Congestive Heart Failure Results In Which Of The Following Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 18, 2025 · 7 min read
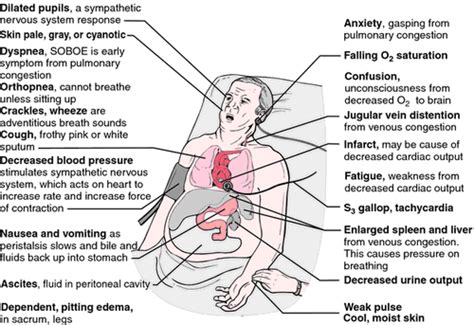
Table of Contents
Congestive Heart Failure: Understanding the Consequences
Congestive heart failure (CHF), also known as heart failure, is a serious condition where the heart can't pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. This isn't necessarily a complete heart failure, but rather a failure of the heart to function effectively. Understanding the consequences of CHF is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals. This comprehensive guide will explore the various results and complications associated with congestive heart failure, helping to answer the question: "Congestive heart failure results in which of the following?" We'll examine the symptoms, underlying causes, and the wide-ranging effects this condition can have on the body.
The Underlying Mechanisms of Congestive Heart Failure
Before delving into the consequences, it's important to grasp the fundamental mechanisms behind CHF. The heart, a powerful muscle, works tirelessly to pump oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. In CHF, this pumping action is weakened. This can stem from various factors, including:
-
Weakened Heart Muscle (Systolic Dysfunction): The heart muscle may become weakened and enlarged (cardiomegaly), reducing its ability to contract forcefully and pump blood effectively. This is often associated with conditions like coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and high blood pressure.
-
Stiff Heart Muscle (Diastolic Dysfunction): The heart muscle may become stiff and less able to relax and fill with blood properly between beats. This reduces the amount of blood the heart can pump out with each contraction. High blood pressure and certain heart diseases contribute to this.
-
Valve Problems: Damaged or narrowed heart valves can impede the smooth flow of blood through the heart, increasing the workload and ultimately leading to CHF.
-
Heart Rhythm Disturbances (Arrhythmias): Irregular heartbeats can disrupt the efficient pumping action of the heart, contributing to the development of CHF.
These underlying issues create a cascade of consequences, affecting multiple organ systems.
Manifestations of Congestive Heart Failure: The Symptoms
The symptoms of CHF are diverse and depend on the severity of the condition and the specific areas of the heart affected. Many people experience symptoms gradually, while others may experience a sudden onset. Common symptoms include:
-
Shortness of breath (dyspnea): This is often one of the earliest and most prominent symptoms. It can range from mild breathlessness during exertion to severe breathlessness at rest (orthopnea) or while lying down (paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea). This is because the weakened heart struggles to supply enough oxygen to the body's tissues.
-
Fatigue and weakness: The reduced blood flow and oxygen delivery to the body's tissues results in profound fatigue and weakness, even with minimal physical activity.
-
Edema (swelling): Fluid buildup can occur in various parts of the body, including the ankles, feet, legs, and lungs. This swelling is caused by the heart's inability to effectively pump blood, leading to fluid retention.
-
Persistent cough or wheezing: Fluid buildup in the lungs can cause a persistent cough, often accompanied by wheezing.
-
Rapid or irregular heartbeat (palpitations): The heart may attempt to compensate for its reduced pumping ability by beating faster, leading to palpitations.
-
Reduced urine output: The kidneys may reduce urine production in an attempt to retain fluid, contributing to edema.
-
Confusion or impaired thinking: Reduced blood flow to the brain can cause cognitive impairment and confusion, particularly in older adults.
-
Chest pain or pressure: Though not always a primary symptom, chest discomfort can occur due to the increased workload on the heart muscle.
Congestive Heart Failure: A Multi-System Impact
The consequences of CHF extend far beyond the heart itself. The reduced cardiac output affects numerous organ systems, resulting in a range of complications:
1. Respiratory System Complications:
- Pulmonary edema: Fluid buildup in the lungs causes shortness of breath, wheezing, and coughing. This is a life-threatening complication requiring immediate medical attention.
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): In severe cases, pulmonary edema can progress to ARDS, a condition characterized by severe lung inflammation and impaired gas exchange.
- Pneumonia: Fluid buildup in the lungs increases the risk of bacterial or viral pneumonia.
2. Renal System Complications:
- Acute kidney injury (AKI): Reduced blood flow to the kidneys can lead to AKI, impairing their ability to filter waste products from the blood.
- Chronic kidney disease (CKD): Long-term reduced blood flow to the kidneys can contribute to CKD, a progressive loss of kidney function.
3. Neurological System Complications:
- Cognitive impairment: Reduced blood flow to the brain can cause confusion, memory loss, and difficulty concentrating.
- Stroke: CHF can increase the risk of stroke due to the formation of blood clots and the potential for reduced blood flow to the brain.
4. Hepatic System Complications:
- Congestive hepatopathy: Fluid buildup in the liver (due to impaired blood flow) can lead to liver damage and dysfunction.
5. Gastrointestinal System Complications:
- Ascites: Fluid buildup in the abdominal cavity, causing abdominal swelling.
- Anorexia and nausea: Reduced appetite and nausea are common due to decreased blood flow to the gastrointestinal tract.
Diagnostic Methods for Congestive Heart Failure
Diagnosing CHF involves a thorough evaluation of symptoms, medical history, physical examination, and various tests, including:
- Echocardiogram: This ultrasound test provides detailed images of the heart's structure and function, revealing the extent of damage and pumping capacity.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test measures the electrical activity of the heart, identifying irregularities in heart rhythm.
- Chest X-ray: This can reveal fluid buildup in the lungs and enlargement of the heart.
- Blood tests: These can help assess kidney function, electrolyte levels, and the presence of other underlying conditions.
- Cardiac catheterization: This invasive procedure involves inserting a thin, flexible tube into the heart to measure blood pressure and assess blood flow.
Management and Treatment Strategies for CHF
The treatment of CHF aims to manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve the quality of life. Strategies often include:
- Lifestyle modifications: Dietary changes (low-sodium diet), regular exercise (as tolerated), and weight management are crucial.
- Medications: Various medications are used to address different aspects of CHF, including diuretics (to reduce fluid retention), ACE inhibitors and ARBs (to reduce blood pressure and improve heart function), beta-blockers (to slow heart rate and improve contractility), and digoxin (to improve heart function).
- Device therapy: In some cases, devices like implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) or cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be implanted to help regulate heart rhythm and improve pumping efficiency.
- Heart transplantation: In severe cases, a heart transplant may be considered as a last resort.
Prognosis and Prevention of Congestive Heart Failure
The prognosis for CHF varies greatly depending on the severity of the condition, the presence of other medical problems, and the response to treatment. Early diagnosis and aggressive management can significantly improve the outcome.
Preventing CHF involves addressing underlying risk factors, such as:
- Controlling high blood pressure: Maintaining healthy blood pressure levels is crucial in preventing heart damage.
- Managing diabetes: Effective control of diabetes reduces the risk of heart disease.
- Quitting smoking: Smoking significantly increases the risk of heart disease.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Obesity strains the heart, increasing the risk of CHF.
- Regular exercise: Regular physical activity strengthens the heart and improves overall cardiovascular health.
- Managing cholesterol levels: High cholesterol contributes to atherosclerosis, which can damage the heart.
Answering the Quizlet Question: Congestive Heart Failure Results In…
Based on the information provided, congestive heart failure results in a wide range of complications affecting multiple organ systems. A comprehensive answer to the "Congestive heart failure results in which of the following?" quizlet question might include, but is not limited to:
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea): A cardinal symptom due to fluid buildup in the lungs.
- Fatigue and weakness: Due to reduced oxygen delivery to tissues.
- Edema (swelling): Fluid retention in various parts of the body.
- Pulmonary edema: Fluid in the lungs, a life-threatening complication.
- Acute kidney injury (AKI): Reduced blood flow to the kidneys.
- Cognitive impairment: Reduced blood flow to the brain.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats exacerbating the condition.
- Increased risk of stroke: Due to blood clot formation and reduced cerebral blood flow.
- Reduced exercise tolerance: Due to decreased cardiac output and oxygen delivery.
- Ascites: Fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of CHF's consequences is essential for effective management and improved patient outcomes. This condition requires a holistic approach involving lifestyle modifications, medication, and potentially advanced therapies to address the systemic impacts and improve quality of life. Early diagnosis and proactive management are key to mitigating the severe consequences of this prevalent cardiovascular disease.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
If An Individual Is Heterozygous For A Particular Trait
Mar 18, 2025
-
If You Add More Enzyme The Reaction Will
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Purpose Of A Hazcom Program Is To Ensure That
Mar 18, 2025
-
Describe The Continuous Nature Of The Physical Fitness Concept
Mar 18, 2025
-
High Levels Of Cholesterol Can First Lead Directly To
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Congestive Heart Failure Results In Which Of The Following Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
