Drug Abuse Can Often Lead To Suicide Because __________.
Breaking News Today
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
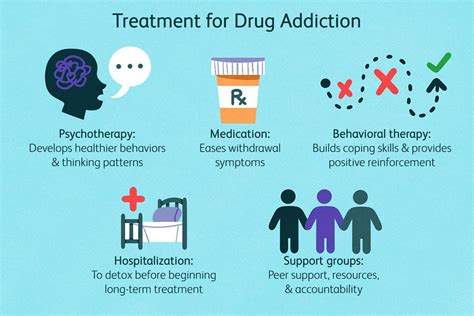
Table of Contents
Drug Abuse Can Often Lead to Suicide Because… a Complex Interplay of Factors
Drug abuse and suicide are tragically intertwined, with substance misuse significantly increasing the risk of self-harm and death by suicide. It's not a simple cause-and-effect relationship; rather, it's a complex interplay of several factors that contribute to this devastating connection. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective prevention and intervention strategies.
The Neurological Impact: Altered Brain Chemistry and Function
One of the most significant reasons drug abuse can lead to suicide is the profound impact on brain chemistry and function. Many drugs of abuse, including opioids, stimulants, and depressants, directly alter neurotransmitter systems in the brain. These neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, play crucial roles in regulating mood, emotions, and cognitive function.
Disrupted Serotonin Pathways and Depression:
Serotonin, a key neurotransmitter involved in mood regulation, is profoundly affected by many drugs. Chronic drug use can lead to serotonin depletion, resulting in severe depression, anxiety, and irritability. This neurochemical imbalance can significantly increase suicidal ideation and attempts. The feeling of hopelessness and worthlessness, often hallmarks of depression, are amplified by the drug's impact on the brain's reward system.
Dopamine Dysregulation and Addiction:
Dopamine, associated with pleasure and reward, is hijacked by drugs of abuse. The initial euphoric effects of drugs create powerful reinforcement, leading to addiction. However, prolonged drug use can actually deplete dopamine levels, resulting in anhedonia – the inability to experience pleasure. This lack of pleasure, coupled with the intense cravings and withdrawal symptoms, can lead to feelings of despair and hopelessness, driving individuals towards suicide.
Norepinephrine Imbalance and Anxiety:
Norepinephrine, involved in stress response and anxiety, is also affected. Some drugs can initially increase norepinephrine levels, leading to heightened anxiety and paranoia. However, prolonged use often results in depletion, leading to decreased energy, fatigue, and increased emotional vulnerability, further increasing suicide risk.
The Psychological Impact: Mental Health Disorders and Cognitive Distortion
Drug abuse often exacerbates pre-existing mental health conditions or triggers new ones, significantly increasing the risk of suicide.
Exacerbation of Pre-existing Mental Illness:
Many individuals who abuse drugs already struggle with underlying mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Drug use can worsen these conditions, intensifying symptoms and making it harder to cope, increasing the likelihood of suicidal thoughts and behaviors. The drugs essentially become a self-medication strategy that fails miserably and worsens the underlying problem.
Development of New Mental Health Issues:
Drug abuse itself can induce or exacerbate a range of mental health problems. Psychotic episodes, paranoia, and severe anxiety are commonly reported among long-term drug users. These symptoms can further contribute to feelings of hopelessness, isolation, and worthlessness, making suicide seem like the only escape.
Cognitive Distortion and Impaired Judgment:
Drug abuse can significantly impair judgment and decision-making capabilities. The altered state of consciousness can distort an individual's perception of reality, leading to impulsive behaviors, including suicide attempts. The ability to rationally assess risk and consequences is severely compromised, making individuals more vulnerable to acting on suicidal impulses.
The Social Impact: Isolation, Relationship Breakdown, and Loss of Support
Drug abuse frequently leads to social isolation and strained relationships, eroding the support systems vital for mental well-being.
Damaged Relationships and Loss of Support:
Substance abuse puts a strain on relationships with family and friends. The dishonesty, unreliability, and unpredictable behavior associated with addiction can lead to conflict, resentment, and ultimately, the breakdown of support networks. The loss of these crucial social connections further isolates individuals, increasing their vulnerability to suicide.
Loss of Employment and Financial Instability:
Drug abuse often impacts employment, leading to job loss and financial instability. This loss of financial security can increase stress and hopelessness, adding to the burden of mental health challenges and increasing suicide risk. The lack of financial resources can also limit access to treatment and support.
Legal Problems and Incarceration:
Drug-related crimes can lead to legal problems and incarceration, further isolating individuals and removing them from supportive environments. The stigma associated with criminal justice involvement can also increase feelings of shame and hopelessness.
The Physical Impact: Physical Health Problems and Pain
The physical consequences of drug abuse contribute to the overall burden of suffering, increasing the risk of suicide.
Physical Health Deterioration:
Many drugs have severe physical consequences, causing organ damage, chronic pain, and other debilitating health problems. The chronic pain and discomfort can lead to feelings of despair and hopelessness, while the physical deterioration can further reduce self-esteem and increase the desire to end suffering.
Withdrawal Symptoms:
Withdrawal from many drugs is extremely painful and distressing. The physical and psychological discomfort experienced during withdrawal can intensify feelings of hopelessness and increase the risk of suicide attempts. The overwhelming nature of withdrawal symptoms can make it difficult for individuals to seek help.
The Interaction of Factors: A Multifaceted Problem
It's crucial to understand that suicide risk in individuals with substance abuse isn't solely determined by one factor. It's the complex interplay of the neurological, psychological, social, and physical impacts of drug abuse that creates a lethal combination. The synergistic effect of these factors amplifies the risk, leading to a significantly increased probability of suicidal thoughts and actions.
Breaking the Cycle: Prevention and Intervention Strategies
Addressing the complex link between drug abuse and suicide requires a multi-pronged approach focusing on prevention, early intervention, and comprehensive treatment.
Prevention Efforts:
- Education: Educating young people about the risks of drug abuse and its potential consequences, including suicide, is vital. This education should include information on mental health, stress management, and healthy coping mechanisms.
- Early Intervention: Identifying and addressing substance use disorders early is crucial. Early intervention programs can prevent escalation to severe addiction and reduce the risk of mental health complications.
- Reducing Stigma: Reducing the stigma associated with drug abuse and mental health problems is essential to encourage individuals to seek help without fear of judgment.
Treatment Strategies:
- Integrated Treatment: Treating co-occurring substance abuse and mental health disorders simultaneously is crucial. Integrated treatment approaches address both the addiction and the mental health concerns effectively.
- Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT): MAT combines medications with counseling and behavioral therapies to treat addiction. MAT can be particularly effective for opioid and alcohol addiction.
- Therapy: Various therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), and motivational interviewing, can help individuals manage cravings, develop coping skills, and address underlying mental health issues.
- Support Groups: Support groups like Narcotics Anonymous (NA) and Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) provide a safe and supportive environment for individuals recovering from addiction.
Access to Care:
Ensuring access to affordable and quality mental health and substance abuse treatment is essential. This includes increasing the availability of treatment programs, expanding access to medication-assisted treatment, and improving the integration of mental health and addiction services.
Conclusion: A Call for Comprehensive Action
The connection between drug abuse and suicide is a serious public health concern requiring a comprehensive and multifaceted response. By understanding the intricate interplay of factors contributing to this devastating relationship, we can develop and implement effective prevention and intervention strategies to save lives. This requires a collaborative effort involving healthcare professionals, policymakers, educators, community organizations, and individuals themselves. It's a collective responsibility to break the cycle of addiction and suicide and build a future where individuals struggling with substance abuse have access to the support and treatment they need to recover and thrive. The ultimate goal is to foster hope, resilience, and a pathway to recovery for those affected.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Hesi Case Studies Heart Failure With Atrial Fibrillation
Mar 25, 2025
-
A Food Handler Has Finished Grilling A Chicken Breast
Mar 25, 2025
-
4 04 Quiz Buying Clothes And Shopping 2
Mar 25, 2025
-
You Can Practice Drive With A Valid Special Learners Permit
Mar 25, 2025
-
In The Third Party Payment System The Patient Is The
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Drug Abuse Can Often Lead To Suicide Because __________. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
