Review Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
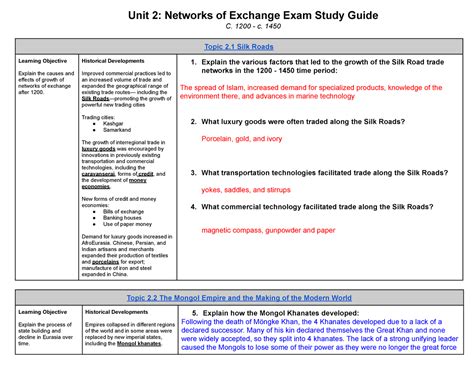
Table of Contents
AP World History Unit 2 Review: Mastering the Classical Era (c. 600 BCE – 600 CE)
This comprehensive guide will help you conquer AP World History Unit 2, focusing on the Classical Era (c. 600 BCE – 600 CE). We'll cover key empires, societal structures, and technological advancements, all tailored for effective exam preparation. Think of this as your ultimate AP World History Unit 2 review Quizlet alternative – more detailed, more engaging, and ultimately, more helpful.
Key Empires of the Classical Era: A Comparative Analysis
This period witnessed the rise and fall of significant empires, each leaving a lasting impact on world history. Understanding their similarities and differences is crucial.
1. The Persian Empire:
- Centralized Government: The Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great implemented an efficient administrative system, using satraps (provincial governors) and a sophisticated network of roads and communication. This efficient bureaucracy allowed for effective control over a vast territory.
- Religious Tolerance: Unlike many empires of the time, Persia generally practiced religious tolerance, allowing conquered peoples to maintain their own beliefs and customs. This fostered stability and minimized resistance.
- Royal Road: This extensive network facilitated trade, communication, and military movements, connecting the far reaches of the empire. This infrastructure investment was key to maintaining control.
2. The Greek City-States (Poleis):
- Direct and Representative Democracy: Athens, particularly, experimented with direct democracy, involving citizens directly in governance. Other city-states, like Sparta, favored oligarchies or other forms of government. Understanding the variations in Greek governance is key.
- Hellenistic Culture: Alexander the Great’s conquests spread Greek culture (Hellenistic culture) across a vast area, influencing art, architecture, philosophy, and science. This cultural fusion created a unique blend of traditions.
- Competition and Warfare: The constant competition and warfare between Greek city-states, exemplified by the Peloponnesian War, ultimately weakened them, making them vulnerable to conquest. Analyzing these conflicts is critical to understanding the era's dynamics.
3. The Roman Empire:
- Republic to Empire: Rome transitioned from a republic, with a senate and elected officials, to an empire under emperors, marking a significant shift in power structures. This transition was marked by internal strife and instability.
- Pax Romana: This "Roman Peace" was a period of relative stability and prosperity within the empire, fostering economic growth and cultural development. Understanding the factors contributing to, and the limits of, this peace is vital.
- Infrastructure and Technology: The Romans excelled in engineering and infrastructure, building roads, aqueducts, and public buildings that endured for centuries. Analyzing Roman engineering's impact on their society and longevity is important.
- Law and Governance: Roman law had a profound and lasting impact on legal systems worldwide. The development and influence of Roman law should be understood.
4. The Mauryan and Gupta Empires of India:
- Centralized Administration vs. Decentralized Governance: The Mauryan Empire under Chandragupta Maurya was highly centralized, whereas the Gupta Empire was more decentralized, allowing for greater regional autonomy. This contrast reveals differing approaches to imperial control.
- Hinduism and Buddhism: Both empires were significantly influenced by Hinduism and Buddhism, shaping their social structures, beliefs, and cultural practices. Analyzing the interaction between religion and politics is crucial.
- Technological and Scientific Advances: India made significant contributions in mathematics, astronomy, and medicine during this period, including the development of the concept of zero. This illustrates India's significant contribution to global knowledge.
5. The Han Dynasty of China:
- Confucianism and Bureaucracy: The Han Dynasty implemented a meritocratic bureaucracy based on Confucian principles, emphasizing education and civil service examinations. This established a lasting pattern in Chinese governance.
- Economic Prosperity and Trade: The Han Dynasty enjoyed a period of significant economic prosperity, with extensive trade networks extending along the Silk Road. Understanding the factors contributing to this economic success is vital.
- Technological Innovations: The Han Dynasty saw advancements in agriculture, technology, and manufacturing, further strengthening its economy and power. These innovations laid the groundwork for future Chinese advancements.
Societal Structures and Interactions
Beyond political structures, understanding the social fabric of these classical societies is crucial.
Social Hierarchies:
Each empire had its own distinct social hierarchy. For instance, Rome's hierarchy was largely based on wealth and status, while India's caste system rigidly defined social roles. Comparing and contrasting these hierarchies is essential for a complete understanding. Consider exploring terms like patriarchy, slavery, and social mobility within each context.
Trade and Exchange:
The Silk Road, connecting East and West, facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies. Understanding the extent and impact of this trade network is critical. Explore the role of merchants, the spread of religions (like Buddhism), and the economic consequences of long-distance trade.
Religious and Cultural Interactions:
This period witnessed the spread of major religions like Buddhism, Christianity, and Hinduism. Examining their interactions, syncretism (the blending of different religious traditions), and the impact on cultural landscapes is vital. Focus on the factors contributing to their spread and their impact on different societies.
Technological Advancements and Their Impact
Classical civilizations made significant technological advancements that shaped their societies and influenced future developments.
Agriculture and Irrigation:
Advancements in irrigation techniques allowed for increased agricultural productivity, supporting larger populations and enabling the growth of cities. Examples include the qanat system in Persia and sophisticated irrigation techniques in China.
Metallurgy and Weaponry:
The development of iron metallurgy led to the creation of more effective weaponry and tools, contributing to military dominance and societal advancement. Analyze the role of iron in shaping warfare and the societal impact of new technologies.
Writing and Record Keeping:
The development and refinement of writing systems allowed for the recording of history, literature, and laws, preserving knowledge and contributing to cultural transmission. Consider the importance of literacy and how writing systems differed across cultures.
Preparing for the AP World History Exam: Tips and Strategies
Effective preparation is key to succeeding on the AP World History exam.
Active Recall and Practice:
Instead of passively rereading notes, actively recall key information. Use flashcards (though not just Quizlet!), practice questions, and create timelines to reinforce your learning.
Comparative Analysis:
The AP World History exam emphasizes comparative analysis. Practice comparing and contrasting different civilizations, their societal structures, and their achievements.
Theme-Based Organization:
Organize your studying around major themes like state building, technology, culture, and interaction. This will help you synthesize information and draw connections between different civilizations.
Contextualization:
Always place events within their historical context. Understanding the causes and consequences of events is crucial.
Utilizing Multiple Resources:
Don't limit yourself to a single resource. Explore textbooks, primary source documents, and reputable online materials to gain a comprehensive understanding of the period.
This comprehensive review offers a robust alternative to a simple AP World History Unit 2 Review Quizlet. By engaging with the material actively and employing effective study strategies, you can confidently tackle the Classical Era and achieve success on the AP World History exam. Remember to focus on understanding the interconnectedness of events and civilizations, and don't hesitate to explore further resources to deepen your knowledge. Good luck!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Yo 1 Of 1 Cafe En La Manana
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Topics Relate Directly To The Themes Developed In Frankenstein
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Undefined Terms Are Needed To Define Parallel Lines
Mar 25, 2025
-
Match Each Health Screening To The Correct Disease
Mar 25, 2025
-
The Financial Responsibility Law Requires You To Have
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Ap World History Unit 2 Review Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
