Incorrect Techniques Generally Lead To Ligament And Tendon Damage.
Breaking News Today
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
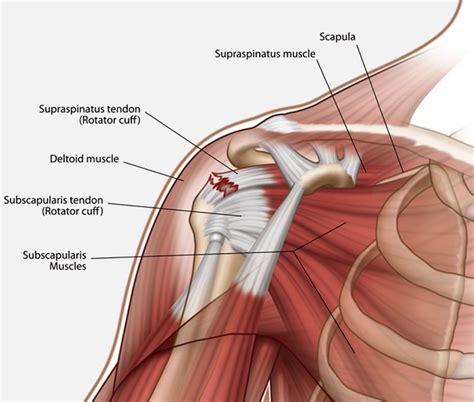
Table of Contents
Incorrect Techniques Generally Lead to Ligament and Tendon Damage
Ligaments and tendons are crucial components of our musculoskeletal system, providing stability, support, and facilitating movement. Ligaments connect bones to bones, forming joints and ensuring their structural integrity. Tendons, on the other hand, connect muscles to bones, transmitting the force generated by muscle contractions to produce movement. While incredibly strong and resilient, both ligaments and tendons are susceptible to injury, and improper techniques in various activities are a leading cause of this damage. Understanding these incorrect techniques and their consequences is crucial for injury prevention and promoting long-term musculoskeletal health.
Understanding Ligaments and Tendons: A Foundation for Prevention
Before delving into the specific techniques that cause damage, it's vital to grasp the fundamental differences and functions of ligaments and tendons. This understanding lays the groundwork for appreciating why certain movements and actions can be detrimental.
Ligaments: The Joint Stabilizers
Ligaments are tough, fibrous bands of connective tissue composed primarily of collagen fibers. Their primary role is to stabilize joints by restricting excessive movement and preventing dislocations. They are less elastic than tendons, meaning they have a limited range of stretch before sustaining damage. This limited elasticity is precisely what makes them vulnerable to injury when subjected to forces beyond their capacity.
Tendons: The Force Transmitters
Tendons, also composed primarily of collagen fibers, are responsible for transmitting the force generated by muscles to bones. They are more elastic than ligaments, allowing them to withstand repetitive loading and stretching. However, this elasticity is not limitless, and excessive or repetitive strain can lead to tendon injuries.
Incorrect Techniques: The Culprits Behind Ligament and Tendon Damage
A wide array of activities and incorrect techniques can contribute to ligament and tendon injuries. These injuries range from minor sprains and strains to complete tears, requiring varying degrees of treatment and recovery time.
1. Improper Lifting Techniques: Back, Shoulder, and Knee Injuries
Improper lifting techniques are a major culprit behind numerous ligament and tendon injuries, especially in the back, shoulders, and knees. Lifting heavy objects with a bent back, instead of using the legs and maintaining a straight back, puts immense stress on the ligaments of the spine and can lead to strains or even herniated discs. Similarly, lifting with outstretched arms or twisting the body while lifting increases the risk of shoulder injuries, such as rotator cuff tears. Lifting heavy objects with the knees straight places excessive stress on the knee ligaments, potentially resulting in anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) or medial collateral ligament (MCL) injuries.
Correct Lifting Techniques:
- Bend at the knees and hips: Keep your back straight and engage your core muscles.
- Keep the load close to your body: Avoid reaching out.
- Lift smoothly and avoid jerking: Use your leg muscles to power the lift.
- Use assistance when needed: Don't hesitate to ask for help with heavy objects.
2. Overuse Injuries: Repetitive Strain and Microtears
Repetitive strain injuries (RSI) are common among athletes and individuals whose work involves repetitive movements. These repetitive movements, if performed incorrectly or with excessive force, can cause microscopic tears in tendons and ligaments. These micro-tears accumulate over time, leading to inflammation, pain, and decreased function. Examples include tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis), golfer's elbow (medial epicondylitis), and carpal tunnel syndrome.
Prevention of Overuse Injuries:
- Proper warm-up and cool-down: Prepare your muscles and joints before and after activity.
- Maintain correct posture: Avoid repetitive strain on any one joint or muscle group.
- Take regular breaks: Avoid prolonged periods of repetitive motion.
- Use proper tools and techniques: Employ ergonomic strategies and tools to minimize strain.
3. Sudden, High-Impact Movements: Sprains and Tears
Sudden, high-impact movements, such as a sudden twisting motion of the knee during a sporting activity, can cause significant ligament damage. This can lead to sprains (partial tears) or complete tears of the ligaments. Similarly, falling or landing awkwardly can lead to ankle sprains, wrist fractures, or other ligament injuries.
Reducing the Risk of High-Impact Injuries:
- Proper training and conditioning: Build strength and flexibility to improve stability and reduce the risk of injury.
- Use appropriate safety equipment: Wear protective gear during sports or activities with a high risk of falls or impacts.
- Listen to your body: Don't push yourself beyond your limits. Rest when needed.
4. Improper Sports Technique: A Wide Range of Injuries
Incorrect techniques in sports significantly increase the risk of ligament and tendon injuries. For example, improper running technique can lead to plantar fasciitis, shin splints, or knee injuries. In basketball, improper jumping techniques can strain the ankles and knees. Incorrect throwing motions in baseball or tennis can cause shoulder or elbow injuries. In football, tackles and collisions, if performed incorrectly, can result in numerous ligament and tendon injuries throughout the body.
Improving Sports Technique:
- Seek professional coaching: Learn correct techniques from qualified instructors.
- Practice regularly: Consistent practice helps build muscle memory and improve technique.
- Focus on proper form over intensity: It's better to perform movements correctly at a lower intensity than incorrectly at a high intensity.
5. Inadequate Warm-up and Stretching: Reduced Flexibility and Increased Risk
Inadequate warm-up and stretching before physical activity reduce muscle and joint flexibility. Stiff muscles and joints are more prone to injury because they are less able to absorb stress and strain. Lack of flexibility increases the risk of muscle strains, ligament sprains, and tendonitis.
Importance of Proper Warm-up and Stretching:
- Warm-up: Increases blood flow to muscles, improving their elasticity and reducing the risk of injury.
- Stretching: Improves flexibility, range of motion, and reduces muscle stiffness. Focus on both static and dynamic stretches.
6. Ignoring Pain Signals: Exacerbating Injuries
Ignoring pain signals is a critical mistake. Pain is the body's way of indicating that something is wrong. Continuing an activity despite pain can lead to minor injuries becoming severe, potentially requiring extensive rehabilitation or surgery.
Responding to Pain:
- Rest: Stop the activity that is causing pain.
- Ice: Apply ice to the injured area to reduce inflammation.
- Compression: Use a bandage to provide support and reduce swelling.
- Elevation: Keep the injured area elevated to reduce swelling.
- Seek medical attention: Consult a doctor or physical therapist if the pain persists or worsens.
Prevention and Rehabilitation: A Holistic Approach
Preventing ligament and tendon injuries requires a holistic approach that combines proper technique, regular exercise, and mindful lifestyle choices. Rehabilitation, when injuries occur, should focus on restoring function and preventing recurrence.
Prevention Strategies:
- Regular Exercise: Strength training and cardiovascular exercise improve muscle strength, endurance, and flexibility, all crucial for injury prevention.
- Proper Nutrition: A balanced diet provides the building blocks for healthy tendons and ligaments.
- Adequate Rest and Recovery: Allow sufficient time for your body to recover after strenuous activity.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts added strain on joints and ligaments.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking impairs blood flow and healing.
Rehabilitation Strategies:
- Rest and Ice: Initial management focuses on reducing inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: A crucial component of rehabilitation, focusing on restoring range of motion, strength, and flexibility.
- Medication: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair torn ligaments or tendons.
Conclusion: Mastering Technique, Minimizing Risk
Incorrect techniques are a major contributor to ligament and tendon damage. By understanding the mechanics of these injuries, adopting correct techniques in all activities, and prioritizing prevention and rehabilitation, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of experiencing these debilitating injuries and maintain long-term musculoskeletal health. Remember, prevention is always better than cure. Prioritizing proper form, listening to your body, and seeking professional guidance when necessary are key steps toward a lifetime of pain-free movement.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Unit For Sample Standard Deviation Would Be
Mar 16, 2025
-
Used Fuel Assemblies Are Typically Considered
Mar 16, 2025
-
A Fine For Speeding In A Work Zone Is
Mar 16, 2025
-
Computers With Ai Use Human Intelligence To Make Decisions
Mar 16, 2025
-
Gmaw And Fcaw Are Semiautomatic Welding Processes
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Incorrect Techniques Generally Lead To Ligament And Tendon Damage. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
