How Does A Nominating Caucus Differ From A Primary Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
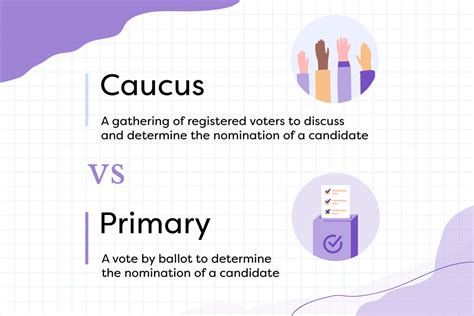
Table of Contents
How Does a Nominating Caucus Differ from a Primary? A Comprehensive Guide
The American political landscape features a fascinating array of processes for selecting candidates for office. Two of the most frequently discussed are the nominating caucus and the primary election. While both aim to narrow the field of candidates for a particular party, their mechanics, participation levels, and overall impact differ significantly. This article delves deep into the nuances of caucuses and primaries, highlighting their key differences and shedding light on their respective strengths and weaknesses.
Understanding the Nominating Caucus
A nominating caucus is a local meeting where members of a political party gather to discuss and choose their preferred candidates for upcoming elections. Think of it as a grassroots, face-to-face deliberation process. Unlike primaries, which are secret-ballot elections, caucuses involve open discussions and often multiple rounds of voting, with participants openly expressing their support for candidates.
Key Characteristics of Caucuses:
-
Open Discussion and Debate: A central feature of caucuses is the opportunity for passionate debate among party members. Supporters of various candidates articulate their reasons for support, attempting to sway undecided voters. This participatory nature can be highly engaging but also time-consuming.
-
Multiple Rounds of Voting: Often, a candidate needs to secure a majority (over 50%) of the votes in the first round. If no candidate reaches this threshold, those supporting eliminated candidates may "realign" and vote for another candidate in subsequent rounds. This process can lead to strategic maneuvering and coalition-building.
-
Public Declaration of Support: Unlike the secrecy of a primary ballot, caucus participants openly declare their support for a candidate. This public nature can lead to pressure to conform to group opinion, particularly for those in smaller communities.
-
Lower Voter Turnout: Caucuses typically experience significantly lower voter turnout than primaries. This is partially due to the time commitment required (meetings can last several hours) and the less accessible format for many voters.
-
Emphasis on Party Loyalty: Caucuses tend to attract more politically active and engaged party members, emphasizing strong party loyalty and ideological commitment. This can sometimes lead to a less representative sample of the overall party electorate compared to primaries.
Understanding the Primary Election
A primary election is a secret-ballot election where registered voters of a political party cast their votes to select their preferred candidates for upcoming elections. This is a much more structured and formalized process compared to a caucus.
Key Characteristics of Primaries:
-
Secret Ballot: Voters cast their votes privately, free from the pressure of public declaration. This ensures greater anonymity and protects voters from potential social pressure.
-
Single Round Voting: Usually, a single round of voting is sufficient to determine the winning candidate. The candidate securing the most votes wins the nomination, often without requiring a majority.
-
Higher Voter Turnout: Primaries generally attract significantly higher voter turnout than caucuses. The convenience of voting at a polling place and the shorter time commitment contribute to this higher participation rate.
-
Greater Representation: Due to higher turnout, primaries often offer a more representative sample of the party's electorate, encompassing a wider range of views and demographics.
-
Less Emphasis on Party Loyalty (Potentially): While still affiliated with a specific party, primaries can sometimes attract individuals who are less deeply invested in the party's internal dynamics.
Head-to-Head Comparison: Caucus vs. Primary
| Feature | Caucus | Primary |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Local meeting, open discussion, multiple rounds | Secret-ballot election, single round |
| Voter Turnout | Significantly lower | Significantly higher |
| Participation | Requires more time and commitment | More convenient and accessible |
| Secrecy | Public declaration of support | Secret ballot |
| Debate | Significant opportunity for debate and discussion | Limited opportunity for public discussion |
| Representation | Potentially less representative | Potentially more representative |
| Party Loyalty | High emphasis on party loyalty | Less emphasis on party loyalty (potentially) |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Caucuses
Advantages:
- Greater Deliberation: Caucuses offer a more in-depth opportunity for party members to engage in substantive discussions about candidates and their platforms.
- Stronger Party Unity: The participatory nature of caucuses can foster a greater sense of party unity and shared purpose among participants.
- Grassroots Involvement: Caucuses emphasize grassroots participation and empower party members to directly influence the selection of their candidates.
Disadvantages:
- Low Turnout: The time commitment and less convenient format often result in significantly lower turnout, potentially excluding many party members from the process.
- Inaccessible to Many: The time commitment, need for travel to a specific location, and potential scheduling conflicts can make caucuses inaccessible to working individuals, parents, and those with mobility challenges.
- Potential for Domination by Organized Groups: Well-organized groups within the party can potentially exert disproportionate influence over the outcome of a caucus.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Primaries
Advantages:
- Higher Turnout: Primaries generally attract a much larger segment of the party electorate, leading to a more representative selection process.
- Convenience and Accessibility: The convenience and accessibility of voting at a polling station attract a wider range of participants, irrespective of their availability on a specific evening.
- Secret Ballot and Reduced Pressure: The secret ballot protects voters from social pressure and ensures greater freedom of choice.
Disadvantages:
- Less Deliberation: The streamlined format of primaries offers limited opportunity for in-depth discussion and debate about candidates.
- Potential for Negative Campaigning: The competitive nature of primaries can sometimes lead to negative campaigning and attacks on candidates' reputations.
- Higher Costs: Conducting and administering a primary election involves greater logistical expenses compared to organizing a caucus.
The Role of Caucuses and Primaries in the Nomination Process
Both caucuses and primaries play a crucial role in the larger process of nominating candidates for political office. Their differing characteristics lead to different outcomes, impacting the types of candidates who emerge and the overall tone of the campaign. While primaries tend to favor candidates with broader appeal and the ability to mobilize support across a wider range of voters, caucuses often favor candidates with strong organizational skills and the ability to connect with more ideologically committed party members.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Method
The choice between a caucus and a primary ultimately reflects a trade-off between inclusivity and deliberative engagement. Primaries offer greater inclusivity and voter participation, while caucuses provide more opportunity for in-depth deliberation and potentially stronger party unity. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, and the best approach for a particular party or jurisdiction may depend on various factors, including the size of the electorate, the political culture of the area, and the specific goals of the party's nomination process. The ongoing debate about the relative merits of caucuses and primaries continues to shape the evolution of American political processes.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Where Can You Obtain An Immunization Against Tuberculosis
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Is True Of A Database
Mar 25, 2025
-
A Melodic Line That Moves By Small Intervals Is Called
Mar 25, 2025
-
Drug Abuse Can Often Lead To Suicide Because
Mar 25, 2025
-
Traffic School Final Exam Answers California 2024
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Does A Nominating Caucus Differ From A Primary Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
