Which Of These Organelles Produces H2o2 As A By Product
Breaking News Today
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
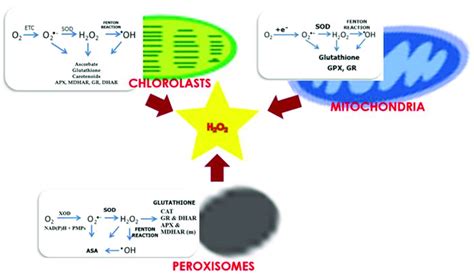
Table of Contents
Which Organelle Produces H₂O₂ as a Byproduct? The Role of Peroxisomes
The production of hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) as a byproduct is a key characteristic of a specific cellular organelle: the peroxisome. While other organelles might indirectly contribute to H₂O₂ generation, peroxisomes are uniquely designed and dedicated to its controlled production and subsequent detoxification. Understanding the role of peroxisomes in H₂O₂ metabolism is crucial to comprehending cellular function, oxidative stress, and various diseases.
The Peroxisome: A Hub of Oxidative Reactions
Peroxisomes are single-membrane-bound organelles found in virtually all eukaryotic cells. They are highly dynamic, constantly changing in size and number depending on the cell's metabolic needs. Their primary function revolves around oxidation reactions, particularly those involving fatty acids and other potentially harmful molecules. This oxidative process is precisely where H₂O₂ comes into play.
Key Enzymes and Reactions
The hallmark enzyme of peroxisomes is catalase. This enzyme plays a crucial role in neutralizing the potentially toxic H₂O₂ produced within the organelle. Catalase efficiently catalyzes the decomposition of H₂O₂ into water (H₂O) and oxygen (O₂), a process known as catalysis. This prevents the buildup of H₂O₂ which, in high concentrations, can cause significant cellular damage through oxidative stress.
Beyond catalase, peroxisomes house a variety of other enzymes involved in diverse metabolic pathways, many of which generate H₂O₂ as a byproduct. These include:
- Acyl-CoA oxidases: These enzymes are central to the β-oxidation of very-long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs). This process generates acetyl-CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle for energy production, but also produces H₂O₂ as a byproduct.
- Amino acid oxidases: These enzymes catalyze the oxidative deamination of amino acids, producing H₂O₂ and ammonia.
- D-amino acid oxidase: This enzyme specifically targets D-amino acids, isomers of the L-amino acids typically used in protein synthesis. The oxidation of D-amino acids also leads to H₂O₂ production.
- Xanthine oxidase: This enzyme participates in purine metabolism, generating uric acid and H₂O₂.
These are just a few examples, and the specific enzymatic content of peroxisomes can vary significantly depending on the cell type and its metabolic demands. The common thread is that these enzymes utilize molecular oxygen (O₂) as an electron acceptor, leading to the formation of H₂O₂ as a reactive oxygen species (ROS).
H₂O₂: A Double-Edged Sword
Hydrogen peroxide, while a byproduct, isn't simply waste. It plays a critical role in various cellular processes, including:
- Signaling: At low concentrations, H₂O₂ acts as a signaling molecule, modulating various cellular pathways, including those involved in cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis (programmed cell death). This signaling role involves the oxidation of specific proteins and lipids, triggering downstream cascades.
- Defense against Pathogens: Peroxisomes and the H₂O₂ they produce are involved in the immune response. The oxidative power of H₂O₂ can contribute to the destruction of invading pathogens, acting as a first line of defense against infection. Neutrophils, a type of white blood cell, use a specialized form of H₂O₂ production, known as the respiratory burst, to kill bacteria.
However, this dual nature of H₂O₂ highlights its importance in maintaining a delicate balance. Excessive H₂O₂ accumulation is detrimental, leading to oxidative stress, which can damage cellular components, including DNA, proteins, and lipids. This damage can contribute to aging, various diseases, and even cell death.
The Importance of Catalase and Other Antioxidant Systems
The crucial role of catalase in neutralizing H₂O₂ cannot be overstated. Its high efficiency ensures that the potentially harmful levels of H₂O₂ generated within peroxisomes are swiftly converted into harmless water and oxygen. However, catalase isn't the only line of defense. Other antioxidant systems within the cell work in conjunction to mitigate the damaging effects of H₂O₂ and other ROS:
- Glutathione peroxidase: This enzyme uses glutathione as a reducing agent to convert H₂O₂ to water.
- Superoxide dismutase (SOD): While not directly involved in H₂O₂ metabolism, SOD converts superoxide radicals (O₂⁻) into H₂O₂, which can then be further processed by catalase or glutathione peroxidase.
- Other antioxidants: Various other molecules, such as vitamin C and vitamin E, act as scavengers of ROS, further reducing oxidative stress.
The coordinated action of these antioxidant systems is essential in maintaining cellular homeostasis and protecting against the damaging consequences of excessive ROS production.
Peroxisomal Disorders: When H₂O₂ Metabolism Goes Wrong
Dysfunction in peroxisomal function, particularly in H₂O₂ metabolism, can lead to severe inherited disorders known as peroxisomal disorders. These disorders arise from mutations in genes encoding peroxisomal proteins, affecting the import of enzymes into peroxisomes, the activity of specific enzymes, or the biogenesis of peroxisomes themselves.
The consequences can be severe, ranging from neurological problems to liver and kidney dysfunction. The accumulation of VLCFAs, due to impaired β-oxidation, and the resultant oxidative stress are key contributors to the pathogenesis of these disorders. The inability to efficiently neutralize H₂O₂ exacerbates the cellular damage.
Beyond Peroxisomes: Other Sources of H₂O₂
While peroxisomes are the primary site of H₂O₂ production, other organelles and cellular processes can contribute to its generation, albeit indirectly or in smaller quantities. For example:
- Mitochondria: These powerhouses of the cell produce ROS, including superoxide radicals and H₂O₂, as byproducts of oxidative phosphorylation. However, the primary function of mitochondria is energy production, not H₂O₂ metabolism.
- Endoplasmic reticulum (ER): The ER also contributes to ROS production during protein folding and other processes.
- Plasma membrane: NADPH oxidases, located in the plasma membrane, can produce superoxide radicals, which can be converted to H₂O₂.
However, it's important to emphasize that these sources are not dedicated to H₂O₂ production like peroxisomes. They primarily serve other cellular functions, and H₂O₂ generation is a secondary consequence.
Conclusion: The Central Role of Peroxisomes in H₂O₂ Metabolism
In conclusion, peroxisomes are the primary organelles responsible for producing H₂O₂ as a byproduct of their essential metabolic functions. The efficient detoxification of this potentially harmful molecule by catalase and other antioxidant systems is crucial for maintaining cellular health and preventing oxidative stress. Dysfunction in peroxisomal H₂O₂ metabolism can have profound consequences, leading to a range of severe disorders. Understanding the intricate interplay between peroxisomes, H₂O₂, and antioxidant systems remains essential for advancing our knowledge of cellular biology, disease mechanisms, and potential therapeutic interventions. Future research will undoubtedly further unravel the complexities of peroxisomal function and its crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis. The delicate balance between H₂O₂ production and detoxification is a testament to the sophistication and resilience of cellular processes.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
True Or False Professional And Technical Communication Is Research Oriented
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Best Describes The Terrorist Planning Cycle
Mar 18, 2025
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
Life Insurance Exam Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Direct Carry Is Used To Transfer A Patient
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of These Organelles Produces H2o2 As A By Product . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
