Fertilizer In Waterways Can Lead To An Increase In _______.
Breaking News Today
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
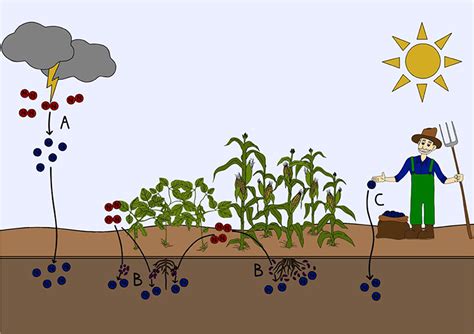
Table of Contents
- Fertilizer In Waterways Can Lead To An Increase In _______.
- Table of Contents
- Fertilizer in Waterways Can Lead to an Increase in Algal Blooms and Eutrophication: A Comprehensive Overview
- Understanding the Nutrient Connection: Fertilizer and Algal Growth
- The Domino Effect: Eutrophication and its Consequences
- The Role of Different Fertilizer Types and Application Methods
- Mitigation Strategies: Preventing Fertilizer Runoff
- The Long-Term Impacts and the Need for Collective Action
- Conclusion: A Sustainable Future for Our Waterways
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Fertilizer in Waterways Can Lead to an Increase in Algal Blooms and Eutrophication: A Comprehensive Overview
Fertilizers, while essential for boosting agricultural yields, pose a significant threat to aquatic ecosystems when they enter waterways. This influx of nutrients, primarily nitrogen and phosphorus, fuels an alarming increase in algal blooms and accelerates the process of eutrophication, with cascading consequences for water quality, biodiversity, and human health. This article delves into the intricate relationship between fertilizer runoff, algal blooms, eutrophication, and the devastating environmental impacts they trigger.
Understanding the Nutrient Connection: Fertilizer and Algal Growth
Agricultural fertilizers are formulated to provide plants with the essential nutrients they need for optimal growth. These nutrients, primarily nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P), are readily absorbed by plants. However, when excessive amounts of fertilizer are applied or when rainfall causes runoff, significant quantities of these nutrients end up in rivers, lakes, and coastal waters.
This surplus of nitrogen and phosphorus acts like a potent stimulant for algal growth. Algae, microscopic aquatic plants, are naturally present in all water bodies. However, under nutrient-rich conditions, they experience explosive growth, forming dense, visible mats known as algal blooms. These blooms can vary in color, from green to red or brown, depending on the dominant algal species.
The Domino Effect: Eutrophication and its Consequences
The excessive growth of algae, fueled by fertilizer runoff, initiates a chain reaction known as eutrophication. This process dramatically alters the aquatic ecosystem, leading to a series of detrimental effects:
-
Oxygen Depletion: As algae die and decompose, bacteria consume large amounts of dissolved oxygen in the water. This process, called decomposition, drastically reduces the oxygen levels available for fish, other aquatic animals, and other organisms. This hypoxia or anoxia (complete lack of oxygen) can lead to widespread fish kills and the death of other aquatic life.
-
Habitat Degradation: Algal blooms can physically smother aquatic plants and reduce sunlight penetration into the water column. This limits the growth of submerged vegetation, which provides crucial habitat and food sources for many aquatic organisms. The resulting loss of biodiversity can significantly impact the overall health of the ecosystem.
-
Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs): Some algal species produce toxins that are harmful to humans, animals, and marine life. These harmful algal blooms (HABs) can contaminate drinking water sources, leading to illness or even death in humans and animals. Shellfish can accumulate these toxins, making them unsafe for consumption.
-
Water Quality Degradation: Eutrophication severely impacts water quality, making it unsuitable for various purposes. The water may become cloudy, discolored, and foul-smelling due to the presence of decaying algae and other organic matter. This negatively affects recreational activities, tourism, and the aesthetic value of the water body.
-
Economic Impacts: The consequences of eutrophication extend far beyond environmental damage. It can have severe economic impacts on fisheries, tourism, and water treatment industries. The costs associated with cleaning up contaminated water, treating illnesses caused by HABs, and compensating for lost fisheries can be substantial.
The Role of Different Fertilizer Types and Application Methods
The impact of fertilizers on waterways varies depending on the type of fertilizer used and the method of application.
-
Inorganic Fertilizers: These synthetic fertilizers typically contain higher concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus compared to organic fertilizers. Their rapid release of nutrients into the soil increases the risk of runoff and subsequent eutrophication.
-
Organic Fertilizers: These fertilizers, derived from natural sources like animal manure or compost, generally release nutrients more slowly. This slower release can reduce the risk of runoff, though it doesn't eliminate it entirely. However, improper handling and application of organic fertilizers can still contribute to nutrient pollution.
-
Fertilizer Application Methods: The way fertilizers are applied greatly influences the amount of runoff. Broadcasting fertilizers over large areas, especially on sloped land, increases the risk of runoff compared to methods like banding or injecting fertilizer directly into the soil.
Mitigation Strategies: Preventing Fertilizer Runoff
Preventing fertilizer runoff and its subsequent negative impacts on waterways requires a multi-pronged approach:
-
Best Management Practices (BMPs): Implementing BMPs in agriculture is crucial to minimize nutrient runoff. These practices include:
- Nutrient Management Planning: Conducting soil tests to determine the precise amount of fertilizer needed, avoiding over-fertilization.
- Cover Cropping: Planting cover crops during fallow periods helps absorb excess nutrients and prevent soil erosion.
- Buffer Strips: Establishing vegetated buffer strips along waterways helps filter out nutrients and sediment before they enter the water.
- No-Till Farming: Reducing or eliminating tillage helps maintain soil structure and reduces erosion, minimizing nutrient loss.
- Precision Agriculture: Utilizing technology like GPS-guided applicators to precisely apply fertilizers reduces the risk of over-application.
-
Improved Wastewater Treatment: Upgrading wastewater treatment plants to effectively remove nitrogen and phosphorus from treated wastewater is essential. Advanced treatment methods can significantly reduce nutrient discharge into waterways.
-
Public Awareness and Education: Raising public awareness about the importance of responsible fertilizer use and the impact of nutrient pollution on water quality is vital. Educating farmers, homeowners, and the general public about BMPs and responsible fertilizer management can contribute to a significant reduction in nutrient runoff.
-
Policy and Regulation: Governments play a critical role in implementing and enforcing regulations to control fertilizer use and protect water quality. This can include setting limits on nutrient application rates, requiring farmers to develop nutrient management plans, and establishing water quality standards.
-
Restoration Efforts: In areas already impacted by eutrophication, restoration efforts may be necessary to rehabilitate the damaged ecosystems. These efforts can include removing excess nutrients, replanting native vegetation, and restoring degraded habitats.
The Long-Term Impacts and the Need for Collective Action
The consequences of fertilizer runoff are far-reaching and long-lasting. The degradation of water quality, loss of biodiversity, and negative impacts on human health demand urgent action. Addressing this challenge requires a collective effort involving farmers, policymakers, scientists, and the public. By adopting sustainable agricultural practices, improving wastewater treatment, and promoting public awareness, we can significantly reduce the amount of fertilizers entering waterways and protect our precious aquatic ecosystems.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Future for Our Waterways
The problem of fertilizer-induced eutrophication is a complex one, requiring integrated and multifaceted solutions. While fertilizers are essential for food production, their irresponsible use poses a significant threat to the health of our waterways. By embracing sustainable agricultural practices, implementing effective policies, and fostering a strong sense of environmental stewardship, we can strive towards a future where our waterways are healthy, vibrant, and productive ecosystems. The ongoing research and development of innovative solutions, such as advanced nutrient removal technologies and improved fertilizer formulations, also offer promising avenues for mitigating the negative impacts of fertilizers on aquatic environments. The preservation of our water resources is not merely an environmental concern; it is a fundamental aspect of human well-being and economic prosperity. A collective commitment to responsible fertilizer management is critical for securing a sustainable future for generations to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Benefits For A Medicare Supplement Policy Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Virus Is Also Known As Stomach Flu Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Ati Teas Version 7 Answer Key Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Quizlet Chapter 7 Lord Of The Flies
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Clinical Manifestation Is Associated With Cellulitis Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Fertilizer In Waterways Can Lead To An Increase In _______. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
