Which Statement About Epilepsy Is Most Accurate
Breaking News Today
Apr 02, 2025 · 5 min read
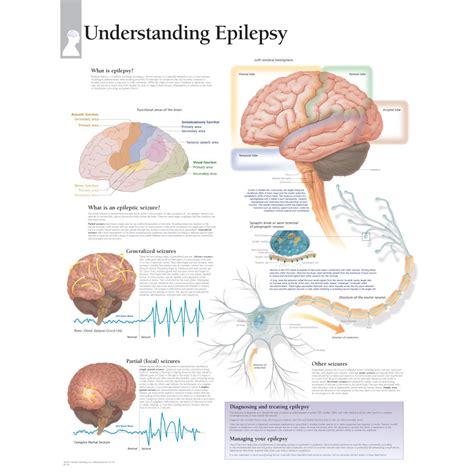
Table of Contents
Which Statement About Epilepsy is Most Accurate? Debunking Myths and Understanding the Facts
Epilepsy, a neurological disorder affecting millions worldwide, is often shrouded in misunderstanding and misinformation. While the condition itself is complex, understanding the accurate statements about epilepsy is crucial for effective management, reducing stigma, and improving the lives of those affected. This comprehensive article will delve into common misconceptions and present the most accurate statements regarding epilepsy, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and living with the condition.
What is Epilepsy? A Neurological Perspective
The most accurate statement regarding epilepsy is that it's a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent, unprovoked seizures. This definition highlights two key aspects:
-
Recurrent seizures: A single seizure doesn't necessarily equate to epilepsy. Epilepsy is defined by the recurrence of seizures. These seizures are sudden, transient disturbances of brain function caused by abnormal excessive neuronal activity.
-
Unprovoked seizures: Seizures can be triggered by various factors (fever, sleep deprivation, alcohol withdrawal), but in epilepsy, many seizures occur spontaneously without an identifiable cause. This distinguishes epileptic seizures from seizures caused by specific, temporary events.
Debunking Common Myths About Epilepsy
Many misconceptions surrounding epilepsy hinder accurate understanding and contribute to societal stigma. Let's address some of the most prevalent myths:
Myth 1: Epilepsy is contagious.
Reality: Epilepsy is not contagious. It's a neurological disorder, not an infectious disease. It cannot be spread through touch, saliva, or any other form of contact.
Myth 2: People with epilepsy are intellectually disabled.
Reality: While some individuals with epilepsy may experience cognitive challenges, the vast majority do not have intellectual disabilities. The severity of cognitive impairment, if any, varies greatly depending on the type and severity of epilepsy, as well as other contributing factors.
Myth 3: All seizures are the same.
Reality: Seizures are incredibly diverse. They vary significantly in their symptoms, duration, and underlying causes. Some seizures may involve subtle changes in awareness or behavior (absence seizures), while others may cause dramatic convulsions (tonic-clonic seizures). This diversity necessitates accurate diagnosis and individualized treatment plans.
Myth 4: People with epilepsy can't drive.
Reality: The ability to drive with epilepsy depends on several factors, including seizure frequency, type of seizures, and the individual's response to treatment. Many individuals with well-controlled epilepsy can drive safely. However, driving regulations vary by location, and individuals must comply with local laws and medical advice regarding driving.
Myth 5: There's no cure for epilepsy.
Reality: While there isn't a single "cure" applicable to all forms of epilepsy, many individuals achieve seizure freedom or significant seizure reduction through medication, surgery, or other treatments. The goal of treatment is not necessarily to "cure" epilepsy, but to manage it effectively and improve the quality of life for those affected.
Causes and Types of Epilepsy
The causes of epilepsy are multifaceted and not always fully understood. Several factors can contribute to its development:
-
Genetics: Genetic factors play a significant role in some types of epilepsy, with certain genes increasing susceptibility.
-
Brain injury: Traumatic brain injury, stroke, or infections (meningitis, encephalitis) can damage brain tissue and trigger epileptic activity.
-
Developmental abnormalities: Conditions present at birth or during early development can sometimes lead to epilepsy.
-
Other neurological disorders: Certain neurological conditions, such as cerebral palsy, are often associated with epilepsy.
-
Tumors: Brain tumors can sometimes cause seizures.
Epilepsy is categorized into various types, each characterized by distinct seizure patterns and underlying mechanisms. These include:
-
Focal (partial) seizures: These originate in a specific area of the brain. They may be simple (no loss of awareness) or complex (with altered awareness).
-
Generalized seizures: These involve both hemispheres of the brain simultaneously. Types include tonic-clonic seizures (grand mal), absence seizures (petit mal), myoclonic seizures, and atonic seizures.
-
Unknown epilepsy: This category encompasses cases where the cause of epilepsy remains unclear despite thorough investigation.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Epilepsy
Accurate diagnosis of epilepsy is crucial for effective management. This typically involves:
-
Detailed medical history: Gathering information about seizure characteristics, family history, and medical conditions.
-
Neurological examination: Assessing neurological function and identifying any abnormalities.
-
Electroencephalography (EEG): Recording brainwave activity to detect abnormal electrical discharges indicative of epileptic activity.
-
Neuroimaging: Techniques like MRI and CT scans can identify structural abnormalities in the brain that may contribute to epilepsy.
Treatment options for epilepsy vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. They may include:
-
Anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs): These medications are the primary treatment for most individuals with epilepsy. Many different AEDs are available, and the choice depends on the individual's response and potential side effects.
-
Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be an option to remove the area of the brain causing seizures (especially for focal epilepsy).
-
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS): A device implanted under the skin stimulates the vagus nerve, potentially reducing seizure frequency.
-
Ketogenic diet: A high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that can be effective in some cases, particularly for children with epilepsy.
Living With Epilepsy: Strategies for Management and Support
Living with epilepsy requires a holistic approach encompassing medical management, lifestyle adjustments, and emotional support. Individuals with epilepsy and their families benefit from:
-
Regular medical check-ups: Monitoring seizure control and adjusting treatment as needed.
-
Education and self-management: Understanding the condition, triggers, and warning signs.
-
Lifestyle modifications: Avoiding known seizure triggers (sleep deprivation, alcohol, stress).
-
Emotional support: Addressing the emotional challenges associated with epilepsy, such as anxiety, depression, and social stigma.
-
Support groups: Connecting with others who understand the experience of living with epilepsy.
Conclusion: Accurate Information, Empowering Individuals
The most accurate statement about epilepsy is that it's a complex neurological disorder characterized by recurrent, unprovoked seizures, but it's not a life sentence of limitations. With accurate information, appropriate medical care, and strong support systems, individuals with epilepsy can lead fulfilling and productive lives. Understanding the facts, dispelling myths, and advocating for increased awareness are crucial steps towards empowering those affected and fostering a more inclusive and supportive society. Remember, epilepsy is a manageable condition, not a life-defining sentence. With the right support and understanding, those living with epilepsy can thrive and live full, meaningful lives.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Correctly Label The Intrinsic Muscles Of The Hand
Apr 03, 2025
-
An Underwriter Determines That An Applicants Risk
Apr 03, 2025
-
Signs Of A Pulmonary Blast Injury Include
Apr 03, 2025
-
Wild Animals Are Not Considered A Natural Resource
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Communication Strategies Contribute To Providing Successful
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Statement About Epilepsy Is Most Accurate . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
