In An Oligopolistic Market Consumer Choice Is
Breaking News Today
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
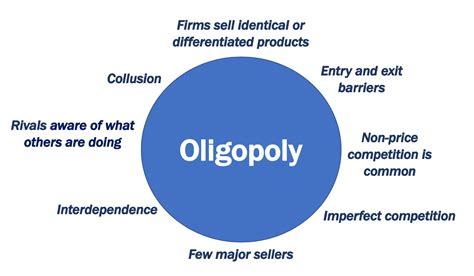
Table of Contents
In an Oligopolistic Market, Consumer Choice Is… Limited? A Deep Dive into Market Power and Consumer Welfare
The question of consumer choice in an oligopolistic market is complex and multifaceted. While proponents of free markets often laud the benefits of competition, the reality of oligopoly—a market dominated by a few powerful firms—presents a nuanced picture. This article will delve into the intricacies of consumer choice within oligopolistic structures, exploring the limitations imposed by market power, the strategies employed by firms to influence consumer behavior, and the ultimate impact on consumer welfare.
Understanding Oligopoly: A Market Structure Defined
Before exploring the specifics of consumer choice, it's crucial to understand the defining characteristics of an oligopolistic market. An oligopoly is characterized by:
- A small number of large firms: The market share is concentrated among a handful of dominant players, significantly limiting the presence of smaller competitors.
- High barriers to entry: Significant obstacles, such as high capital requirements, economies of scale, or legal restrictions, prevent new firms from easily entering the market. This protects the established firms' dominance.
- Interdependence of firms: The actions of one firm significantly impact the others. Pricing decisions, advertising strategies, and product innovation are all carefully considered in relation to competitors' anticipated responses. This leads to strategic behavior, often resulting in less aggressive competition than in a perfectly competitive market.
- Potential for collusion: While illegal in many jurisdictions, firms in an oligopoly may engage in tacit or explicit collusion to manipulate prices, output, or market share. This further restricts consumer choice.
The Limitations on Consumer Choice in an Oligopoly
The defining features of an oligopoly directly impact consumer choice, frequently leading to a less favorable outcome than in more competitive markets. These limitations include:
1. Limited Product Variety and Innovation:
With fewer competitors, there's less pressure to innovate and offer diverse product choices. Firms might focus on maintaining their existing market share rather than investing heavily in research and development to create new or improved products. This results in a smaller range of options for consumers, potentially limiting their ability to find a product perfectly suited to their needs and preferences. The absence of significant competitive pressure reduces the incentive for firms to constantly strive for product differentiation.
2. Higher Prices and Reduced Consumer Surplus:
The lack of robust competition often leads to higher prices than would prevail in a more competitive market. Firms, knowing they have less immediate threat from rivals, can exercise their market power to charge premium prices. This reduces consumer surplus – the difference between the price consumers are willing to pay and the actual price they pay. Consumers effectively pay more for less choice.
3. Non-Price Competition and Manipulative Marketing:
Oligopolistic firms often engage in intense non-price competition. This can involve extensive advertising campaigns aiming to build brand loyalty and create artificial demand. While advertising can provide useful information, it can also be used to manipulate consumer preferences, create brand perception differences that don't reflect actual product quality, and ultimately limit true consumer choice based on rational comparison.
4. Homogenous Products and Lack of Differentiation:
In some oligopolies, products are relatively homogenous, meaning they are very similar to one another. This lack of significant differentiation can lead consumers to rely on price as the primary factor in their purchasing decisions. This reinforces the negative impacts of the oligopoly's pricing power.
5. Barriers to Entry Stifle Competition:
High barriers to entry discourage new entrants, preventing the introduction of competing products or services. This strengthens the market power of established firms and limits the potential for increased choice.
Strategic Interactions and Their Impact on Consumer Choice
The interdependence of firms in an oligopoly leads to complex strategic interactions that significantly affect consumer choice. Understanding these interactions is key to grasping the limitations on consumer freedom in this market structure:
1. Price Wars:
While less common in the long run due to their destructive impact on profits, price wars can offer temporary benefits to consumers in terms of lower prices. However, these are unsustainable unless there's a significant shift in the market's power dynamics or a change in the cost structure for the firms involved.
2. Collusion and Cartels:
Explicit collusion, where firms agree to fix prices or restrict output, is illegal but occurs nonetheless. Tacit collusion, where firms implicitly coordinate their actions without overt agreement, is harder to detect and prosecute. Both forms severely restrict consumer choice by artificially raising prices and reducing product variety.
3. Game Theory and Strategic Decision-Making:
The strategic interactions of oligopolistic firms can be analyzed using game theory. Models like the prisoner's dilemma illustrate how firms might choose to restrict output or raise prices, even if it's not in their collective best interest to do so (it is, however, in their individual best interest, in the short term). The outcome frequently leads to suboptimal outcomes for consumers.
4. Product Differentiation and Branding Strategies:
Firms invest heavily in branding and product differentiation to create perceived differences between their offerings, even if these differences are minimal. This strategy can limit price competition and allow firms to charge higher prices, despite offering essentially similar products.
Assessing Consumer Welfare in Oligopolistic Markets
The ultimate question is: How does an oligopolistic market structure affect consumer welfare? While some might argue that oligopolies can drive innovation through economies of scale and R&D investments, the evidence largely suggests that the negative impacts on consumer choice and welfare are significant:
- Higher Prices: This is perhaps the most direct negative consequence. Consumers pay more for goods and services than they would in a more competitive market.
- Reduced Choice: Limited product variety and innovation restrict consumers’ ability to find products that precisely match their needs and preferences.
- Inefficient Resource Allocation: Oligopolies may not allocate resources efficiently. The focus on maximizing profits might lead to underinvestment in innovation or production efficiency.
- Potential for Exploitation: The concentrated market power allows firms to potentially exploit consumers through higher prices or deceptive marketing practices.
Mitigating the Negative Impacts: Regulatory Interventions and Consumer Empowerment
Governments can play a crucial role in mitigating the negative impacts of oligopolistic markets on consumer choice. These interventions include:
- Antitrust Laws and Regulations: Strict enforcement of antitrust laws aimed at preventing monopolies and cartels is essential. Regulations that promote competition and prevent anti-competitive behavior can help ensure a more level playing field.
- Deregulation: In some cases, deregulation can increase competition. However, this must be carefully managed to avoid exacerbating negative externalities.
- Promoting Transparency: Increased transparency in pricing and product information can empower consumers to make more informed choices.
- Consumer Protection Laws: Strengthening consumer protection laws can shield consumers from deceptive marketing practices and unfair pricing strategies.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Struggle for Consumer Choice in Oligopolistic Markets
The existence of oligopolies presents a significant challenge to maintaining robust consumer choice. While the allure of economies of scale and potential innovation exists, the inherent limitations imposed by concentrated market power often outweigh these benefits. Higher prices, reduced product variety, and manipulative marketing strategies consistently disadvantage consumers. Therefore, a balanced approach involving robust regulatory oversight, alongside consumer empowerment through education and information, remains crucial for ensuring that consumer choice remains a meaningful aspect of even oligopolistic markets. The ongoing struggle to strike this balance remains a central challenge in modern economics and regulatory policy. The debate over the optimal level of intervention, balancing the promotion of competition with the acceptance of some degree of market concentration, continues to be a critical area of research and policy discussion.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Life Insurance Exam Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Direct Carry Is Used To Transfer A Patient
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Emancipation Proclamation Of January 1 1863 Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
These Cards Will Get You Drunk Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Did Quizlet Get Rid Of Q Chat
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about In An Oligopolistic Market Consumer Choice Is . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
