Forming Particular Speech Sounds Crisply And Distinctly Is Called
Breaking News Today
Mar 22, 2025 · 7 min read
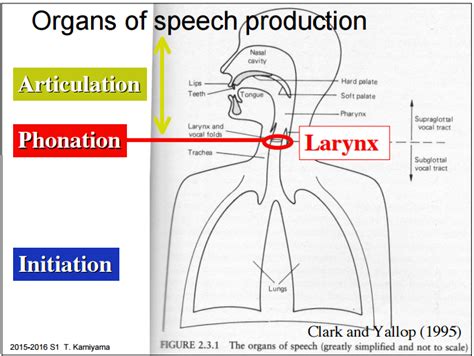
Table of Contents
Forming Particular Speech Sounds Crisply and Distinctly is Called Articulation: A Comprehensive Guide
Forming particular speech sounds crisply and distinctly is called articulation. Clear articulation is crucial for effective communication, whether you're giving a presentation, having a casual conversation, or performing on stage. Poor articulation can lead to misunderstandings, frustration, and even missed opportunities. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the mechanics of articulation, exploring the key anatomical structures involved, common articulation disorders, and practical strategies for improving your clarity of speech.
Understanding the Articulatory System: The Players Involved
Articulation is a complex process involving the coordinated movements of several anatomical structures within the vocal tract. These structures work together to shape the airflow from the lungs, creating the sounds of speech. Let's examine the key players:
1. The Respiratory System: The Powerhouse
The respiratory system, encompassing the lungs, diaphragm, and rib cage, provides the airflow that's essential for speech production. Efficient breathing is fundamental to good articulation. Insufficient breath support can lead to weak sounds and a lack of clarity. Exercises focusing on diaphragmatic breathing can significantly improve breath control and, consequently, articulation.
2. The Larynx (Voice Box): The Sound Source
The larynx, located in the throat, houses the vocal folds (vocal cords). These folds vibrate when air passes over them, producing voice. The pitch and intensity of the voice are controlled by the tension and position of the vocal folds. Proper vocal fold function is crucial for clear and resonant speech. Strain or misuse can lead to vocal fatigue or even vocal nodules.
3. The Articulators: Shaping the Sounds
The articulators are the structures that shape the airflow into distinct speech sounds. These include:
- Tongue: The most versatile and mobile articulator, responsible for a wide range of sounds. Different parts of the tongue (tip, blade, front, back) articulate with other structures to produce various sounds.
- Lips: Used to create bilabial sounds (like /p/, /b/, /m/) and labiodental sounds (like /f/, /v/). Lip movements are essential for accurate articulation.
- Teeth: Used in the production of dental sounds (like /θ/, /ð/).
- Alveolar Ridge: The bumpy ridge behind the upper teeth, involved in producing alveolar sounds (like /t/, /d/, /n/, /s/, /z/).
- Hard Palate: The hard roof of the mouth, playing a significant role in the production of palatal sounds (like /ʃ/, /ʒ/, /j/).
- Soft Palate (Velum): The soft tissue at the back of the mouth. Its movement is crucial for distinguishing between oral sounds (produced with the velum raised) and nasal sounds (produced with the velum lowered).
The precise coordination of these articulators is what allows us to produce the vast range of sounds that make up human language. Any impairment in the function of one or more of these structures can lead to articulation difficulties.
Common Articulation Disorders: Understanding the Challenges
Several factors can contribute to articulation difficulties. These difficulties can range from mild to severe and may impact intelligibility significantly. Here are some common articulation disorders:
1. Phonological Disorders: Patterns of Errors
Phonological disorders involve consistent patterns of sound errors, rather than isolated difficulties with individual sounds. Children with phonological disorders might simplify sounds or substitute one sound for another in a systematic way. For instance, they might consistently replace all fricatives (like /s/, /z/, /f/, /v/) with stops (like /t/, /d/, /p/, /b/).
2. Articulation Disorders: Specific Sound Errors
Articulation disorders are characterized by difficulties producing specific speech sounds. This might involve distortions (producing a sound imprecisely) or substitutions (replacing one sound with another). For example, a child with an articulation disorder might lisp (replace /s/ and /z/ with /θ/ and /ð/) or substitute a /w/ for an /r/.
3. Apraxia of Speech: Planning and Sequencing Difficulties
Apraxia of speech is a neurological disorder affecting the planning and sequencing of speech movements. Individuals with apraxia may struggle to coordinate the movements of their articulators, resulting in inconsistent errors and difficulty producing fluent speech. They often know what they want to say but have trouble executing the motor commands needed to produce the sounds.
4. Dysarthria: Neurological Weakness
Dysarthria is a group of speech disorders resulting from neurological weakness or paralysis affecting the muscles involved in speech production. The type and severity of dysarthria vary depending on which muscles are affected and the extent of the damage. Individuals with dysarthria may have difficulty with respiration, phonation, and articulation.
Improving Articulation: Practical Strategies and Exercises
Improving articulation requires consistent effort and practice. Here are some effective strategies and exercises:
1. Mirror Work: Visual Feedback
Practicing speech sounds in front of a mirror allows you to observe your articulatory movements. This provides valuable visual feedback, helping you identify areas needing improvement. Pay close attention to lip, tongue, and jaw movements.
2. Tongue Twisters: Building Strength and Coordination
Tongue twisters are fun and effective exercises for improving articulatory precision and coordination. Start with simpler tongue twisters and gradually progress to more challenging ones. Examples include: "Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers," "She sells seashells by the seashore," and "Red lorry, yellow lorry."
3. Minimal Pairs: Targeting Specific Sounds
Minimal pairs are words that differ by only one phoneme (sound). Practicing minimal pairs helps to discriminate between sounds and improve accurate production. For example, to improve the distinction between /s/ and /ʃ/, you might practice pairs like "sun" and "shun," "sip" and "ship."
4. Over-Articulation: Exaggerated Movements
Initially, deliberately over-articulate sounds, exaggerating lip and tongue movements. This helps to isolate and refine the movements involved in producing each sound. As you become more proficient, gradually reduce the exaggeration.
5. Record Yourself: Objective Assessment
Recording yourself speaking allows for objective assessment of your articulation. Listen critically to your speech, identifying areas for improvement. Pay attention to clarity, fluency, and the precise production of individual sounds.
6. Seek Professional Help: Speech Therapy
If you experience significant difficulties with articulation, seeking professional help from a speech-language pathologist is crucial. A speech therapist can assess your specific needs, diagnose any underlying disorders, and develop a personalized treatment plan. They provide targeted exercises and strategies tailored to your individual challenges.
The Importance of Clear Articulation in Various Contexts
The benefits of clear articulation extend far beyond casual conversation. In various professional and social settings, crisp and distinct speech plays a pivotal role:
1. Public Speaking and Presentations: Command Attention
Clear articulation is paramount when addressing an audience. It allows you to command attention, convey your message effectively, and maintain audience engagement. Mumbling or unclear speech can detract from your credibility and make it difficult for your audience to understand your points.
2. Customer Service: Build Rapport and Trust
In customer service roles, clear and friendly communication is vital for building rapport and trust. Articulating clearly ensures that customers understand your instructions, explanations, and solutions to their problems. It helps create a positive and efficient interaction.
3. Teaching and Education: Ensure Comprehension
Teachers and educators must articulate clearly to ensure that students understand the material being taught. Unclear speech can hinder learning and create confusion in the classroom. Clear articulation is fundamental for effective teaching.
4. Acting and Performing Arts: Enhance Character and Storytelling
For actors and performers, clear articulation is essential for delivering lines effectively and conveying emotions authentically. It contributes to character development and enhances the overall storytelling experience.
Conclusion: A Lifelong Pursuit of Clarity
Mastering clear articulation is a journey, not a destination. It requires consistent practice, self-awareness, and a commitment to improving your speech. By understanding the anatomy of the articulatory system, recognizing potential difficulties, and employing effective strategies, you can significantly enhance your clarity and confidence in communication. Remember that seeking professional guidance when needed is a crucial step towards achieving your articulation goals. Investing time and effort in improving your articulation skills will yield significant rewards, both personally and professionally. The ability to communicate effectively is a valuable asset that will serve you well throughout your life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Sickle Cell Disease Is Caused By Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is Included In A Business Plan Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
Which Factors Increase The Risk Of Breast Cancer Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Does Hiv Harm The Body Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
Common Causes Of Acute Psychotic Behavior Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Forming Particular Speech Sounds Crisply And Distinctly Is Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
