Explain How Idealogical Orientation Influenced Voters Choice In An Election
Breaking News Today
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
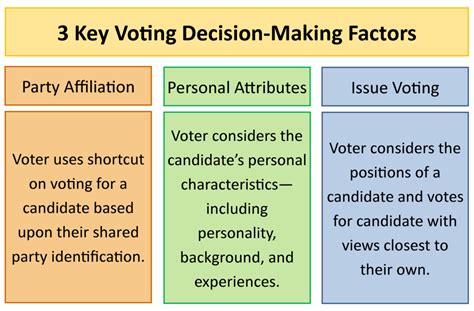
Table of Contents
How Ideological Orientation Influences Voter Choice in an Election
Understanding why voters make the choices they do during an election is a complex undertaking. While numerous factors contribute – from candidate charisma to economic conditions – ideological orientation plays a pivotal, often underestimated, role. This article delves deep into the intricate relationship between ideology and voter behavior, exploring how deeply held beliefs shape electoral decisions and contribute to the broader political landscape.
Defining Ideological Orientation
Before we delve into the influence of ideology on voting patterns, it's crucial to define what we mean by "ideological orientation." Ideology, in this context, refers to a system of beliefs and values that shape a person's understanding of the world and their place within it. This isn't merely a collection of opinions; it's a more deeply rooted framework that guides perspectives on social, economic, and political issues.
Common ideological orientations include:
-
Liberalism: Generally advocates for social justice, individual rights, and government intervention to address societal inequalities. This often includes support for social programs, environmental protection, and regulations on businesses.
-
Conservatism: Typically emphasizes individual responsibility, limited government intervention, and the preservation of traditional values. This often translates to support for lower taxes, free markets, and a strong national defense.
-
Socialism: Advocates for social ownership and control of the means of production and distribution of goods and services. It often emphasizes economic equality and social welfare.
-
Libertarianism: Prioritizes individual liberty and minimal government intervention in all aspects of life, both economic and social.
It's important to note that these are broad categories, and individuals rarely perfectly fit into one neat box. Many voters hold a combination of beliefs that fall across different ideological spectrums, often described as being "moderate" or "centrist". However, understanding the core tenets of these ideologies helps us understand the underlying motivations driving voter choices.
The Impact of Ideological Orientation on Voting Decisions
Ideological orientation profoundly impacts voting decisions in several ways:
1. Party Identification and Candidate Selection:
A voter's ideology strongly influences their party affiliation. Liberals are more likely to identify with left-leaning parties, while conservatives lean towards right-leaning parties. This party identification, in turn, significantly simplifies the candidate selection process. Voters often default to selecting the candidate from their preferred party, even without extensive knowledge of each individual candidate's platform. This "party line voting" is a powerful illustration of ideology's sway over electoral behavior.
2. Issue Prioritization and Policy Preferences:
Ideology dictates which issues voters deem most important and how they prioritize those issues. For example, a liberal voter might prioritize environmental protection, social justice, and healthcare reform, while a conservative might focus on economic growth, national security, and individual liberty. These priorities directly impact their evaluation of candidates and their platforms. A candidate who strongly advocates for policies aligning with a voter's ideological priorities is more likely to secure their vote.
3. Evaluation of Candidate Statements and Actions:
Voters interpret candidate statements and actions through the lens of their own ideology. A statement that a liberal voter might view as progressive and socially responsible could be seen as radical and irresponsible by a conservative voter. Similarly, a candidate's actions, such as voting record or public statements, are assessed based on their congruence with the voter's ideological framework. This filtering process often leads to selective perception and confirmation bias, reinforcing pre-existing beliefs.
4. Influence on Political Participation:
Ideology motivates political engagement. Voters strongly identified with a particular ideology are more likely to participate actively in the political process, engaging in activities like campaigning, donating to political parties, and attending rallies. This active participation further solidifies ideological divides and reinforces the influence of ideology on the electoral outcome.
The Role of Media and Social Influence
The influence of ideology is not solely an individual affair. Media consumption and social interactions significantly shape and reinforce ideological orientations.
1. Media Bias and Selective Exposure:
Media outlets often exhibit ideological biases, consciously or unconsciously. This means that the news and information presented can reinforce pre-existing beliefs or introduce new perspectives that either strengthen or challenge a voter’s ideological stance. Furthermore, individuals often engage in "selective exposure," consuming media that aligns with their existing beliefs and avoiding information that contradicts them. This further entrenches ideological divides and limits exposure to diverse perspectives.
2. Social Networks and Echo Chambers:
Social networks, while offering opportunities for diverse viewpoints, often create "echo chambers" where individuals primarily interact with like-minded individuals. This constant reinforcement of similar beliefs can strengthen ideological convictions and limit exposure to alternative perspectives, leading to polarization and potentially, more extreme views.
3. The Impact of Political Discourse:
The nature of political discourse significantly impacts ideological influence. Highly divisive and polarized rhetoric can further solidify ideological positions, making it more difficult for voters to consider alternative perspectives. Conversely, constructive and respectful dialogue that facilitates understanding across ideological divides can promote greater nuance and less rigid adherence to specific ideologies.
Shifts in Ideological Orientation and Electoral Outcomes
Ideological orientations are not static; they can evolve over time due to various factors like:
-
Major historical events: Significant events such as economic crises, wars, or social movements can drastically shift the ideological landscape. These events can lead to reassessments of existing beliefs and potential realignments of voter allegiances.
-
Generational differences: Different generations often hold distinct ideological orientations shaped by the historical context in which they grew up. These generational shifts can significantly alter the electorate’s ideological composition and influence voting patterns over time.
-
Changing social norms: Evolving social norms and attitudes towards issues like same-sex marriage, abortion, or environmental protection can influence ideological orientations and electoral choices. What was once considered a peripheral issue might become a central concern, influencing voter preferences.
These shifts in ideological orientation can have profound consequences on electoral outcomes. A significant shift in the ideological composition of the electorate can lead to the rise of new political parties, changes in government policies, and a redefinition of the political spectrum.
Conclusion: The Enduring Influence of Ideology
Ideological orientation is a fundamental factor shaping voter choice in elections. It significantly impacts party identification, issue prioritization, candidate evaluation, and political participation. While other factors like candidate charisma, economic conditions, and specific policy proposals certainly play a role, the underlying ideological framework provides a crucial lens through which voters interpret information and make their electoral choices. Understanding the influence of ideology is essential to comprehending voting patterns, analyzing electoral outcomes, and fostering a more informed and engaged citizenry. Moreover, recognizing the roles of media bias, social influence, and the potential for ideological shifts provides crucial context for understanding the ever-evolving dynamics of the electoral process. The interplay between individual beliefs, societal factors, and historical context continues to shape the complex relationship between ideology and voting decisions, making it a continually fascinating area of study in political science.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Did He Actually Slow Scientific Progress In Western Europe
Mar 27, 2025
-
Ati Rn Maternal Newborn Online Practice 2023 A
Mar 27, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Period Cost
Mar 27, 2025
-
Hay 13 6 Chicas Y 20 12 Chicos
Mar 27, 2025
-
Se Sugiere Buscar Una Casa En Un Barrio Seguro Safe
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Explain How Idealogical Orientation Influenced Voters Choice In An Election . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
