Correctly Label The Pathway For The Cardiac Conduction System.
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
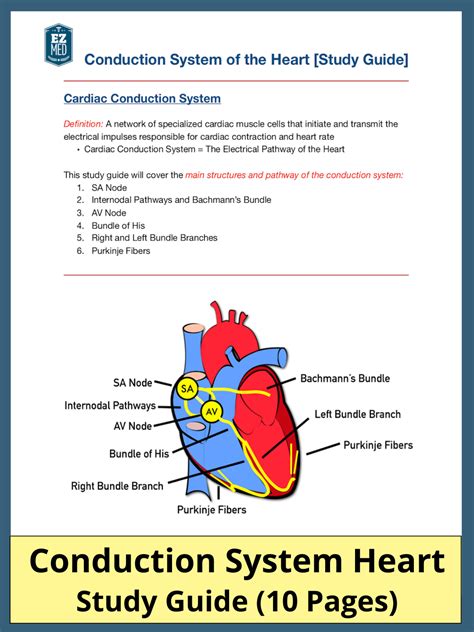
Table of Contents
Correctly Labeling the Pathway for the Cardiac Conduction System
The human heart, a tireless powerhouse, beats rhythmically throughout our lives, thanks to a sophisticated internal electrical conduction system. Understanding this system is crucial for anyone studying physiology, cardiology, or related fields. This article provides a comprehensive guide to correctly labeling the pathway of the cardiac conduction system, covering its components, functions, and clinical significance. We'll delve into the intricacies of each structure, ensuring a clear and thorough understanding of this vital physiological process.
The Cardiac Conduction System: A Masterpiece of Electrical Coordination
The cardiac conduction system is a network of specialized cardiac muscle cells that initiate and coordinate the contraction of the heart chambers. This coordinated contraction, or synchronous depolarization, ensures efficient blood pumping throughout the circulatory system. Disruptions in this system can lead to various cardiac arrhythmias, highlighting the critical importance of its precise function.
The system is composed of several key components, each playing a unique role in orchestrating the heartbeat:
1. Sinoatrial (SA) Node: The Heart's Natural Pacemaker
The sinoatrial (SA) node, located in the right atrium near the superior vena cava, is the primary pacemaker of the heart. It spontaneously generates electrical impulses at a rate of approximately 60-100 beats per minute (bpm) in a healthy adult. These impulses are the initiating event of each heartbeat. The SA node's unique ability to depolarize spontaneously stems from its specialized pacemaker cells, which exhibit automaticity—the capacity to generate action potentials without external stimulation.
Key Characteristics of the SA Node:
- Automaticity: Spontaneous generation of action potentials.
- Rhythmicity: Regular generation of action potentials.
- Conductivity: Transmission of impulses to adjacent cardiac cells.
The SA node's inherent rhythmicity sets the heart rate, though this can be influenced by the autonomic nervous system (ANS). The sympathetic nervous system increases heart rate, while the parasympathetic nervous system (via the vagus nerve) slows it down.
2. Atrioventricular (AV) Node: Gatekeeper of Impulses
After the SA node initiates an impulse, it travels through the atrial myocardium, causing atrial contraction. The impulse then reaches the atrioventricular (AV) node, located in the interatrial septum near the tricuspid valve. The AV node plays a crucial role as a gatekeeper, delaying the impulse for approximately 0.1 seconds. This delay allows the atria to fully contract and empty their blood into the ventricles before ventricular contraction begins.
The Importance of AV Node Delay:
- Atrial emptying: Ensures complete emptying of the atria into the ventricles.
- Ventricular filling: Maximizes ventricular filling volume.
- Coordinated contraction: Facilitates coordinated contraction of the atria and ventricles.
The AV node's slow conduction velocity is due to its smaller diameter fibers and fewer gap junctions compared to other parts of the conduction system. This inherent delay is essential for the heart's efficient pumping action.
3. Bundle of His: The Bridge Between Atria and Ventricles
From the AV node, the impulse travels down the Bundle of His, also known as the atrioventricular bundle. This bundle is a collection of specialized conducting fibers that penetrates the fibrous skeleton separating the atria and ventricles. The Bundle of His is the only electrical connection between the atria and ventricles, ensuring unidirectional impulse transmission. This unique structure prevents retrograde conduction—the backward flow of impulses—maintaining the proper sequence of cardiac contractions.
4. Right and Left Bundle Branches: Dividing the Impulse
At the interventricular septum, the Bundle of His divides into the right and left bundle branches. These branches further divide into smaller Purkinje fibers, ensuring rapid conduction of the impulse to all parts of the ventricles. The right bundle branch supplies the right ventricle, while the left bundle branch supplies the left ventricle. The left bundle branch further subdivides into anterior and posterior fascicles to ensure complete ventricular depolarization.
Ensuring Complete Ventricular Depolarization:
- Rapid conduction: The Purkinje fibers conduct impulses at a remarkably high speed, enabling near-simultaneous ventricular contraction.
- Ventricular synchrony: This rapid and widespread conduction ensures coordinated contraction of the ventricles, maximizing ejection fraction.
The efficient and rapid conduction through the bundle branches and Purkinje fibers is essential for powerful and synchronized ventricular contraction, the driving force behind systemic circulation.
5. Purkinje Fibers: The Final Destination
The Purkinje fibers are the terminal branches of the conduction system. These specialized cells have a large diameter and many gap junctions, enabling rapid impulse transmission throughout the ventricular myocardium. The Purkinje fibers distribute the electrical impulse throughout the ventricles, causing their coordinated contraction from the apex upwards. This coordinated contraction ensures efficient ejection of blood into the pulmonary artery and the aorta.
The Role of Purkinje Fibers:
- Rapid ventricular depolarization: Ensures near-simultaneous contraction of ventricular muscle fibers.
- Efficient blood ejection: Leads to forceful ejection of blood into the pulmonary and systemic circulations.
The Purkinje fiber network is essential for the efficient and coordinated contraction of the ventricles, ensuring effective blood pumping.
Clinical Significance of the Cardiac Conduction System
Understanding the cardiac conduction system is paramount in diagnosing and treating various cardiac arrhythmias. Disruptions in the conduction pathway can lead to a variety of conditions, including:
- Heart blocks: Disruptions in the conduction pathway, often at the AV node, resulting in slowed or blocked impulse transmission. This can lead to bradycardia (slow heart rate) or even cardiac arrest.
- Atrial fibrillation: Irregular and rapid atrial contractions, often caused by abnormal electrical activity in the atria.
- Ventricular tachycardia: Rapid and irregular ventricular contractions, a potentially life-threatening condition.
- Ventricular fibrillation: Chaotic and disorganized ventricular contractions, resulting in ineffective blood pumping and requiring immediate defibrillation.
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG) is a crucial diagnostic tool for evaluating the electrical activity of the heart and identifying abnormalities in the conduction system. Analyzing the ECG waveforms allows clinicians to pinpoint the location and nature of conduction disturbances. Treatment strategies vary depending on the specific condition and may involve medication, pacemakers, or other interventional procedures.
The Importance of Accurate Labeling
Accurately labeling the components of the cardiac conduction system is not just a matter of rote memorization; it's crucial for understanding the underlying mechanisms of heart function and diagnosing cardiac disorders. A precise understanding of the sequential activation of each component—from the SA node's initiation to the Purkinje fibers' final distribution—is essential for comprehending the intricate dance of electrical signals that orchestrate each heartbeat.
Visual aids, such as diagrams and animations, can greatly enhance learning and retention. By actively visualizing the pathway and associating the structures with their functions, one can build a strong foundation for understanding this critical physiological system. Regularly reviewing the pathway and its clinical implications will solidify understanding and improve diagnostic skills.
Conclusion: Mastering the Cardiac Conduction System
The cardiac conduction system is a remarkable example of biological engineering, ensuring the rhythmic and coordinated contraction of the heart. Understanding the pathway of this system, from the SA node to the Purkinje fibers, is critical for comprehending normal heart function and diagnosing various cardiac arrhythmias. Through careful study, using visual aids, and clinical correlation, one can master the intricate details of this vital system and appreciate its significance in maintaining life. This knowledge is foundational not only for medical professionals but also for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of human physiology. By thoroughly understanding and correctly labeling each component, we can better appreciate the remarkable complexity and elegance of the human heart.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Describe The Continuous Nature Of The Physical Fitness Concept
Mar 18, 2025
-
High Levels Of Cholesterol Can First Lead Directly To
Mar 18, 2025
-
True Or False Professional And Technical Communication Is Research Oriented
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Best Describes The Terrorist Planning Cycle
Mar 18, 2025
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Correctly Label The Pathway For The Cardiac Conduction System. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
