Explain What Distinguishes Acute And Chronic Sports Injuries.
Breaking News Today
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
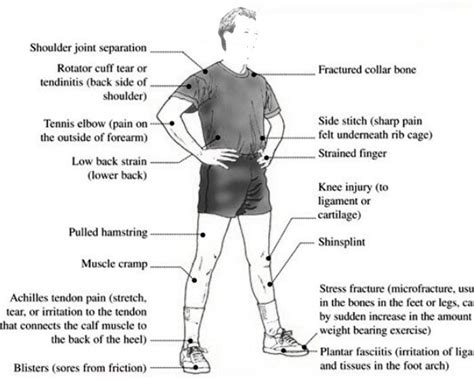
Table of Contents
Acute vs. Chronic Sports Injuries: Understanding the Differences
Sports injuries are an unfortunate reality for athletes of all levels, from weekend warriors to professional competitors. However, not all sports injuries are created equal. Understanding the key distinctions between acute and chronic injuries is crucial for proper diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. This comprehensive guide will delve into the characteristics, causes, symptoms, treatment approaches, and prevention strategies for both acute and chronic sports injuries.
What is an Acute Sports Injury?
An acute sports injury occurs suddenly, usually as a result of a specific incident like a collision, a fall, or a sudden twisting motion. These injuries are typically characterized by a rapid onset of pain and swelling. The damage is often localized to a specific area of the body. Think of a sprained ankle during a basketball game, a hamstring tear during a sprint, or a concussion after a head impact in football.
Characteristics of Acute Injuries:
- Sudden onset: The injury happens instantaneously.
- Specific mechanism of injury: A clear event triggers the injury.
- Localized pain and swelling: Pain and inflammation are concentrated in the injured area.
- Obvious signs of trauma: Visible signs like bruising, bleeding, or deformity might be present.
- Immediate pain: Pain is typically severe and immediate.
Common Examples of Acute Sports Injuries:
- Muscle strains: Sudden overstretching or tearing of a muscle.
- Ligament sprains: Stretching or tearing of a ligament, often resulting in instability of a joint.
- Fractures: Breaks in a bone.
- Dislocations: Bones in a joint are forced out of their normal position.
- Concussions: Brain injury caused by a blow to the head.
- ACL tears: Tear of the anterior cruciate ligament in the knee.
Treatment and Rehabilitation of Acute Injuries:
The immediate treatment of acute injuries focuses on the RICE protocol: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. This helps to control pain, swelling, and inflammation. Further treatment may include:
- Immobilization: Using a splint, cast, or brace to protect the injured area.
- Pain medication: Over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers.
- Physical therapy: To restore range of motion, strength, and function.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair torn ligaments, tendons, or muscles.
What is a Chronic Sports Injury?
A chronic sports injury, also known as an overuse injury, develops gradually over time. It's the result of repetitive stress, strain, or improper biomechanics, not a single traumatic event. These injuries often manifest as persistent pain, stiffness, and gradual loss of function. Think of runner's knee, tennis elbow, or plantar fasciitis.
Characteristics of Chronic Injuries:
- Gradual onset: Symptoms develop slowly over weeks or months.
- Repetitive stress: Caused by repeated movements or overuse of a particular body part.
- Diffuse pain: Pain may be widespread and not easily localized.
- Insidious onset: Symptoms might start subtly and gradually worsen.
- Persistent symptoms: Pain and discomfort often persist even at rest.
Common Examples of Chronic Sports Injuries:
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of a tendon.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of a bursa (fluid-filled sac that cushions joints).
- Stress fractures: Tiny cracks in a bone caused by repetitive stress.
- Shin splints: Pain along the shinbone, often caused by overuse.
- Runner's knee: Pain around the kneecap, often caused by overuse and poor biomechanics.
- Plantar fasciitis: Inflammation of the plantar fascia, the thick tissue on the bottom of the foot.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome: Compression of the median nerve in the wrist.
Treatment and Rehabilitation of Chronic Injuries:
Treatment for chronic injuries focuses on addressing the underlying cause of the injury and managing pain and inflammation. This may include:
- Rest and modification of activity: Reducing or modifying activities that aggravate the injury.
- Physical therapy: To improve flexibility, strength, and biomechanics.
- Stretching and strengthening exercises: To address muscle imbalances and improve joint stability.
- Anti-inflammatory medications: To reduce pain and inflammation.
- Orthotics: Custom-made shoe inserts or supports to correct biomechanical issues.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation in some cases.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be considered as a last resort.
Distinguishing Acute from Chronic Injuries: A Comparison Table
| Feature | Acute Injury | Chronic Injury |
|---|---|---|
| Onset | Sudden | Gradual |
| Mechanism | Single traumatic event | Repetitive stress or overuse |
| Pain | Severe, localized, immediate | Dull, aching, diffuse, may be present at rest |
| Swelling | Often significant, immediate | May be mild or absent |
| Inflammation | Significant, immediate | May be present but often less severe |
| Symptoms | Obvious signs of trauma (e.g., bruising) | Less obvious, insidious onset |
| Treatment | RICE protocol, immobilization, pain relief | Rest, modification of activity, physical therapy |
Prevention of Sports Injuries: A Holistic Approach
Preventing both acute and chronic sports injuries requires a multi-faceted approach. Here are some key strategies:
For Acute Injuries:
- Proper warm-up and cool-down: Preparing your body for activity and allowing it to recover afterward.
- Appropriate training and conditioning: Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of training to avoid sudden stress on the body.
- Using proper techniques: Learning and using correct techniques for specific sports to minimize risk of injury.
- Using protective equipment: Wearing appropriate protective gear such as helmets, pads, and mouthguards.
- Staying hydrated: Maintaining adequate hydration to optimize performance and reduce risk of injury.
For Chronic Injuries:
- Appropriate training volume and intensity: Avoiding excessive training and gradually increasing workload.
- Proper rest and recovery: Allowing adequate time for rest and recovery between training sessions.
- Correcting biomechanical issues: Identifying and addressing any biomechanical inefficiencies that contribute to injury.
- Strengthening and flexibility training: Focusing on strengthening muscles and improving flexibility to improve joint stability and reduce risk of injury.
- Proper footwear: Wearing supportive and appropriate footwear for the activity.
- Listening to your body: Paying attention to your body's signals and resting when needed.
The Role of Medical Professionals
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are critical for optimal recovery from both acute and chronic sports injuries. Consulting with a medical professional, such as a physician, physiotherapist, or athletic trainer, is essential. They can accurately diagnose the injury, develop an individualized treatment plan, and provide guidance on rehabilitation and injury prevention.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between acute and chronic sports injuries is crucial for athletes and healthcare providers. By understanding the characteristics, causes, and treatment approaches for each type of injury, athletes can take proactive steps to prevent injuries and ensure optimal recovery when injuries do occur. Remember that prevention is key, and a holistic approach encompassing proper training, conditioning, and recovery strategies is essential for a long and healthy athletic career. Don't hesitate to seek professional guidance when needed – your health and well-being are paramount.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Identify The Parts Of The Fibrous Layer
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Characteristic Of Plants
Mar 28, 2025
-
A Patient With Spontaneous Respirations Is Breathing
Mar 28, 2025
-
Vicente Es De Costa Rica El Es De
Mar 28, 2025
-
Explain The Reciprocal Relationship Between Human Society And Limiting Factors
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Explain What Distinguishes Acute And Chronic Sports Injuries. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
