Capitalism Is An Economic System In Which Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 24, 2025 · 7 min read
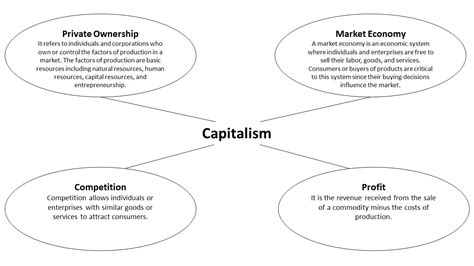
Table of Contents
Capitalism: An Economic System – A Deep Dive
Capitalism, a dominant economic system shaping our global landscape, is far more complex than a simple definition suggests. This in-depth exploration will dissect its core tenets, explore its various forms, analyze its advantages and disadvantages, and address common misconceptions. We'll delve into the nuances of capitalist principles, investigating its historical evolution, its impact on society, and its future prospects.
What is Capitalism? A Definition Beyond the Basics
Capitalism is an economic system characterized by private ownership of the means of production, market-based competition, and the profit motive. In essence, individuals and corporations, not the state, control the resources and production processes. This system thrives on the free exchange of goods and services, driven by supply and demand. However, this seemingly straightforward definition hides a multitude of variations and complexities.
Key Characteristics of Capitalism:
- Private Property: Individuals and businesses have the right to own and control property, including land, factories, and resources. This fosters innovation and investment, as owners have a vested interest in the success of their ventures.
- Free Markets: Prices are determined by supply and demand, with minimal government intervention. This competition ideally leads to efficiency and innovation as businesses strive to offer the best goods and services at the most competitive prices.
- Profit Motive: The pursuit of profit drives economic activity. Businesses aim to maximize their profits, leading to investment, expansion, and job creation. This incentive is considered a crucial engine of economic growth.
- Competition: Multiple businesses compete for customers, leading to lower prices, better quality products, and greater innovation. This competition is often considered the cornerstone of capitalist efficiency.
- Limited Government Intervention: While the degree of government intervention varies across capitalist systems, the ideal is minimal interference in the free market. This allows for greater economic freedom and flexibility.
Variations in Capitalist Models: Laissez-faire vs. Mixed Economies
It's crucial to understand that capitalism isn't monolithic. Different countries and societies implement capitalist principles in diverse ways. Two prominent examples are laissez-faire capitalism and mixed economies.
1. Laissez-faire Capitalism: This represents a "pure" form of capitalism with minimal government regulation. The belief is that the market will self-regulate, leading to optimal efficiency and economic growth. Historically, this model has been associated with periods of rapid industrialization and wealth creation, but also with significant income inequality and potential for market failures.
2. Mixed Economies: The majority of modern capitalist economies fall under this category. Mixed economies combine elements of free markets with government intervention. Governments may regulate industries, provide social safety nets (like unemployment benefits and healthcare), and invest in public goods (like infrastructure and education). This approach seeks to balance the benefits of free markets with social welfare considerations, mitigating some of the negative consequences of pure capitalism.
The Advantages of Capitalism: Innovation, Efficiency, and Growth
Capitalism's success stems from several key advantages:
- Innovation and Technological Advancement: The profit motive incentivizes businesses to constantly innovate and improve their products and services. This leads to technological advancements that benefit society as a whole. Competition further pushes businesses to adopt new technologies and processes to gain a competitive edge.
- Economic Efficiency: Market forces, driven by supply and demand, allocate resources efficiently. Businesses respond to consumer demand, producing goods and services that people want and need. This contrasts with centrally planned economies where misallocation of resources is a common problem.
- Economic Growth: The pursuit of profit stimulates investment and economic growth. Increased investment in capital goods (machinery, technology) leads to higher productivity and economic expansion. This growth, in turn, creates jobs and raises living standards.
- Consumer Choice: A competitive market offers consumers a wide range of choices regarding goods and services. This empowers consumers and leads to greater satisfaction. The ability to choose promotes market dynamism and keeps businesses accountable.
- Individual Freedom: Capitalism often aligns with individual freedoms, emphasizing personal responsibility and the right to pursue one's own economic interests. This entrepreneurial spirit fuels innovation and economic dynamism.
The Disadvantages of Capitalism: Inequality, Instability, and Externalities
Despite its advantages, capitalism also presents significant challenges:
- Income Inequality: Capitalism can exacerbate income inequality, concentrating wealth in the hands of a few while leaving many others behind. This disparity can lead to social unrest and instability. The gap between the rich and the poor can widen significantly, creating social and economic tensions.
- Economic Instability: Capitalist systems are prone to economic cycles, including booms and busts. Recessions and depressions can cause widespread unemployment and suffering. The pursuit of profit can sometimes lead to reckless speculation and financial instability.
- Market Failures: Free markets don't always operate perfectly. Market failures occur when the market fails to allocate resources efficiently, leading to inefficiencies, monopolies, or negative externalities. Examples include pollution and environmental damage.
- Exploitation of Labor: The pursuit of profit can sometimes lead to the exploitation of workers, with low wages, poor working conditions, and insufficient worker protections. This can create significant social inequalities and ethical concerns.
- Monopoly Power: Unfettered capitalism can lead to the concentration of economic power in the hands of a few large corporations. These monopolies can stifle competition, raise prices, and limit consumer choice.
Addressing the Criticisms: Mitigating Capitalism's Drawbacks
Many of the criticisms leveled against capitalism can be addressed through appropriate regulations and policies. This doesn't necessarily equate to abandoning capitalism entirely, but rather to modifying and improving the system.
- Progressive Taxation: Progressive tax systems, where higher earners pay a larger percentage of their income in taxes, can help redistribute wealth and reduce income inequality. This can fund social programs and alleviate poverty.
- Social Safety Nets: Government-provided social safety nets, such as unemployment benefits, healthcare, and affordable housing, can protect vulnerable populations from the harsh realities of market fluctuations. These programs mitigate the risks associated with economic downturns.
- Environmental Regulations: Strong environmental regulations are needed to address the negative externalities of capitalist production, such as pollution and climate change. These regulations help internalize environmental costs and promote sustainable practices.
- Labor Laws: Robust labor laws, including minimum wage laws, worker safety regulations, and protections against discrimination, are essential to prevent exploitation and ensure fair treatment of workers. Strong labor unions can also play a critical role in advocating for workers' rights.
- Antitrust Laws: Antitrust laws are crucial to preventing monopolies and fostering competition. These laws prevent anti-competitive practices and ensure fair market conditions.
The Future of Capitalism: Adapting to Change
Capitalism is constantly evolving, adapting to new technological advancements, social changes, and global challenges. The future of capitalism likely hinges on its ability to address its inherent shortcomings and adapt to a changing world.
- Sustainable Capitalism: Growing awareness of environmental issues is pushing for the development of more sustainable forms of capitalism. Businesses are increasingly adopting environmentally friendly practices and investing in renewable energy.
- Technological Disruption: Rapid technological advancements are reshaping the economy, creating new opportunities and challenges. Artificial intelligence, automation, and the gig economy are transforming the nature of work and requiring adaptations to the capitalist model.
- Globalization and Trade: Globalization has intertwined economies worldwide, creating both opportunities and challenges. Managing global trade effectively and fairly requires international cooperation and regulations.
- Social Responsibility: Increasingly, consumers and investors are demanding greater social responsibility from businesses. Companies are being pressured to consider the ethical and social impact of their operations.
Conclusion: A nuanced understanding of a complex system
Capitalism is a multifaceted and dynamic economic system with both significant advantages and inherent flaws. Its success hinges on a balance between free markets and appropriate government regulation. Addressing issues like income inequality, economic instability, and environmental degradation is crucial to ensuring a more just and sustainable capitalist system in the future. Understanding the nuances of this system – its variations, its strengths, and its weaknesses – is essential for informed participation in the economic discourse and for shaping a more equitable and prosperous future. This deep dive has aimed to provide a comprehensive overview of capitalism, illuminating its complexities and challenges for a better grasp of its role in our globalized world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Set Of Characters With The Same Design And Shape
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Main Therapeutic Goal Of Rebt Is To
Mar 26, 2025
-
Presence Of Chronic Suprapubic Catheter Icd 10
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Model Does An Antivirus Software Operate Off Of
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Jungle By Upton Sinclair Answer Key
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Capitalism Is An Economic System In Which Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
