Driving When Tired Sick Or Medicated Causes
Breaking News Today
Mar 26, 2025 · 6 min read
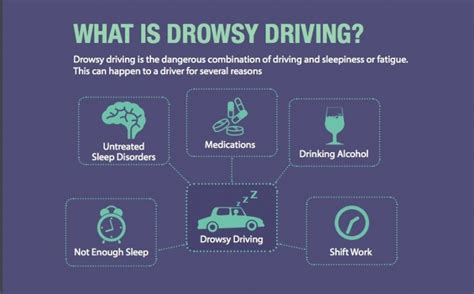
Table of Contents
Driving When Tired, Sick, or Medicated: Understanding the Dangers and Risks
Driving is a privilege and a responsibility that demands our full attention and alertness. Impaired driving, caused by fatigue, illness, or medication, significantly increases the risk of accidents and has devastating consequences. This article delves into the dangers of driving under these conditions, exploring the causes, effects, and crucial steps to prioritize safety on the road.
The Dangers of Driving While Tired
Fatigue is a major culprit in road accidents. When tired, our reaction time slows, judgment becomes impaired, and our ability to focus diminishes. Even a short period of sleep deprivation can have profound effects on driving ability, making it comparable to driving under the influence of alcohol.
Causes of Driver Fatigue:
- Sleep Deprivation: The most common cause. Lack of adequate sleep, consistently getting less than seven to nine hours per night, significantly increases fatigue-related risks.
- Long Drives: Extended periods behind the wheel, without sufficient breaks, lead to accumulating fatigue.
- Shift Work: Irregular sleep schedules disrupt the body's natural sleep-wake cycle, making it difficult to stay alert.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Sleep apnea, insomnia, and other sleep disorders can contribute to chronic fatigue.
- Monotonous Driving: Driving long stretches of monotonous roads can be surprisingly tiring.
- Alcohol and Drug Use: Although not directly fatigue, these substances significantly worsen the effects of tiredness and impair judgment.
- Mental Stress: Worry, anxiety, and stress can drain energy and increase fatigue.
Effects of Fatigue on Driving:
- Slower Reaction Time: This increases the likelihood of being unable to react quickly enough to avoid accidents.
- Impaired Judgment: Decision-making becomes poor, leading to risky maneuvers and poor assessment of situations.
- Microsleeps: Brief periods of unintended sleep while driving, leading to complete loss of control.
- Reduced Awareness: Decreased alertness to surrounding traffic and road conditions.
- Difficulty Maintaining Lane Position: Wandering across lanes or drifting off the road.
- Increased Risk of Collisions: Fatigue is a major contributing factor in many car crashes.
The Perils of Driving While Sick
Driving while unwell significantly compromises driving ability. Symptoms like fever, dizziness, and nausea impair concentration, coordination, and judgment, creating a dangerous combination behind the wheel.
Causes of Illness-Impaired Driving:
- Viral Infections: Colds, the flu, and other viral illnesses can cause fatigue, headaches, and muscle aches, affecting driving performance.
- Bacterial Infections: Bacterial infections, like strep throat or pneumonia, often lead to more severe symptoms, including fever and chills.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea can significantly impair driving abilities.
- Allergies: Severe allergic reactions can lead to drowsiness, impaired vision, and difficulty breathing.
- Migraines: Severe headaches can cause visual disturbances and intense pain, making driving extremely dangerous.
Effects of Illness on Driving:
- Reduced Alertness: Illness often causes lethargy and decreased mental acuity.
- Impaired Coordination: Muscle weakness and coordination problems can make it difficult to control the vehicle.
- Blurred Vision: Illness can affect vision, leading to difficulty seeing clearly.
- Drowsiness: Many illnesses induce drowsiness, increasing the risk of microsleeps.
- Delayed Reaction Time: Slower reaction times significantly increase the likelihood of accidents.
- Weakened Judgment: Illness can affect decision-making abilities, leading to poor choices while driving.
The Risks of Driving Under the Influence of Medication
Many prescription and over-the-counter medications can cause drowsiness, dizziness, or other side effects that impair driving ability. It’s crucial to understand the potential effects of any medication before operating a vehicle.
Medications that Impair Driving:
- Sedatives and Tranquilizers: These medications cause drowsiness and impair cognitive function.
- Pain Relievers (Opioids): Opioids can significantly impair judgment, reaction time, and coordination.
- Antihistamines: Many antihistamines cause drowsiness and blurred vision.
- Muscle Relaxants: These medications can cause drowsiness, weakness, and dizziness.
- Blood Pressure Medications: Some blood pressure medications can cause dizziness and lightheadedness.
- Antidepressants: Certain antidepressants can cause drowsiness or other side effects that affect driving.
Effects of Medication on Driving:
- Drowsiness and Fatigue: This is a common side effect of many medications, leading to decreased alertness and reaction time.
- Impaired Coordination: Some medications can affect coordination, making it difficult to control the vehicle.
- Blurred Vision: Blurry vision significantly reduces driving safety.
- Dizziness and Lightheadedness: These symptoms can lead to loss of control and accidents.
- Slowed Reaction Time: This increases the risk of being unable to respond appropriately to unexpected situations.
- Impaired Judgment: Medication can affect judgment and decision-making skills.
Staying Safe on the Road: Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Prioritizing safety on the road requires proactive measures to avoid driving while fatigued, sick, or medicated.
Preventing Fatigue-Related Accidents:
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for seven to nine hours of quality sleep per night.
- Plan Breaks During Long Drives: Take regular breaks to stretch, walk around, and stay alert.
- Avoid Driving During Peak Sleepiness Times: Avoid driving between midnight and 6:00 AM, when drowsiness is most pronounced.
- Share the Driving: If on a long trip, share the driving responsibilities with a passenger.
- Stay Hydrated and Eat Regularly: Dehydration and hunger can worsen fatigue.
- Avoid Driving When Overtired: If feeling overly tired, find a safe place to rest or find alternative transportation.
Preventing Illness-Impaired Driving:
- Don't Drive When Sick: If experiencing symptoms such as fever, dizziness, or nausea, avoid driving.
- Seek Medical Attention: Consult a doctor for severe illness.
- Allow Ample Rest and Recovery: Ensure adequate rest to recover from illness before driving.
Preventing Medication-Impaired Driving:
- Read Medication Labels Carefully: Pay close attention to potential side effects, especially drowsiness or dizziness.
- Talk to Your Doctor or Pharmacist: Discuss potential driving implications of your medications.
- Avoid Driving When Symptoms Appear: Do not drive if you experience drowsiness, dizziness, or other side effects.
- Find Alternative Transportation: Consider public transportation, ride-sharing services, or asking a friend or family member for a ride.
- Don't Mix Medications and Alcohol: Combining medications with alcohol can severely impair driving abilities.
Legal Ramifications of Impaired Driving
Driving while tired, sick, or medicated can lead to severe legal consequences, including:
- Traffic Tickets: Receiving tickets for traffic violations, like speeding or unsafe lane changes.
- License Suspension or Revocation: Depending on the severity of the offense and your driving record, your driving privileges may be suspended or revoked.
- Criminal Charges: In cases involving accidents or injuries, drivers can face criminal charges.
- Insurance Penalties: Insurance premiums may increase significantly after an impaired driving incident.
- Civil Lawsuits: Victims of accidents caused by impaired drivers may file civil lawsuits seeking compensation for damages.
Conclusion: Prioritize Safety
Driving safely is paramount. The consequences of driving while tired, sick, or medicated can be catastrophic, affecting not only the driver but also other road users. By understanding the risks and taking proactive steps to prioritize safety, we can significantly reduce the number of accidents caused by impaired driving. Always remember, your safety and the safety of others are of utmost importance. Choosing to not drive when impaired is a responsibility we all share to keep our roads safe for everyone.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Nos Alojamos En Un Hotel Malo De La Capital
Mar 29, 2025
-
From A Security Perspective The Best Rooms Are
Mar 29, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True Of Psychologically Healthy People
Mar 29, 2025
-
The Ultimate Goal Of Lean Operations Is To Have
Mar 29, 2025
-
La Esposa De Mi Padre Pero No Soy Su Hijo
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Driving When Tired Sick Or Medicated Causes . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
