Costs Developed Which Identify What Products Should Cost Are Called
Breaking News Today
Mar 27, 2025 · 6 min read
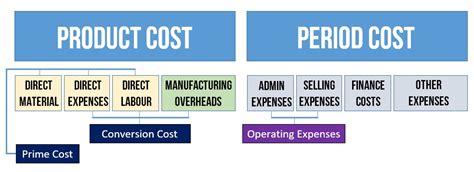
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Costing Methods That Determine Product Pricing
Determining the right price for a product is a crucial aspect of any successful business. Pricing too high can alienate customers, while pricing too low can undermine profitability. The methods used to calculate the cost of a product, therefore, are paramount. These methods, collectively known as costing methods, are the bedrock upon which effective pricing strategies are built. This comprehensive guide delves into the various costing methods used to determine what products should cost, exploring their intricacies, applications, and limitations.
Understanding the Importance of Accurate Costing
Before diving into specific methods, it's vital to grasp why accurate costing is so critical. Inaccurate cost estimations can lead to several detrimental outcomes:
- Loss of Profitability: Underestimating costs can result in selling products at a loss, jeopardizing the financial health of the business.
- Uncompetitive Pricing: Overestimating costs can lead to inflated prices, making the product less attractive to customers compared to competitors.
- Poor Inventory Management: Inaccurate costing can distort inventory valuations, hindering effective stock management and potentially leading to stockouts or overstocking.
- Inefficient Resource Allocation: Misunderstanding the cost structure can lead to poor resource allocation, hindering operational efficiency and innovation.
Accurate costing provides the foundation for informed decision-making regarding:
- Pricing Strategies: Understanding the cost of production enables businesses to set competitive and profitable prices.
- Profit Maximization: By accurately determining costs, businesses can optimize pricing to maximize profits.
- Investment Decisions: Accurate costing allows businesses to evaluate the profitability of new products and investments.
- Cost Control: Identifying the cost drivers enables businesses to implement cost-reduction measures.
Major Costing Methods: A Detailed Exploration
Several costing methods exist, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The choice of method depends on factors like the nature of the business, the complexity of the product, and the level of detail required.
1. Absorption Costing:
This traditional method allocates both variable and fixed manufacturing overhead costs to the cost of goods sold (COGS). It's widely used because of its simplicity and compliance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
- How it works: All manufacturing costs – direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead – are assigned to each unit produced. Fixed overhead is allocated based on a predetermined overhead rate, often using a production volume measure like machine hours or direct labor hours.
- Advantages: Simple to understand and implement, complies with GAAP, provides a complete product cost including fixed costs.
- Disadvantages: Can distort product costs if production fluctuates, fixed costs are not directly related to production volume, less useful for short-term decision-making.
2. Variable Costing:
This method only includes variable manufacturing costs in the COGS. Fixed manufacturing overhead is treated as a period expense, expensed in the period it's incurred.
- How it works: Only direct materials, direct labor, and variable manufacturing overhead are allocated to each unit. Fixed manufacturing overhead is expensed separately.
- Advantages: Provides a clearer picture of the impact of production volume on profitability, useful for short-term decision-making, highlights contribution margin.
- Disadvantages: Does not comply with GAAP, may not accurately reflect the full cost of production, does not consider fixed costs in pricing decisions.
3. Activity-Based Costing (ABC):
This sophisticated method assigns overhead costs based on the activities that consume resources. It's particularly useful for businesses with diverse products and complex manufacturing processes.
- How it works: Identifies cost pools based on activities, assigns costs to these pools, and allocates costs to products based on their consumption of activities.
- Advantages: More accurate cost allocation, improved understanding of cost drivers, more effective cost control, more accurate pricing decisions.
- Disadvantages: Complex and time-consuming to implement, requires detailed data collection and analysis, potentially high implementation costs.
4. Marginal Costing:
This method focuses solely on the variable costs incurred in producing an additional unit of output. It's often used for short-term pricing and production decisions.
- How it works: Only variable costs are considered. Fixed costs are ignored as they remain constant regardless of the production level.
- Advantages: Simple to understand and apply, useful for short-term decision-making like pricing and accepting special orders, easy to understand the impact of changes in production volume on profit.
- Disadvantages: Ignores fixed costs, which can lead to inaccurate pricing in the long run, inappropriate for long-term strategic decisions.
5. Standard Costing:
This method involves pre-determining the expected costs of production for each unit. Actual costs are then compared to these standards to identify variances and improve efficiency.
- How it works: Standard costs for materials, labor, and overhead are established based on historical data, industry benchmarks, and engineering estimates. Actual costs are compared to these standards, and variances are analyzed.
- Advantages: Enables proactive cost control, helps identify areas for improvement, facilitates performance evaluation, provides a basis for budgeting and forecasting.
- Disadvantages: Requires significant upfront effort to establish standards, standards may become outdated, requires continuous monitoring and adjustment.
6. Target Costing:
This method works backward from a pre-determined target price to determine the allowable cost of production. It's particularly effective in competitive markets.
- How it works: The desired selling price is established first, considering market conditions and competitor pricing. The target profit margin is then deducted to arrive at the maximum allowable cost of production.
- Advantages: Encourages cost-consciousness from the outset, promotes innovation and efficiency, helps in achieving competitive pricing.
- Disadvantages: Can be challenging to achieve the target cost, may require significant innovation and cost-reduction efforts, may lead to compromises in quality if not managed carefully.
Choosing the Right Costing Method
The selection of the most suitable costing method is a critical decision that hinges on several factors:
- Industry: The nature of the industry and its competitive landscape will influence the chosen method.
- Product Complexity: Simple products may require less sophisticated methods, while complex products might necessitate ABC costing.
- Production Volume: High-volume production may favor absorption costing, while lower volumes may benefit from variable costing.
- Decision-Making Needs: Short-term decisions might utilize marginal costing, while long-term strategies might employ absorption or ABC costing.
- Data Availability: The availability of detailed data will dictate the feasibility of more complex methods like ABC costing.
- Company Size and Resources: Larger companies with more resources may be able to adopt sophisticated methods, while smaller companies might opt for simpler methods.
Beyond the Basics: Integrating Costing with Pricing Strategies
Costing methods provide the foundation for effective pricing strategies. Understanding the cost of production is just the first step. Businesses must also consider:
- Market Demand: Pricing should reflect the market's willingness to pay.
- Competitor Pricing: Competitive analysis is crucial to ensure the price is competitive.
- Value Proposition: The price should reflect the value the product offers to the customer.
- Pricing Objectives: Businesses must define clear pricing objectives, such as maximizing profit or gaining market share.
By combining accurate costing with a well-defined pricing strategy, businesses can optimize profitability, achieve competitive advantage, and build a sustainable business model. The selection and implementation of appropriate costing methods is not just a technical exercise; it's a strategic decision that significantly impacts the overall success of the business. Continuous evaluation and refinement of the chosen costing method are crucial to ensure it remains aligned with the evolving needs and objectives of the business.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Best Describes A Like Plan Change
Mar 30, 2025
-
Tus Disquetes Encima De La Computadora
Mar 30, 2025
-
Suggested Initial Dose Of Epinephrine Nrp 8th Edition
Mar 30, 2025
-
When Is The Best Time To Check For Identification
Mar 30, 2025
-
The Things They Carried Summary By Chapter
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Costs Developed Which Identify What Products Should Cost Are Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
