Edema May Be Caused By Which Of The Following Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 31, 2025 · 6 min read
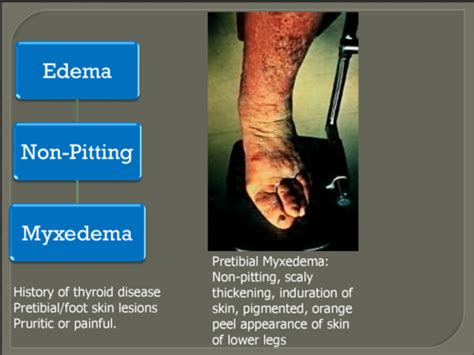
Table of Contents
Edema: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis – A Comprehensive Guide
Edema, the medical term for swelling, occurs when excess fluid builds up in the body's tissues. It's a common symptom, not a disease itself, indicating an underlying condition. Understanding the potential causes of edema is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. This comprehensive guide explores the various factors that can lead to edema, helping you understand why swelling occurs and what steps can be taken.
What is Edema?
Edema manifests as swelling in various body parts, often the legs, ankles, and feet. However, it can also affect the hands, arms, face, and even internal organs. The severity ranges from mild to severe, impacting daily life and overall well-being. The fluid accumulation is typically caused by imbalances in the body's circulatory system, lymphatic system, or both.
Key Characteristics of Edema:
- Swelling: The hallmark symptom, often noticeable visually or by palpation (touching the affected area).
- Pitting: When pressure is applied to the swollen area, an indentation (pit) may remain for a short time. This is characteristic of many types of edema.
- Pain: Edema can be painless or cause discomfort, depending on the underlying cause and severity.
- Location: The location of edema can provide clues about the possible cause. For instance, edema in the legs might suggest heart failure, while facial edema might indicate kidney problems.
- Skin Changes: The skin over the swollen area might appear stretched, shiny, or discolored.
Causes of Edema: A Deep Dive
Edema's causes are diverse and often interconnected. Understanding these causes is crucial for effective management. Here's a breakdown of the major categories:
1. Cardiovascular Issues:
- Heart Failure: The heart's inability to pump blood efficiently leads to fluid buildup in the body's tissues, often manifesting as edema in the legs and ankles. This is because the blood pools in the lower extremities due to reduced cardiac output. Keywords: Congestive heart failure, CHF, left-sided heart failure, right-sided heart failure, cardiac edema.
- Venous Insufficiency: Problems with the veins' ability to return blood to the heart cause blood to pool in the lower extremities, leading to edema. This is often accompanied by varicose veins and leg pain. Keywords: Chronic venous insufficiency, CVI, venous stasis, varicose veins, leg edema.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): A blood clot in a deep vein, often in the leg, can obstruct blood flow and cause significant edema. This is a serious condition requiring immediate medical attention. Keywords: Blood clots, thrombosis, leg swelling, pulmonary embolism, DVT symptoms.
2. Renal (Kidney) Problems:
- Kidney Disease: Impaired kidney function prevents the proper excretion of fluid and electrolytes, leading to fluid retention and edema. This often presents as generalized edema or swelling in the face and hands. Keywords: Nephrotic syndrome, chronic kidney disease, CKD, renal failure, kidney edema.
- Nephrotic Syndrome: A specific type of kidney disease characterized by significant protein loss in the urine, causing fluid retention and edema. Keywords: Proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, glomerulonephritis, nephrotic syndrome edema.
3. Liver Disease:
- Cirrhosis: Severe scarring of the liver impairs its ability to produce proteins that help regulate fluid balance, leading to ascites (abdominal edema) and peripheral edema. Keywords: Liver cirrhosis, ascites, hepatic edema, portal hypertension.
4. Nutritional Deficiencies:
- Protein Deficiency: Low protein levels in the blood reduce the blood's ability to retain fluid, leading to edema. This is often seen in malnutrition or conditions affecting protein absorption. Keywords: Hypoalbuminemia, malnutrition, kwashiorkor, protein-energy malnutrition, PEM.
5. Medications:
Certain medications, including some blood pressure medications, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and corticosteroids, can contribute to edema as a side effect. Keywords: Medication side effects, drug-induced edema, NSAIDs, corticosteroids, ACE inhibitors.
6. Pregnancy:
Fluid retention is common during pregnancy due to hormonal changes and increased blood volume. This often leads to mild edema in the legs and ankles. Keywords: Pregnancy edema, gestational edema, preeclampsia, pregnancy-induced hypertension.
7. Lymphatic System Disorders:
- Lymphedema: Damage or blockage of the lymphatic system, which drains fluid from the tissues, causes fluid accumulation and swelling. This can be primary (congenital) or secondary (caused by surgery, infection, or injury). Keywords: Lymphatic drainage, lymphatic obstruction, filariasis, post-surgical lymphedema, breast cancer-related lymphedema.
8. Allergic Reactions:
- Angioedema: A severe allergic reaction that causes rapid swelling, often in the face, lips, and throat. This requires immediate medical attention. Keywords: Angioedema, allergic reaction, anaphylaxis, urticaria, hives.
9. Infections:
Infections can cause inflammation and fluid buildup in the affected area. This is often localized edema. Keywords: Cellulitis, abscess, localized edema, inflammatory response.
10. Injuries and Obstructions:
Trauma, injuries, and obstructions (like a blood clot) can impede fluid drainage and cause localized edema.
Diagnosing the Cause of Edema:
Diagnosing the underlying cause of edema requires a thorough medical evaluation. The process often involves:
- Physical Examination: A doctor will assess the location, severity, and characteristics of the edema, looking for pitting, skin changes, and other signs.
- Medical History: A detailed medical history, including current medications, past illnesses, and family history, is essential.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests to check kidney function, liver function, protein levels, and electrolyte levels. Urine tests may be conducted to assess for proteinuria.
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans may be used to visualize blood vessels, organs, or the lymphatic system and identify any abnormalities.
Treatment of Edema:
Treatment depends entirely on the underlying cause. Addressing the root cause is crucial. However, some general measures may be helpful:
- Elevation: Elevating the swollen limbs can help reduce fluid accumulation.
- Compression: Compression stockings or bandages can improve blood flow and reduce swelling.
- Diuretics: Medications that help the body eliminate excess fluid, often prescribed for edema associated with heart failure or kidney disease. Note: Diuretics should only be used under medical supervision.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy weight, following a low-sodium diet, and regular exercise can help manage edema.
Edema: A Quizlet-Style Review
Let's test your understanding with a quizlet-style review of some of the key concepts covered:
Question 1: Which of the following is NOT a common cause of edema?
a) Heart failure b) Kidney disease c) Vitamin C deficiency d) Liver disease
Answer: c) Vitamin C deficiency
Question 2: Pitting edema is characterized by:
a) Hard, non-indenting swelling b) A temporary indentation after applying pressure c) Swelling only in the hands and feet d) Absence of any pain or discomfort
Answer: b) A temporary indentation after applying pressure
Question 3: Which condition is associated with significant protein loss in the urine, leading to edema?
a) Venous insufficiency b) Nephrotic syndrome c) Lymphedema d) Cellulitis
Answer: b) Nephrotic syndrome
Question 4: Ascites refers to:
a) Edema in the lower extremities b) Edema in the face c) Fluid accumulation in the abdomen d) Edema due to allergic reactions
Answer: c) Fluid accumulation in the abdomen
Question 5: Which of the following is NOT a common treatment strategy for edema?
a) Elevating the affected limb b) Using compression stockings c) Administering antibiotics d) Prescribing diuretics (under medical supervision)
Answer: c) Administering antibiotics (although antibiotics might be indicated if an infection is causing the edema).
This comprehensive guide provides a foundational understanding of edema, its numerous causes, diagnostic approaches, and treatment strategies. Remember, self-treating edema is not recommended. Always consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. Early intervention is key to managing underlying conditions and preventing complications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Patients Refusal Of Ems Treatment Must Be
Apr 02, 2025
-
In The Hospitality Industry The Concept Of Perishability Means
Apr 02, 2025
-
Where Do Broadside Collisions Most Commonly Occur
Apr 02, 2025
-
El Aprendizaje Servicio Consiste En Ir A Cursos De Verano
Apr 02, 2025
-
Completa Las Oraciones Usando El Preterito De Ser O Ir
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Edema May Be Caused By Which Of The Following Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
