If An Incision Cuts The Heart Into
Breaking News Today
Mar 29, 2025 · 5 min read
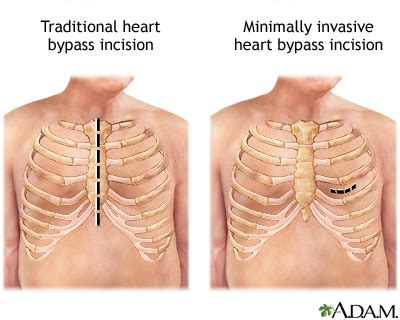
Table of Contents
If an Incision Cuts the Heart Into… Exploring the Implications of Cardiac Surgery
Cardiac surgery, while a marvel of modern medicine, involves intricate procedures with significant risks. One question that often arises, particularly among those unfamiliar with the complexities of the field, concerns the implications of an incision cutting the heart. This article delves into the various scenarios, the surgical techniques employed, and the potential consequences, offering a comprehensive overview for informational purposes only. It is crucial to remember that this information is for educational purposes and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns.
Understanding the Heart's Structure and Function
Before exploring the impact of incisions on the heart, it's vital to understand its intricate structure and function. The heart, a powerful muscular pump, is divided into four chambers: two atria (upper chambers) and two ventricles (lower chambers). These chambers work in a coordinated manner to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart's electrical conduction system, a complex network of specialized cells, regulates the rhythmic beating of the heart. The heart is also encased in a protective sac called the pericardium.
The Heart's Layers:
- Epicardium: The outermost layer, a thin membrane that protects the heart.
- Myocardium: The thickest layer, composed of cardiac muscle responsible for the heart's contractions.
- Endocardium: The innermost layer, lining the chambers and valves.
Understanding these layers is crucial because surgical incisions often target specific areas depending on the type of procedure.
Types of Cardiac Surgery and Incision Techniques
Cardiac surgery encompasses a broad spectrum of procedures, each requiring specific incision techniques. The location and depth of the incision are carefully planned to minimize damage to surrounding tissues and organs while achieving the surgical objective.
Common Cardiac Surgical Procedures:
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): This procedure involves bypassing blocked coronary arteries to restore blood flow to the heart muscle. Incisions may be made in the sternum (breastbone) to access the heart, allowing surgeons to work on the coronary arteries.
- Valve Repair or Replacement: This procedure addresses damaged or diseased heart valves. Access to the heart may involve incisions similar to those used in CABG, allowing surgeons to repair or replace the affected valve.
- Cardiac Pacemaker Implantation: This procedure involves implanting a device to regulate the heart's rhythm. Incisions are typically made in the chest or upper arm.
- Heart Transplant: This procedure involves replacing a diseased heart with a healthy donor heart. The incision is typically a larger, more extensive one than in other procedures.
- Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) Repair: This corrects a hole in the wall between the heart's upper chambers. Access is often through a smaller incision.
Minimally Invasive Techniques:
Recent advances have led to the development of minimally invasive cardiac surgery techniques. These techniques use smaller incisions, often between ribs, to access the heart, resulting in reduced trauma, shorter recovery times, and less scarring.
The Implications of Incisions Cutting into the Heart Muscle
While the goal of cardiac surgery is to repair or replace damaged parts of the heart, any incision carries risks. Directly cutting into the heart muscle itself is a delicate procedure requiring expertise and precision.
Hemorrhage and Bleeding:
Cutting into the heart muscle can lead to significant bleeding. Specialized surgical techniques, including the use of sutures, cautery, and cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB), are employed to control bleeding effectively. CPB temporarily takes over the functions of the heart and lungs, allowing surgeons to work on a still, bloodless heart.
Damage to the Conduction System:
The heart's electrical conduction system is responsible for regulating its rhythm. Damage to this system during surgery can lead to arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), which can be life-threatening. Careful surgical planning and techniques are crucial to avoid injury to these delicate structures.
Myocardial Injury:
Any incision into the heart muscle causes some degree of injury. The extent of the injury depends on the size and location of the incision and the surgeon's skill. Post-operative monitoring is essential to detect and manage any myocardial injury.
Infection:
Any surgical incision carries a risk of infection. Strict aseptic techniques and post-operative care are vital to minimizing this risk.
Post-Operative Care and Recovery
Post-operative care after cardiac surgery is crucial for a successful outcome. This involves monitoring vital signs, managing pain, preventing complications, and supporting the patient's recovery.
Monitoring Vital Signs:
Continuous monitoring of heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and other vital signs is essential to detect any early signs of complications.
Pain Management:
Pain management is a critical aspect of post-operative care. Appropriate pain medications are used to keep the patient comfortable and promote healing.
Prevention of Complications:
Efforts are made to prevent complications such as infection, bleeding, and arrhythmias. This may include the use of antibiotics, blood thinners, and other medications.
Rehabilitation:
Cardiac rehabilitation plays a vital role in the recovery process. This involves a structured program of exercise, education, and lifestyle changes to help the patient regain strength and improve their overall health.
Technological Advancements in Minimally Invasive Cardiac Surgery
The field of cardiac surgery is constantly evolving, with significant advancements in minimally invasive techniques. These techniques offer several advantages:
- Smaller Incisions: Leading to less pain, less scarring, and faster recovery.
- Reduced Trauma: Minimizing the impact on surrounding tissues and organs.
- Shorter Hospital Stays: Enabling patients to return home sooner.
- Improved Cosmetic Outcomes: Resulting in less visible scarring.
Robotic surgery and other advanced techniques are increasingly used in minimally invasive cardiac procedures, enhancing precision and minimizing invasiveness.
Ethical Considerations in Cardiac Surgery
Cardiac surgery raises several ethical considerations, especially regarding risk assessment, informed consent, and resource allocation. Open communication between the surgeon, patient, and family is essential to ensure that the patient understands the risks and benefits of the procedure.
Conclusion
Incisions cutting into the heart, while a part of many life-saving cardiac surgeries, require meticulous surgical planning and execution. While the risks are real, modern surgical techniques and advancements in minimally invasive surgery have greatly improved patient outcomes and minimized complications. The ultimate success of these procedures depends on the expertise of the surgical team, the patient's overall health, and thorough post-operative care. Remember to always seek advice from qualified medical professionals for any health concerns. This article serves solely as an informational overview and should not be construed as medical advice.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Careers In Business Management And Administration Quizlet
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Records Freeze Includes Which Of The Following
Apr 01, 2025
-
3 To 11 Rule Of Customer Service
Apr 01, 2025
-
Behaviorism Focuses On Making Psychology An Objective Science By
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Lump In The Testes Can Be Caused By Quizlet
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about If An Incision Cuts The Heart Into . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
