Fungal Infections Are More Common Than Bacterial Or Viral Infections.
Breaking News Today
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
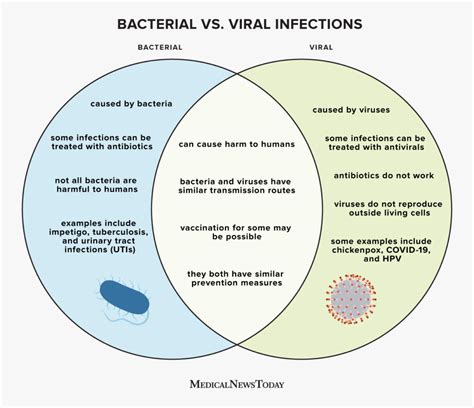
Table of Contents
Fungal Infections: The Silent Pandemic Outnumbering Bacteria and Viruses
The world of infectious diseases is vast and complex, often dominated by narratives surrounding bacteria and viruses. However, a significant player often remains underestimated: fungi. Contrary to popular belief, fungal infections are far more prevalent than many realize, frequently outnumbering both bacterial and viral infections globally. This article delves deep into the underestimated realm of fungal diseases, exploring their prevalence, diverse manifestations, risk factors, and the urgent need for increased awareness and research.
The Hidden Prevalence of Fungal Infections
While bacterial and viral infections often grab headlines due to their dramatic outbreaks and associated morbidity, fungal infections quietly impact a significantly larger population. The sheer diversity of fungi, coupled with their ability to adapt and thrive in various environments, contributes to their widespread presence. Estimates suggest that fungal infections affect billions worldwide annually, with a substantial proportion remaining undiagnosed or misdiagnosed.
This underestimation stems from several factors:
- Asymptomatic Infections: Many fungal infections are asymptomatic or present with mild, nonspecific symptoms, easily mistaken for other conditions. This leads to delayed diagnosis or missed cases entirely.
- Diagnostic Challenges: Accurate diagnosis of fungal infections often requires specialized laboratory techniques, which may not be readily available in all healthcare settings. This lack of access hinders accurate prevalence assessments.
- Lack of Awareness: Both the public and healthcare professionals often lack awareness of the wide range of fungal diseases and their potential severity. This contributes to underreporting and delayed intervention.
The Diverse World of Fungal Infections: From Superficial to Systemic
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms exhibiting incredible diversity in their morphology, physiology, and pathogenic potential. Their infections range from superficial skin conditions to life-threatening systemic diseases. Let's explore some key categories:
1. Superficial Fungal Infections (Mycoses): These infections primarily affect the outermost layers of skin, hair, and nails.
- Tinea (Ringworm): A common fungal infection causing circular, scaly rashes on the skin. Different types affect various body parts (e.g., tinea pedis – athlete's foot; tinea capitis – scalp ringworm).
- Candidiasis (Yeast Infection): Caused by Candida species, commonly affecting the mouth (thrush), vagina, and skin folds.
- Dermatophytosis: A group of fungal infections affecting the skin, hair, and nails, often presenting with itching, scaling, and discoloration.
2. Subcutaneous Fungal Infections: These infections involve deeper layers of skin and subcutaneous tissues, often resulting from traumatic inoculation.
- Sporotrichosis: A chronic infection often associated with contact with plants and soil.
- Chromoblastomycosis: A chronic, granulomatous infection causing warty lesions on the skin.
- Mycetoma: A chronic, localized infection involving skin, subcutaneous tissue, and bone.
3. Systemic Fungal Infections: These infections spread throughout the body, affecting internal organs and posing significant health risks. They are particularly dangerous for immunocompromised individuals.
- Coccidioidomycosis (Valley Fever): An inhalation-based infection caused by Coccidioides species, prevalent in arid and semi-arid regions.
- Histoplasmosis: Another inhalation-based infection caused by Histoplasma capsulatum, found in bird and bat droppings.
- Blastomycosis: A fungal infection affecting the lungs and other organs, commonly associated with exposure to soil and decaying organic matter.
- Cryptococcosis: A serious infection caused by Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gattii, affecting the lungs and central nervous system. It poses a significant threat to individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Aspergillosis: Caused by Aspergillus species, this can range from allergic reactions to invasive infections affecting the lungs, sinuses, and other organs. It is a major concern for immunocompromised individuals, particularly those with leukemia or undergoing organ transplantation.
- Candidiasis (Systemic): In immunocompromised individuals, Candida species can spread beyond superficial tissues, causing life-threatening systemic infections.
Risk Factors for Fungal Infections
Several factors increase an individual's susceptibility to fungal infections:
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with HIV/AIDS, undergoing chemotherapy, organ transplantation, or suffering from other immunocompromising conditions are at significantly higher risk.
- Antibiotic Use: Prolonged or inappropriate antibiotic use can disrupt the natural balance of the body's microbiota, allowing opportunistic fungi to proliferate.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels create a favorable environment for fungal growth.
- Chronic Diseases: Conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and cystic fibrosis can increase the risk of fungal lung infections.
- Exposure to Fungi: Occupation (e.g., agriculture, construction), geographical location (areas with high fungal spores), and lifestyle choices (e.g., exposure to damp environments) can influence risk.
- Age: Infants and older adults are more vulnerable to severe fungal infections.
The Urgent Need for Enhanced Research and Awareness
The widespread prevalence of fungal infections, coupled with the significant morbidity and mortality associated with some systemic mycoses, highlights the critical need for intensified research and public health initiatives.
Areas requiring urgent attention include:
- Development of Novel Antifungal Drugs: The limited arsenal of effective antifungal drugs, along with the increasing incidence of antifungal resistance, underscores the urgent need for novel therapeutic agents.
- Improved Diagnostic Tools: Rapid and accurate diagnostic methods are essential for timely intervention and improved patient outcomes. Research into point-of-care diagnostics is crucial.
- Public Health Surveillance: Strengthening surveillance systems to better track the incidence and distribution of fungal infections is vital for effective public health planning and response.
- Increased Awareness and Education: Raising awareness among healthcare professionals and the public about the prevalence, risk factors, and clinical manifestations of fungal infections is crucial for early diagnosis and appropriate management.
Conclusion: Reframing the Narrative of Infectious Disease
The reality is that fungal infections are far more common than often acknowledged. They pose a significant global health challenge, affecting individuals across all age groups and socioeconomic backgrounds. While bacterial and viral infections remain significant concerns, shifting the focus to understand and address the widespread burden of fungal diseases is crucial for improving global health outcomes. This requires a multi-pronged approach involving enhanced research, improved diagnostics, public health initiatives, and a fundamental change in societal awareness regarding the silent pandemic of fungal infections. Only through concerted efforts can we effectively combat this underestimated threat and mitigate its devastating impact on human health. Further research into the complex interactions between fungi, the human microbiome, and the environment will be vital to developing innovative prevention and treatment strategies for these often overlooked infections. The future of infectious disease management demands a comprehensive approach that places fungal infections at the forefront.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of These Organelles Produces H2o2 As A By Product
Mar 16, 2025
-
Which Statement Is An Example Of Personification
Mar 16, 2025
-
The Campsite In Montana Is Wayfarers Campground
Mar 16, 2025
-
How Do You Develop An Effective Content Distribution Strategy
Mar 16, 2025
-
A Potential Negative Result Of Trade Agreements Is
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Fungal Infections Are More Common Than Bacterial Or Viral Infections. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
