A Lump In The Testes Can Be Caused By Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
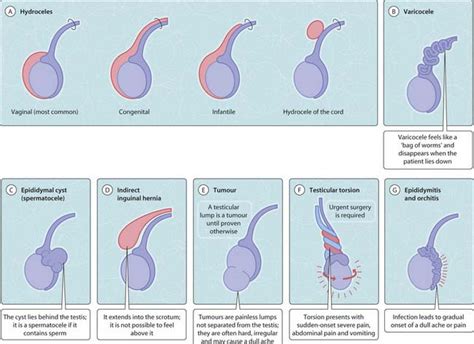
Table of Contents
A Lump in the Testes: Causes, Symptoms, and When to Seek Medical Attention
Finding a lump in your testes can be a frightening experience. It's crucial to understand that while many causes are benign, some can indicate serious health concerns. This article will explore the various potential causes of testicular lumps, emphasizing the importance of seeking prompt medical evaluation. We will not provide a definitive diagnosis; this information is for educational purposes only and should not replace a consultation with a healthcare professional.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
Potential Causes of a Testicular Lump: A Comprehensive Overview
A lump in the testes can stem from a variety of factors, ranging from relatively harmless conditions to more serious medical issues. Let's delve into some of the most common causes:
1. Epididymitis: Inflammation of the Epididymis
The epididymis is a tube-like structure located on the back of each testicle, responsible for storing and transporting sperm. Epididymitis, its inflammation, is often caused by bacterial infection, and can present as a painful, swollen lump in the testicle. Symptoms may include:
- Pain and tenderness: Often localized to the epididymis.
- Swelling: Noticeable enlargement of the affected testicle.
- Fever and chills: Indicative of infection.
- Discomfort during urination: Due to proximity to the urethra.
Treatment: Usually involves antibiotics to combat the infection.
2. Orchitis: Inflammation of the Testicle
Orchitis is the inflammation of one or both testicles. It is often associated with epididymitis (epididymo-orchitis), mumps, or other viral infections. Symptoms mirror those of epididymitis, including:
- Pain and swelling: Significant tenderness and enlargement of the testicle.
- Fever and chills: Systemic signs of infection.
- General malaise: Feeling unwell.
Treatment: Focuses on managing symptoms and treating the underlying infection, often with pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications.
3. Hydrocele: Fluid Accumulation Around the Testicle
A hydrocele is a fluid-filled sac that develops around the testicle. It is usually painless and often presents as a painless swelling. The fluid is typically clear and doesn't usually cause discomfort unless it becomes very large.
- Painless swelling: A smooth, fluid-filled lump.
- Feeling of heaviness: Especially noticeable when the hydrocele is large.
- Translucency: In some cases, a light can shine through the fluid.
Treatment: Often resolves on its own, but larger hydroceles may require surgical drainage or removal.
4. Varicocele: Enlarged Veins in the Scrotum
A varicocele is a condition characterized by enlarged veins within the scrotum, similar to varicose veins in the legs. They often feel like a "bag of worms" and are usually painless, but can cause discomfort in some cases.
- Bag of worms sensation: A characteristic feeling upon palpation.
- Pain: Can range from mild to moderate, often worse after prolonged standing or activity.
- Infertility: In some cases, varicoceles can affect fertility.
Treatment: Often requires no treatment unless causing pain or impacting fertility, with options including surgery or embolization.
5. Spermatocele: Cyst Filled with Sperm
A spermatocele is a cyst that develops near the epididymis and contains sperm or seminal fluid. These cysts are usually painless and feel like a smooth, movable lump.
- Painless lump: Located near the epididymis.
- Small and movable: Often easily palpable.
- Translucency: Sometimes, a light can shine through the cyst.
Treatment: Usually does not require treatment unless causing discomfort or growing significantly.
6. Testicular Cancer: A Serious Concern
Testicular cancer, while less common, is a serious condition requiring prompt medical attention. Lumps associated with testicular cancer can be painless or painful and may feel hard or firm. Other potential symptoms include:
- Hard or firm lump: Unlike the softer texture of some benign lumps.
- Aching or heaviness in the scrotum: Persistent discomfort.
- Enlargement of the testicle: Noticeable increase in size.
- Pain in the lower abdomen or groin: Radiating pain.
Treatment: Depends on the stage and type of cancer, with options including surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment.
7. Inguinal Hernia: Protrusion of Abdominal Tissue
An inguinal hernia occurs when abdominal tissue protrudes into the groin area, sometimes reaching the scrotum. It can cause a lump or swelling in the groin or scrotum.
- Painful or painless lump: Depending on the severity and presence of strangulation.
- Swelling: May increase with straining or coughing.
- Nausea and vomiting: If the hernia becomes strangulated.
Treatment: Surgical repair is usually necessary.
8. Trauma: Injury to the Testicle
Physical trauma to the scrotum can result in swelling, bruising, and the formation of a lump.
- Pain and swelling: Often immediate after the injury.
- Bruising: Discoloration of the scrotum.
- Tenderness to the touch: Increased sensitivity.
Treatment: Usually involves managing pain and swelling with rest, ice, and elevation.
Identifying a Testicular Lump: What to Look For
Recognizing the characteristics of a testicular lump can be helpful in guiding further evaluation. Consider the following:
- Location: Where exactly is the lump located on the testicle or scrotum?
- Size: How large is the lump?
- Shape: Is it round, oval, or irregular in shape?
- Consistency: Is it hard, soft, or firm?
- Pain: Is the lump painful, tender, or painless?
- Mobility: Can the lump be moved easily?
- Associated symptoms: Are there any other symptoms present, such as fever, pain during urination, or abdominal pain?
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
While many testicular lumps are benign, it's crucial to seek immediate medical attention if you notice:
- A sudden onset of severe pain.
- Rapid swelling of the testicle.
- Fever and chills.
- Difficulty urinating.
- A hard lump that doesn't go away.
- Any change in the size or appearance of your testicle.
Delaying medical evaluation can have serious consequences, especially if the lump is cancerous.
The Importance of Self-Exams
Regular testicular self-exams are highly recommended for all males starting in adolescence. Early detection is crucial for the successful treatment of testicular cancer. Familiarize yourself with the normal feel of your testicles and report any changes to your doctor immediately.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
Your doctor will likely conduct a physical examination to assess the lump. Further investigations may include:
- Ultrasound: A non-invasive imaging technique to visualize the internal structures of the testicle.
- Blood tests: To evaluate for infection or other underlying conditions.
- Biopsy: A tissue sample is taken from the lump for microscopic examination. This is crucial in diagnosing testicular cancer.
Conclusion
A lump in the testes can be caused by a variety of conditions, ranging from relatively benign to potentially life-threatening. While this article provides a comprehensive overview of potential causes, it's essential to remember that self-diagnosis is impossible and dangerous. If you discover a lump in your testicle, regardless of its size or symptoms, seek medical attention promptly. Early detection and diagnosis are crucial for successful treatment and management. Don't hesitate to contact your doctor or healthcare provider; your health is paramount. Regular self-exams, coupled with proactive medical care, will significantly improve your chances of early detection and successful management of any testicular issue.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Load Chart Values Can Pinpoint Failures Of
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Must You Do If You Suspect Iphone Efb Tampering
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Was Most Solid Waste Handled In The Middle Ages
Apr 02, 2025
-
Jonas Is A Whole Life Insurance Policyowner
Apr 02, 2025
-
The Number Of Subordinates That One Supervisor Can Manage Effectively
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Lump In The Testes Can Be Caused By Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
