Hayward Earthquake Swarm: USGS Report
Breaking News Today
Feb 14, 2025 · 5 min read
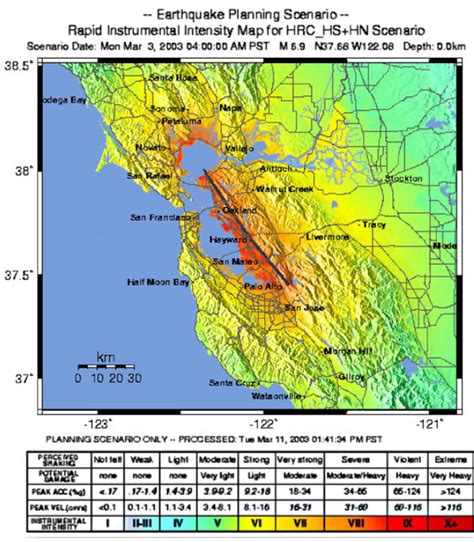
Table of Contents
Hayward Earthquake Swarm: USGS Report: Understanding the Seismic Activity and Future Risks
The recent earthquake swarm near the Hayward Fault in California has understandably raised concerns among residents and seismologists alike. This article delves into the USGS (United States Geological Survey) reports regarding this seismic activity, explaining the swarm's characteristics, the underlying geological processes, and the implications for future earthquake risk in the region. We'll examine the data, explore potential explanations, and discuss what this activity means for preparedness and mitigation efforts.
Understanding Earthquake Swarms
Before we dive into the specifics of the Hayward swarm, let's define what an earthquake swarm actually is. Unlike a typical earthquake sequence that features a mainshock followed by smaller aftershocks, an earthquake swarm involves a series of earthquakes of varying magnitudes clustering in both time and space, without a clear-cut mainshock. The swarm can last for days, weeks, months, or even years, with seismic activity fluctuating in intensity. The cause of earthquake swarms can be complex and often involves the movement of fluids (magma, water) within the Earth's crust, pressure changes along fault lines, or even the stress transfer from nearby tectonic plates.
The Hayward Fault: A Tectonic Hotspot
The Hayward Fault is a major active fault running through the East Bay region of the San Francisco Bay Area. It's part of the larger San Andreas Fault system, a transform boundary where the Pacific and North American tectonic plates meet. The Hayward Fault is capable of producing significant earthquakes, and it's overdue for a large rupture. Historical records show that the fault has generated powerful earthquakes in the past, with significant damage and loss of life. This makes the recent swarm particularly noteworthy and warrants close monitoring by seismologists.
The USGS Report: Key Findings
The USGS continuously monitors seismic activity across the United States, and their reports on the Hayward earthquake swarm provide crucial information for understanding the ongoing events. While the exact details of any particular report will vary depending on the timing of the swarm, key aspects consistently found in USGS reports typically include:
1. Location and Magnitude of Earthquakes:
USGS reports precisely pinpoint the location (latitude and longitude) of each earthquake within the swarm. This helps researchers to map the spatial extent of the seismic activity and identify potential connections to underlying geological structures. The magnitude of each earthquake is also crucial, allowing seismologists to assess the relative energy released and to evaluate the potential for damage. The reports will usually include a distribution of magnitudes, highlighting the frequency of smaller tremors versus larger events.
2. Depth of Earthquakes:
The depth at which the earthquakes originate is a significant factor in determining their impact on the surface. Shallower earthquakes tend to cause more ground shaking and damage than deeper ones. The USGS reports provide this information, allowing scientists to analyze whether the swarm is associated with shallow crustal processes or deeper tectonic interactions.
3. Seismic Wave Analysis:
Detailed analysis of the seismic waves generated by the earthquakes helps seismologists understand the fault plane geometry, the type of faulting (e.g., strike-slip, normal, reverse), and the stress field in the region. This information is critical for understanding the mechanics of the swarm and for refining earthquake hazard assessments.
4. Comparison to Historical Data:
USGS reports often include a comparison of the current swarm's characteristics (location, magnitude, duration) with historical seismic activity in the same region. This helps to establish whether the swarm is unusual or falls within the expected range of natural variability. Such comparisons inform the evaluation of long-term seismic risk.
5. Potential Implications for Future Earthquakes:
Perhaps the most crucial aspect of the USGS reports is their interpretation of the potential implications for future seismic activity. While it's impossible to predict earthquakes with certainty, the swarm's characteristics, combined with geological understanding of the Hayward Fault, provide valuable insights into the likelihood and potential magnitude of future earthquakes. However, it's crucial to remember that even with sophisticated analysis, the exact timing and magnitude of future events remain uncertain.
Interpreting the Data: What Does it All Mean?
The significance of the Hayward earthquake swarm lies in its potential to be a precursor to, or a symptom of, increased stress on the Hayward Fault. While the swarm itself may not be directly indicative of an imminent large earthquake, it highlights the fault's ongoing tectonic activity. The swarm acts as a powerful reminder of the seismic hazard in the Bay Area. The increased frequency of smaller earthquakes can potentially indicate stress build-up on the fault, though this is not a guaranteed predictor of a larger quake.
Preparedness and Mitigation
The USGS reports are not just for scientists; they are critical for public safety and preparedness. The information provides a basis for:
- Improving building codes: Understanding the potential for ground shaking from different earthquake scenarios allows for the development of stricter building codes and retrofitting strategies, particularly in areas close to the Hayward Fault.
- Developing emergency response plans: Local authorities can use the data to refine emergency response plans, including evacuation routes, communication strategies, and resource allocation.
- Public education campaigns: The information from USGS reports is vital for educating the public about earthquake risks, preparedness measures, and what to do during and after an earthquake.
Conclusion:
The Hayward earthquake swarm, as detailed in USGS reports, provides a stark reminder of the ongoing seismic activity along the Hayward Fault. While the swarm itself might not be directly predictive of a major earthquake, it emphasizes the importance of ongoing monitoring, research, and preparedness. The information provided by the USGS is crucial not only for scientific understanding but also for the safety and well-being of communities living in earthquake-prone regions. Continued vigilance and proactive mitigation efforts remain essential in reducing the risk and impact of future earthquakes in the Bay Area. The USGS website serves as a primary source for up-to-date information and should be consulted for the latest developments. Staying informed and prepared is crucial for navigating the seismic realities of living in earthquake country.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Do You Call The Demarcation Point For Fiber Technologies
Mar 12, 2025
-
Which Statement Best Describes The Circular Flow Model
Mar 12, 2025
-
Trac Nghiem Kinh Te Chinh Tri Chuong 6
Mar 12, 2025
-
A State Function Is Best Described As
Mar 12, 2025
-
It Is Important To Avoid Ballistic Stretches Because They Can
Mar 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Hayward Earthquake Swarm: USGS Report . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
