Define Back Channel Cues List 3 Examples Of Backchannel Cues
Breaking News Today
Apr 01, 2025 · 7 min read
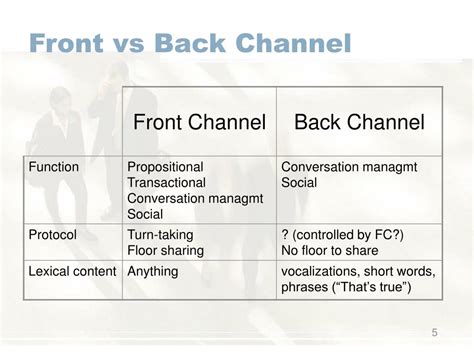
Table of Contents
Decoding the Subtleties: A Deep Dive into Backchannel Cues
In the ever-evolving landscape of communication, understanding the nuances of conversation is paramount. While spoken words often take center stage, a wealth of information resides in the subtle, often unspoken, cues that accompany them. These are the backchannel cues, nonverbal signals that provide feedback and demonstrate engagement during a conversation or presentation. Mastering the art of recognizing and utilizing these cues is crucial for effective communication, whether you're in a boardroom meeting, a casual conversation, or navigating the complexities of online interactions. This article delves deep into the definition of backchannel cues, providing illustrative examples and exploring their significance in various communication contexts.
Defining Backchannel Cues: More Than Just "Uh-huh"
Backchannel cues are nonverbal, paraverbal, or minimally verbal signals that indicate understanding, agreement, interest, or attention during a conversation. These cues act as a continuous feedback loop, confirming to the speaker that the message is being received and understood. They differ from direct verbal responses like "yes" or "I agree," which interrupt the flow of conversation. Instead, backchannel cues subtly acknowledge the speaker without diverting attention from the main narrative. They are vital for maintaining a smooth and engaging communicative exchange. Think of them as the silent orchestra accompanying the solo performance of the primary speaker.
The Multifaceted Nature of Backchannel Cues
Backchannel cues manifest in diverse forms:
-
Nonverbal cues: These include body language signals like nodding, smiling, leaning forward, maintaining eye contact, and subtle hand gestures. These visual cues offer immediate feedback to the speaker.
-
Paraverbal cues: This category encompasses vocalizations such as "uh-huh," "mm-hmm," "right," or small sighs or intakes of breath. These subtle sounds demonstrate engagement without interrupting the speaker's train of thought.
-
Minimally verbal cues: Brief, single-word responses like "okay," "yes," or "interesting" can also function as backchannel cues, provided they're delivered concisely and don't dominate the conversation.
The Importance of Context
It’s crucial to remember that the interpretation of backchannel cues depends heavily on context. A simple nod could indicate agreement in one scenario but mere acknowledgment in another. Similarly, a lack of backchannel cues doesn't automatically signify disinterest; the listener might simply be deeply absorbed in processing the information. Careful observation of the entire communicative landscape—including the setting, relationship between participants, and the nature of the conversation—is vital for accurate interpretation.
Three Illustrative Examples of Backchannel Cues:
Let’s examine three distinct examples to illustrate the diverse nature of backchannel cues and their function in different communicative scenarios:
Example 1: The Nod of Understanding
Imagine a scenario where a project manager is explaining a complex task to a team member. As the manager outlines the steps, the team member subtly nods their head, maintaining eye contact and occasionally leaning forward. These nonverbal cues—the nod, eye contact, and forward lean—serve as backchannel cues, signaling to the manager that the information is being received and understood. The team member's actions reassure the manager that their explanation is clear and effective, fostering a smoother collaborative process. The absence of these cues might prompt the manager to re-explain or clarify, highlighting their importance in ensuring effective communication.
This example underscores the importance of nonverbal backchannel cues in professional settings, enhancing clarity and building rapport between individuals.
Example 2: The Murmur of Agreement
Consider a casual conversation between friends discussing a recent movie. As one friend recounts a particularly amusing scene, the other responds with occasional "mm-hmms" and "uh-huhs." These paraverbal cues—the subtle vocalizations—function as backchannel cues, demonstrating engagement and encouraging the speaker to continue their narrative. They signal agreement or shared understanding without disrupting the flow of the story. The listener's subtle sounds act as a supportive backdrop, creating a comfortable and interactive exchange. The absence of these cues might lead the speaker to believe their story isn't engaging or that the listener is uninterested.
This scenario emphasizes the role of paraverbal cues in informal settings, helping to maintain a natural and engaging conversational rhythm. It highlights how subtle vocalizations can foster a sense of connection and shared experience.
Example 3: The Single-Word Acknowledgment
Imagine a formal presentation where a speaker is delivering important data. After presenting a key finding, the speaker pauses, and a member of the audience responds with a brief "interesting." This minimally verbal cue, delivered concisely, serves as a backchannel cue. It signals attention and encourages the speaker to continue. The audience member's concise feedback keeps the flow of the presentation smooth without causing disruption. Importantly, the single word does not interrupt or dominate the conversation, unlike a lengthy question.
This highlights the effectiveness of minimally verbal cues in formal situations, providing concise feedback without interrupting the main presentation. It underscores the ability of a carefully chosen word to convey engagement without detracting from the flow.
Backchannel Cues in Different Communication Contexts:
The significance of backchannel cues extends far beyond simple conversations. Their role is pivotal in various settings:
1. Professional Settings:
In workplaces, backchannel cues are vital for team collaboration, client interactions, and presentations. They demonstrate engagement, facilitate understanding, and build rapport between colleagues and clients. A lack of backchannel cues might lead to misinterpretations, communication breakdowns, or strained relationships.
2. Educational Settings:
In classrooms, lectures, or online learning environments, backchannel cues from students provide invaluable feedback to instructors. They indicate understanding, engagement, or confusion, helping instructors adjust their teaching methods accordingly. Understanding student backchannel cues aids in creating effective and dynamic learning environments.
3. Online Communication:
In online interactions, such as video conferencing or online forums, backchannel cues can be more challenging to interpret. However, emojis, reactions (like "thumbs up"), and short, concise textual responses can serve a similar purpose, indicating engagement and understanding. Recognizing these cues is essential for navigating the unique dynamics of online interactions.
4. Cross-Cultural Communication:
It's critical to remember that backchannel cues can vary significantly across cultures. What might be considered a sign of engagement in one culture might be interpreted differently in another. Cultural sensitivity and awareness are crucial for accurately interpreting backchannel cues in diverse communication settings. For instance, direct eye contact can be a sign of respect in some cultures but considered rude or challenging in others. A thorough understanding of cultural nuances is essential to avoid misinterpretations.
Mastering the Art of Backchannel Cues:
Becoming adept at both giving and receiving backchannel cues is a skill that enhances communication effectiveness across the board.
Giving Effective Backchannel Cues:
-
Be mindful of your body language: Maintain appropriate eye contact, nod occasionally, and use subtle hand gestures to show engagement.
-
Utilize paraverbal cues judiciously: Use "uh-huh," "mm-hmm," and similar sounds sparingly, avoiding overuse which might distract the speaker.
-
Choose minimal verbal responses wisely: Select short, positive words that acknowledge the speaker without disrupting their flow.
-
Be sensitive to context: Adapt your backchannel cues to the specific setting and relationship between individuals.
Receiving Backchannel Cues Effectively:
-
Pay close attention to nonverbal cues: Observe body language, facial expressions, and posture for indications of engagement or disengagement.
-
Listen for paraverbal cues: Pay attention to subtle vocalizations to gauge the listener's level of understanding and interest.
-
Interpret minimal verbal responses carefully: Consider the context and tone of single-word responses.
-
Be aware of cultural differences: Recognize that backchannel cues vary across cultures.
Conclusion: The Unspoken Language of Engagement
Backchannel cues are the subtle yet powerful signals that enhance and enrich communication. They are the unspoken language of engagement, providing continuous feedback and fostering smoother, more productive interactions. Mastering the art of both giving and receiving these cues is crucial for effective communication in all spheres of life, from professional collaborations to personal relationships. By becoming acutely aware of these nonverbal, paraverbal, and minimally verbal signals, we can unlock a deeper understanding of human interaction and significantly improve our communication skills. This leads to clearer messaging, strengthened relationships, and more successful outcomes in our personal and professional endeavors. The ability to decipher and utilize backchannel cues is not merely a skill; it's a vital component of effective and meaningful communication.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Key Do You Press To Select Adjacent Worksheets
Apr 02, 2025
-
Why Cant Arson Evidence Be Collected In Bags
Apr 02, 2025
-
Which Statement About Epilepsy Is Most Accurate
Apr 02, 2025
-
Pharmacology Made Easy 5 0 The Immune System Test
Apr 02, 2025
-
A Person With High Emotional Intelligence Is Likely To
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Define Back Channel Cues List 3 Examples Of Backchannel Cues . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
