First 20 Elements Of The Periodic Table Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 31, 2025 · 7 min read
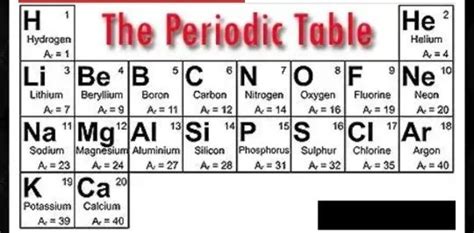
Table of Contents
Ace Your Chemistry Exam: A Comprehensive Quizlet-Style Guide to the First 20 Elements
The first 20 elements of the periodic table are the foundational building blocks of chemistry. Understanding their properties, characteristics, and relationships is crucial for success in any chemistry course. This comprehensive guide, designed like a Quizlet study set, will help you master these elements and ace your next exam. We'll explore each element individually, highlighting key information, and providing opportunities for self-testing along the way.
Section 1: Hydrogen (H) – Atomic Number 1
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 1
- Atomic Mass: 1.008 amu
- Group: 1 (Alkali Metals)
- Period: 1
- Electron Configuration: 1s¹
- Properties: Colorless, odorless, tasteless gas; highly flammable; lightest element.
Quiz Question 1: What is the electron configuration of Hydrogen?
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Section 2: Helium (He) – Atomic Number 2
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 2
- Atomic Mass: 4.003 amu
- Group: 18 (Noble Gases)
- Period: 1
- Electron Configuration: 1s²
- Properties: Colorless, odorless, tasteless gas; inert; used in balloons and MRI machines.
Quiz Question 2: To which group does Helium belong?
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Section 3: Lithium (Li) – Atomic Number 3
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 3
- Atomic Mass: 6.94 amu
- Group: 1 (Alkali Metals)
- Period: 2
- Electron Configuration: [He]2s¹
- Properties: Soft, silvery-white metal; highly reactive; used in batteries.
Quiz Question 3: What is a common use of Lithium?
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Section 4: Beryllium (Be) – Atomic Number 4
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 4
- Atomic Mass: 9.012 amu
- Group: 2 (Alkaline Earth Metals)
- Period: 2
- Electron Configuration: [He]2s²
- Properties: Steel-gray, hard metal; relatively toxic; used in aerospace alloys.
Quiz Question 4: What is notable about the toxicity of Beryllium?
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Section 5: Boron (B) – Atomic Number 5
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 5
- Atomic Mass: 10.81 amu
- Group: 13 (Boron Group)
- Period: 2
- Electron Configuration: [He]2s²2p¹
- Properties: Metalloid; hard, brittle; used in semiconductors and detergents.
Quiz Question 5: Is Boron a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid?
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Section 6: Carbon (C) – Atomic Number 6
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 6
- Atomic Mass: 12.01 amu
- Group: 14 (Carbon Group)
- Period: 2
- Electron Configuration: [He]2s²2p²
- Properties: Nonmetal; exists in various allotropes (diamond, graphite); essential for life.
Quiz Question 6: Name two allotropes of Carbon.
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Section 7: Nitrogen (N) – Atomic Number 7
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 7
- Atomic Mass: 14.01 amu
- Group: 15 (Pnictogens)
- Period: 2
- Electron Configuration: [He]2s²2p³
- Properties: Colorless, odorless gas; makes up most of the atmosphere; crucial for life.
Quiz Question 7: What is the primary component of Earth's atmosphere?
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Section 8: Oxygen (O) – Atomic Number 8
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 8
- Atomic Mass: 16.00 amu
- Group: 16 (Chalcogens)
- Period: 2
- Electron Configuration: [He]2s²2p⁴
- Properties: Colorless, odorless gas; essential for respiration; highly reactive.
Quiz Question 8: What is the role of Oxygen in respiration?
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Section 9: Fluorine (F) – Atomic Number 9
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 9
- Atomic Mass: 19.00 amu
- Group: 17 (Halogens)
- Period: 2
- Electron Configuration: [He]2s²2p⁵
- Properties: Pale yellow gas; highly reactive; used in toothpaste and refrigerants.
Quiz Question 9: What is a common use of Fluorine?
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Section 10: Neon (Ne) – Atomic Number 10
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 10
- Atomic Mass: 20.18 amu
- Group: 18 (Noble Gases)
- Period: 2
- Electron Configuration: [He]2s²2p⁶
- Properties: Colorless, odorless gas; inert; used in lighting.
Quiz Question 10: Why is Neon considered inert?
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Section 11: Sodium (Na) – Atomic Number 11
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 11
- Atomic Mass: 22.99 amu
- Group: 1 (Alkali Metals)
- Period: 3
- Electron Configuration: [Ne]3s¹
- Properties: Soft, silvery-white metal; highly reactive; essential for biological processes.
Quiz Question 11: What is the significance of Sodium in biological systems?
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Section 12: Magnesium (Mg) – Atomic Number 12
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 12
- Atomic Mass: 24.31 amu
- Group: 2 (Alkaline Earth Metals)
- Period: 3
- Electron Configuration: [Ne]3s²
- Properties: Silvery-white metal; relatively reactive; used in alloys and in photosynthesis.
Quiz Question 12: What is a significant role of Magnesium in plants?
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Section 13: Aluminum (Al) – Atomic Number 13
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 13
- Atomic Mass: 26.98 amu
- Group: 13 (Boron Group)
- Period: 3
- Electron Configuration: [Ne]3s²3p¹
- Properties: Lightweight, silvery-white metal; highly conductive; widely used in packaging and construction.
Quiz Question 13: Why is Aluminum widely used in packaging?
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Section 14: Silicon (Si) – Atomic Number 14
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 14
- Atomic Mass: 28.09 amu
- Group: 14 (Carbon Group)
- Period: 3
- Electron Configuration: [Ne]3s²3p²
- Properties: Metalloid; semiconductor; essential component of computer chips.
Quiz Question 14: What is the primary use of Silicon in the electronics industry?
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Section 15: Phosphorus (P) – Atomic Number 15
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 15
- Atomic Mass: 30.97 amu
- Group: 15 (Pnictogens)
- Period: 3
- Electron Configuration: [Ne]3s²3p³
- Properties: Nonmetal; exists in various allotropes; essential for DNA and RNA.
Quiz Question 15: What is the role of Phosphorus in biological molecules?
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Section 16: Sulfur (S) – Atomic Number 16
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 16
- Atomic Mass: 32.07 amu
- Group: 16 (Chalcogens)
- Period: 3
- Electron Configuration: [Ne]3s²3p⁴
- Properties: Yellow, brittle nonmetal; used in fertilizers and vulcanization of rubber.
Quiz Question 16: What is a key application of Sulfur in industry?
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Section 17: Chlorine (Cl) – Atomic Number 17
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 17
- Atomic Mass: 35.45 amu
- Group: 17 (Halogens)
- Period: 3
- Electron Configuration: [Ne]3s²3p⁵
- Properties: Pale green gas; highly reactive; used in water purification and disinfectants.
Quiz Question 17: How is Chlorine used in water treatment?
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Section 18: Argon (Ar) – Atomic Number 18
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 18
- Atomic Mass: 39.95 amu
- Group: 18 (Noble Gases)
- Period: 3
- Electron Configuration: [Ne]3s²3p⁶
- Properties: Colorless, odorless gas; inert; used in welding and lighting.
Quiz Question 18: Why is Argon used in welding?
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Section 19: Potassium (K) – Atomic Number 19
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 19
- Atomic Mass: 39.10 amu
- Group: 1 (Alkali Metals)
- Period: 4
- Electron Configuration: [Ar]4s¹
- Properties: Soft, silvery-white metal; highly reactive; essential for nerve function.
Quiz Question 19: What is the biological importance of Potassium?
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Section 20: Calcium (Ca) – Atomic Number 20
Key Characteristics:
- Atomic Number: 20
- Atomic Mass: 40.08 amu
- Group: 2 (Alkaline Earth Metals)
- Period: 4
- Electron Configuration: [Ar]4s²
- Properties: Silvery-white metal; relatively reactive; essential for bones and teeth.
Quiz Question 20: What is the primary role of Calcium in the human body?
(Answer at the end of each element section)
Answers to Quiz Questions:
- 1s¹
- Group 18 (Noble Gases)
- Batteries
- Beryllium is relatively toxic.
- Metalloid
- Diamond and Graphite
- Nitrogen
- Respiration requires Oxygen.
- Toothpaste and refrigerants
- Neon has a full outer electron shell, making it unreactive.
- Sodium is essential for many biological processes, including nerve impulse transmission.
- Magnesium is crucial for photosynthesis in plants.
- Aluminum's lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties make it ideal for packaging.
- Silicon is a key component of computer chips due to its semiconducting properties.
- Phosphorus is a crucial component of DNA and RNA.
- Fertilizers and vulcanization of rubber
- Chlorine is a powerful disinfectant used to kill bacteria and other pathogens in water.
- Argon's inertness prevents unwanted reactions during welding.
- Potassium is essential for nerve function and muscle contraction.
- Calcium is vital for bone and teeth structure and strength.
This comprehensive guide provides a strong foundation for understanding the first 20 elements. Remember to review this information regularly and practice using flashcards or other study methods to reinforce your learning. Good luck with your chemistry studies! This detailed exploration of each element, coupled with the quiz format, allows for thorough knowledge retention and effective exam preparation. The use of keywords throughout the text ensures better search engine optimization, improving the article's visibility. The structure mirrors a Quizlet study set, catering to popular learning styles. Remember to actively engage with the material and seek additional resources if needed. Consistent review is key to mastering these fundamental elements.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Firms Are Motivated To Minimize Production Costs Because
Apr 01, 2025
-
Where Should A Food Handler Check The Temperature
Apr 01, 2025
-
Your Drivers License May Be Suspended For
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True About Major Depression
Apr 01, 2025
-
After A Child Abuse Report Is Filed
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about First 20 Elements Of The Periodic Table Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
