Presence Of Chronic Suprapubic Catheter Icd 10
Breaking News Today
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
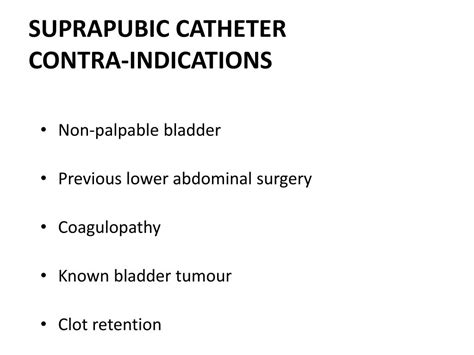
Table of Contents
Presence of Chronic Suprapubic Catheter: ICD-10 Coding and Implications
The presence of a chronic suprapubic catheter represents a significant clinical condition requiring accurate ICD-10 coding for proper documentation and billing. This article delves into the intricacies of ICD-10 coding for this condition, exploring various scenarios, associated complications, and the importance of precise coding for healthcare professionals. We will also discuss the implications of this coding for patient care, reimbursement, and public health data analysis.
Understanding Suprapubic Catheters
A suprapubic catheter (SPC) is a tube inserted surgically through the abdominal wall into the bladder. Unlike urethral catheters, SPCs bypass the urethra, offering several advantages in specific clinical situations. These advantages include:
- Reduced risk of urethral trauma and infection: This is particularly crucial for patients with urethral strictures, prostate enlargement, or recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- Improved patient comfort: SPCs often provide more comfort compared to urethral catheters, especially in long-term use.
- Enhanced mobility and quality of life: The external portion of the SPC is typically smaller and less obtrusive, allowing for greater freedom of movement.
However, SPCs are not without potential complications, including infection, bleeding, bladder stones, and catheter blockage. The "chronic" designation implies long-term use, usually extending beyond several weeks. This prolonged presence necessitates careful monitoring and management.
ICD-10 Coding for Chronic Suprapubic Catheter
The primary ICD-10 code for the presence of a chronic suprapubic catheter is Z99.11 - Presence of indwelling urinary catheter. This code is assigned irrespective of the catheter's type (urethral or suprapubic). It's crucial to remember that this code reflects the presence of the catheter and not the underlying condition necessitating its use.
Why is Z99.11 used and not another code?
Z99.11 is a supplementary code, meaning it's used to provide additional context about the patient's circumstances. It doesn't represent a disease itself but rather a status. Using this code allows for accurate tracking of patients with indwelling catheters, regardless of the reason for catheterization.
Critical Considerations for Accurate Coding:
-
Underlying Condition: The primary diagnosis should always reflect the underlying medical reason for requiring the suprapubic catheter. This could range from neurogenic bladder dysfunction (e.g., multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury) to bladder outlet obstruction (e.g., benign prostatic hyperplasia, stricture) or post-operative urinary retention. These underlying conditions would receive their respective ICD-10 codes, alongside Z99.11.
-
Complications: If the patient experiences complications associated with the SPC, such as UTIs, bladder stones, or catheter-related bloodstream infections, these complications should be coded separately using their corresponding ICD-10 codes. For example, an UTI might be coded as R69 (Urinary Tract Infection), which would then be linked to the Z99.11 and the primary underlying condition.
Examples of ICD-10 Coding Scenarios
Let's examine different clinical scenarios and their respective ICD-10 coding:
Scenario 1: A 70-year-old male with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) requiring a chronic suprapubic catheter for bladder drainage.
- Primary Diagnosis: N40.0 (Benign prostatic hyperplasia)
- Supplementary Code: Z99.11 (Presence of indwelling urinary catheter)
Scenario 2: A 35-year-old female with multiple sclerosis experiencing neurogenic bladder dysfunction and requiring a chronic suprapubic catheter.
- Primary Diagnosis: G35 (Multiple sclerosis)
- Secondary Diagnosis: N31.9 (Unspecified urinary tract infection)
- Supplementary Code: Z99.11 (Presence of indwelling urinary catheter)
Scenario 3: A 60-year-old male post-prostatectomy with a chronic suprapubic catheter due to persistent urinary retention.
- Primary Diagnosis: N42 (Post-operative urinary retention) or a more specific post-prostatectomy ICD code.
- Supplementary Code: Z99.11 (Presence of indwelling urinary catheter)
Implications of Accurate ICD-10 Coding for Suprapubic Catheters
Accurate ICD-10 coding for chronic suprapubic catheters holds significant implications for various aspects of healthcare:
-
Reimbursement: Accurate coding is essential for proper reimbursement from insurance providers. Incorrect coding can lead to claim denials or delays, impacting healthcare facilities' financial stability.
-
Public Health Surveillance: Accurate data on the prevalence of SPC use and associated complications are vital for public health surveillance and research. This information can help identify trends, improve treatment strategies, and inform the development of preventative measures.
-
Quality Improvement: Data on complications associated with SPCs allows for the identification of areas for quality improvement within healthcare facilities. Analyzing these data can lead to better practices in catheter insertion, maintenance, and infection prevention.
-
Patient Care: Accurate documentation ensures that patients receive appropriate care and monitoring. It also ensures effective communication among healthcare professionals involved in the patient's care.
Preventing Complications Associated with Chronic Suprapubic Catheters
While Z99.11 captures the presence of the catheter, successful management necessitates proactive measures to minimize associated complications:
-
Strict aseptic technique: Maintaining sterile conditions during catheter insertion and care is paramount to preventing infections.
-
Regular catheter care: Regular cleaning and maintenance of the catheter and surrounding skin reduce the risk of infection and encrustation.
-
Fluid intake: Adequate fluid intake helps to flush out the bladder and prevent the formation of bladder stones.
-
Regular monitoring: Close monitoring of the patient's urine output, signs of infection, and any catheter-related problems is essential.
Conclusion
The presence of a chronic suprapubic catheter is a complex clinical situation requiring precise and accurate ICD-10 coding. Z99.11 serves as a vital supplementary code, but its application must always be complemented by the primary diagnosis explaining the necessity for the catheter. Accurate coding is essential for proper reimbursement, effective public health surveillance, enhanced quality improvement initiatives, and ultimately, improved patient outcomes. Understanding the nuances of ICD-10 coding for SPCs is crucial for healthcare professionals to ensure the best possible care for their patients while navigating the complexities of medical billing and documentation. Furthermore, focusing on preventative strategies and prompt management of complications will lead to better patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs. This comprehensive approach ensures that patients with chronic suprapubic catheters receive the optimal level of care while contributing to robust and reliable healthcare data.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The 4 Ps Of Marketing Frondescence Food Truck
Mar 29, 2025
-
Which Exfoliant Product Is Used Before Extractions To Soften Debris
Mar 29, 2025
-
The Lean Philosophy Suggests That Workers Are
Mar 29, 2025
-
Explain The Difference Between Symmetry And Asymmetry
Mar 29, 2025
-
A Persons Metabolism Remains Constant Throughout Life
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Presence Of Chronic Suprapubic Catheter Icd 10 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
