How Can Tight Muscles Result In Back Pain Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
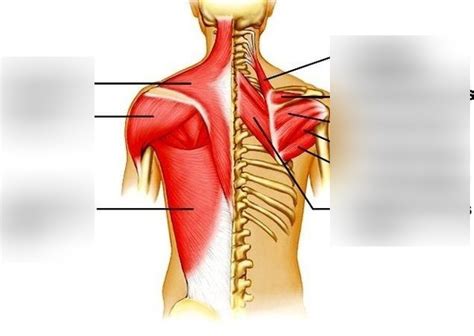
Table of Contents
How Tight Muscles Can Result in Back Pain: A Comprehensive Guide
Back pain is a pervasive problem, affecting millions worldwide. While various factors contribute to this debilitating condition, muscle tightness frequently plays a significant, often overlooked, role. Understanding the intricate relationship between tight muscles and back pain is crucial for effective prevention and management. This comprehensive guide delves into the mechanics of how tight muscles cause back pain, identifying specific muscle groups, exploring contributing factors, and outlining effective strategies for relief and prevention.
The Anatomy of Back Pain: Muscles and Their Role
Our back is a complex network of muscles, ligaments, tendons, and bones. These structures work in concert to support our posture, enable movement, and protect the spinal cord. When these components become imbalanced or compromised, pain ensues. Tight muscles disrupt this delicate balance, leading to a cascade of problems. Several key muscle groups are frequently implicated in back pain stemming from tightness:
-
Erector Spinae Muscles: These long muscles run along the spine, responsible for extension (arching backward) and maintaining posture. Chronic tightness can lead to stiffness, limited range of motion, and pain. Think of them as the "backbone" of your back's support system.
-
Latissimus Dorsi (Lats): These large muscles in the upper back and sides connect to the spine, shoulders, and pelvis. Tight lats can pull the shoulders forward, increasing curvature of the spine (kyphosis) and placing undue stress on the lower back. This posture can contribute significantly to lower back pain.
-
Hip Flexors (Iliopsoas): Located in the front of the hips, these muscles connect the spine to the legs. Tight hip flexors tilt the pelvis forward, increasing the lumbar lordosis (the inward curve of the lower back). This altered posture puts extra strain on the lower back muscles and can exacerbate existing pain.
-
Gluteal Muscles (Glutes): Weakness in the gluteal muscles, often coupled with tightness in other muscles, is a major contributor to back pain. Weak glutes lead to compensatory mechanisms where other muscles, particularly the lower back, overwork to stabilize the pelvis and maintain posture. This strain can easily cause pain.
-
Hamstrings: These muscles at the back of your thighs, when tight, can limit hip extension, affecting pelvic alignment and increasing stress on the lower back.
Mechanisms of Muscle Tightness Leading to Back Pain
Tight muscles don't directly cause back pain in isolation. Rather, the tightness creates a chain reaction that ultimately results in discomfort. Here's how:
-
Postural Imbalances: Tight muscles pull on the spine, altering its natural curves. This misalignment places abnormal stress on the joints, ligaments, and other muscles, leading to pain and discomfort. Poor posture is a significant contributor here.
-
Muscle Spasms: Prolonged muscle tightness can trigger spasms—involuntary contractions—in affected muscles. These spasms are extremely painful and restrict movement.
-
Nerve Compression: Tight muscles can compress nerves that pass through or near the spine. This compression, known as nerve root impingement, can cause radiating pain down the leg (sciatica) or other areas.
-
Reduced Blood Flow: Tight muscles can restrict blood flow to the area, depriving tissues of essential oxygen and nutrients. This can contribute to inflammation and pain.
-
Trigger Points: These are hyperirritable spots in a muscle that, when activated, refer pain to other areas of the body. Trigger points in the back muscles are a common source of localized and referred pain.
-
Inflammation: Prolonged muscle strain and injury trigger the inflammatory response, further contributing to pain and discomfort.
Identifying Contributing Factors to Muscle Tightness
Several factors contribute to the development of tight muscles and subsequent back pain:
-
Sedentary Lifestyle: Prolonged sitting weakens muscles, shortening and tightening them. This is especially true for hip flexors.
-
Poor Posture: Slouching, hunching, and other poor postural habits put undue strain on muscles, leading to tightness and pain.
-
Lack of Physical Activity: Inactivity weakens and tightens muscles, making them more prone to injury and pain.
-
Stress: Stress leads to muscle tension, often manifesting as tightness in the neck, shoulders, and back.
-
Dehydration: Dehydrated muscles are more prone to stiffness and cramps.
-
Underlying Medical Conditions: Conditions like arthritis, fibromyalgia, and scoliosis can contribute to muscle tightness and back pain.
-
Improper Lifting Techniques: Lifting heavy objects incorrectly places significant stress on the back muscles, leading to strain and tightness.
Effective Strategies for Relief and Prevention
Addressing back pain stemming from muscle tightness involves a multi-pronged approach:
-
Stretching: Regular stretching is crucial for lengthening tight muscles and improving flexibility. Focus on stretches that target the erector spinae, lats, hip flexors, glutes, and hamstrings. Gentle, consistent stretching is more effective than forceful stretches.
-
Strength Training: Strengthening the core and supporting muscles helps improve posture, stability, and reduces strain on the back. Exercises focusing on the abdominal muscles, back muscles, and glutes are particularly beneficial.
-
Postural Correction: Pay attention to your posture throughout the day. Sit upright with good support, avoid prolonged sitting, and maintain a neutral spine when standing.
-
Ergonomic Adjustments: Ensure your workstation is ergonomically sound to minimize strain on your back. This includes proper chair height, monitor placement, and keyboard position.
-
Massage Therapy: Massage can help relieve muscle tension, improve blood flow, and reduce pain. Different massage modalities, such as deep tissue massage, can effectively target tight muscles.
-
Heat and Ice Therapy: Heat can relax tight muscles, while ice can reduce inflammation. Alternating heat and ice treatments may provide relief.
-
Yoga and Pilates: These mind-body practices improve flexibility, strength, and posture, which can significantly alleviate back pain.
-
Mindfulness and Stress Reduction Techniques: Stress management techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can help reduce muscle tension related to stress.
-
Hydration: Maintaining adequate hydration ensures muscles function optimally.
-
Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts extra strain on the back, exacerbating muscle tightness and pain.
-
Consult a Healthcare Professional: If back pain is persistent or severe, consult a doctor or physical therapist for proper diagnosis and treatment. They can help rule out serious underlying causes and develop a personalized treatment plan.
Self-Assessment and When to Seek Professional Help
While many can manage back pain from muscle tightness with self-care, knowing when to seek professional help is essential:
-
Severe Pain: Intense, unrelenting pain that interferes with daily activities warrants immediate medical attention.
-
Pain Radiating Down the Leg: This could indicate nerve compression, requiring prompt evaluation.
-
Weakness or Numbness: These symptoms may signal a serious neurological issue.
-
Fever or Unexplained Weight Loss: These could be signs of underlying conditions.
-
Pain Lasting Longer Than a Few Weeks: Persistent pain despite self-care efforts necessitates professional evaluation.
By understanding the intricate relationship between tight muscles and back pain, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this common condition. A holistic approach combining stretching, strengthening, postural correction, stress management, and professional guidance when needed offers the most effective path towards lasting relief and improved back health. Remember, consistent effort is key to achieving lasting results. Prioritize your back health; it supports everything you do.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Typically High Inflation Is A Sign Of
Mar 18, 2025
-
Behaviorism Focuses On Making Psychology An Objective Science By
Mar 18, 2025
-
Debt Is The Most Aggressively Marketed Product
Mar 18, 2025
-
Excessive Eating Caused By Cellular Hunger Is Called
Mar 18, 2025
-
Administrative Civil Or Criminal Sanctions May Be Imposed
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Can Tight Muscles Result In Back Pain Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
