Left Bundle Branch Block Is Characterized By Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
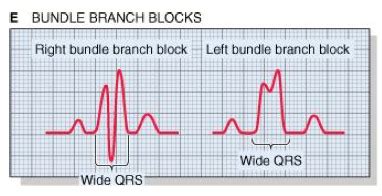
Table of Contents
Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB): A Comprehensive Guide
Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB) is a type of heart block that affects the electrical conduction system of the heart. Understanding LBBB is crucial for healthcare professionals and patients alike, as it can indicate underlying cardiac conditions requiring prompt attention. This comprehensive guide will delve into the characteristics of LBBB, exploring its diagnostic features, associated conditions, management, and prognosis.
What is a Left Bundle Branch Block?
A left bundle branch block (LBBB) occurs when the electrical impulse that coordinates the heartbeat is delayed or blocked from reaching the left ventricle of the heart. The left bundle branch, responsible for conducting electrical signals to the left ventricle, is disrupted, causing the left ventricle to contract later than the right. This disruption leads to characteristic changes in the electrocardiogram (ECG).
Key Characteristics of LBBB on an ECG:
The hallmark of LBBB on an electrocardiogram (ECG) is a widened QRS complex (usually >120 milliseconds), representing the delayed activation of the left ventricle. Several other key characteristics help differentiate LBBB from other conditions. Let's break them down:
1. QRS Complex Widening:
- Significant Widening: The most prominent feature is a QRS duration exceeding 120 milliseconds. This signifies delayed ventricular depolarization due to the impaired conduction pathway in the left bundle branch.
- Measurement: Accurate measurement of the QRS interval is paramount for diagnosis. Any widening should trigger further investigation.
2. Absence of q Waves in the Left Precordial Leads:
- Missing q Waves: In leads V5 and V6 (precordial leads overlying the left ventricle), the characteristic initial small downward deflection (q wave) is absent. This is because the left ventricle is not depolarized first in LBBB. This absence is a crucial differentiating factor from other conditions.
3. Broad, Notched, or Monomorphic R Waves:
- Altered R Waves: The R waves in the left precordial leads (V5, V6) are often broad, notched, or show a wide monomorphic appearance. This reflects the asynchronous activation of the left ventricle.
4. ST-T Wave Changes:
- Inverted T Waves: Often, ST-segment depression and inverted T waves are seen in the leads with prominent R waves. These changes are usually concordant with the QRS complex. While present in many cases, their absence doesn't rule out LBBB.
- Importance of Context: The ST-T wave changes, while suggestive, should be interpreted in conjunction with other ECG findings and the patient's clinical presentation.
5. Left Axis Deviation:
- Potential Shift: While not always present, left axis deviation may occur in LBBB, further contributing to the overall ECG pattern.
Differentiating LBBB from other Conditions:
Several conditions can mimic LBBB on ECG. Careful examination and consideration of the clinical context are necessary for accurate diagnosis. Key differentials include:
- Left Anterior Fascicular Block (LAFB): LAFB affects only a portion of the left bundle branch, resulting in a less pronounced QRS widening (usually between 90-120 milliseconds) and distinct ST-T wave changes.
- Left Posterior Fascicular Block (LPFB): LPFB also involves a partial block in the left bundle branch, producing a different ECG pattern with right axis deviation.
- Hypertrophy: Ventricular hypertrophy (enlargement) can cause QRS widening, but the specific pattern differs from LBBB.
- Ventricular Premature Beats (VPBs): Wide QRS complexes are a feature of VPBs, but the overall ECG rhythm and context distinguish them from LBBB.
Causes of Left Bundle Branch Block:
LBBB is often a secondary finding, meaning it's a consequence of another underlying heart condition. The common causes include:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): This is the most frequent cause, where plaque buildup in the coronary arteries reduces blood flow to the heart muscle, potentially damaging the left bundle branch.
- Hypertension: Chronic high blood pressure damages the heart over time, leading to structural changes and conduction disturbances like LBBB.
- Valvular Heart Disease: Conditions affecting the heart valves (aortic stenosis, mitral regurgitation) can increase the workload on the heart, potentially inducing LBBB.
- Cardiomyopathy: Diseases of the heart muscle itself, such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or dilated cardiomyopathy, can impair electrical conduction.
- Myocarditis: Inflammation of the heart muscle can damage the conduction system and cause LBBB.
- Congenital Heart Defects: Some congenital heart defects may involve abnormalities in the heart's conduction pathways.
Symptoms of Left Bundle Branch Block:
LBBB itself often doesn't cause noticeable symptoms. The symptoms experienced are often linked to the underlying heart condition causing the LBBB. These can include:
- Chest pain or pressure (angina): A common symptom of CAD, a frequent cause of LBBB.
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea): Reduced blood flow due to underlying heart disease can lead to dyspnea.
- Lightheadedness or dizziness: Can result from reduced cardiac output.
- Fatigue: A general feeling of tiredness and weakness.
- Syncope (fainting): In more severe cases, a sudden loss of consciousness.
Diagnosis of Left Bundle Branch Block:
The primary diagnostic tool for LBBB is the electrocardiogram (ECG). A 12-lead ECG allows for detailed analysis of the heart's electrical activity. The characteristic ECG changes described earlier are crucial for the diagnosis. Other diagnostic tests may include:
- Echocardiogram: Uses ultrasound to assess the heart's structure and function, identifying any underlying heart disease.
- Cardiac Catheterization: A procedure to visualize the coronary arteries and assess blood flow, particularly useful if CAD is suspected.
- Cardiac MRI: Provides detailed images of the heart, useful for evaluating heart muscle damage and structure.
Management of Left Bundle Branch Block:
Treatment for LBBB focuses on managing the underlying heart condition causing the block. The approach varies depending on the cause:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Treatment might involve lifestyle modifications (diet, exercise), medications (aspirin, statins, beta-blockers), angioplasty, or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
- Hypertension: Management involves lifestyle changes (diet, exercise) and medication (ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, diuretics).
- Valvular Heart Disease: Treatment depends on the specific valve problem and may include medication or valve repair or replacement surgery.
- Cardiomyopathy: Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and slowing disease progression. This might include medications or implantable devices like pacemakers or defibrillators.
Prognosis of Left Bundle Branch Block:
The prognosis for LBBB varies significantly depending on the underlying cause. If LBBB is caused by a manageable condition like well-controlled hypertension, the outlook is generally good. However, if LBBB is a consequence of severe CAD or cardiomyopathy, the prognosis might be more guarded. Regular follow-up with a cardiologist is crucial to monitor the condition and manage any underlying heart disease.
Lifestyle Modifications for Patients with LBBB:
Regardless of the underlying cause, lifestyle modifications can improve overall heart health and prognosis in patients with LBBB:
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet low in saturated fat, cholesterol, and sodium is essential for cardiovascular health.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity strengthens the heart and improves cardiovascular function.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces strain on the heart.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of heart disease.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate heart problems. Stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can be beneficial.
Conclusion:
Left bundle branch block is a significant electrocardiographic finding that necessitates careful evaluation to identify and manage any underlying cardiac conditions. Accurate diagnosis relies on recognizing the characteristic ECG changes and differentiating LBBB from similar conditions. The prognosis is highly dependent on the underlying cause, and timely management of associated cardiac diseases is crucial for optimizing patient outcomes. Regular follow-up care with a cardiologist, along with lifestyle modifications, contributes to improving the overall health and well-being of individuals with LBBB. This comprehensive understanding allows healthcare professionals to deliver effective and timely care, enhancing the quality of life for patients with this condition. Remember, this information is for educational purposes and should not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Statements About Autopolyploid Individuals Is True
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is The Physical Basis Of The Phototropic Response
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Correctly Describes An Allied Health Professional
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Are The Three Aspects Of Overall Health
Mar 25, 2025
-
Recibiste Tu Regalo De Cumpleanos Si Esta Manana
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Left Bundle Branch Block Is Characterized By Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
