Which Of The Following Statements About Autopolyploid Individuals Is True
Breaking News Today
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
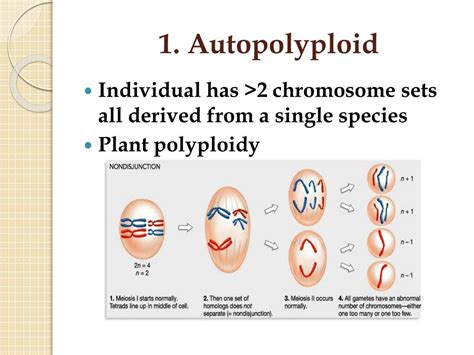
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Statements About Autopolyploid Individuals is True? Delving into the World of Polyploidy
Polyploidy, the condition of possessing more than two complete sets of chromosomes, is a fascinating phenomenon in the biological world, significantly impacting plant evolution and diversity. Autopolyploidy, a specific type of polyploidy, arises from the duplication of chromosome sets within a single species. Understanding the characteristics of autopolyploids is crucial for comprehending plant evolution, speciation, and even agricultural applications. This article will explore various statements about autopolyploid individuals and determine which are true, providing a comprehensive overview of their genetic makeup, phenotypic characteristics, and evolutionary significance.
Understanding Autopolyploidy: A Genetic Perspective
Before delving into specific statements, let's establish a firm understanding of autopolyploidy. It's a type of polyploidy resulting from chromosome duplication within a single species. This means that all chromosomes in an autopolyploid individual are derived from the same ancestral species. This contrasts with allopolyploidy, where chromosome sets originate from different species.
For example, a diploid organism (2n) with two sets of chromosomes might undergo autopolyploidization to become a tetraploid (4n) with four sets of identical chromosomes. Further duplications can lead to higher ploidy levels such as hexaploidy (6n), octoploidy (8n), and even higher multiples.
Mechanisms of Autopolyploid Formation
Several mechanisms contribute to the formation of autopolyploids. These include:
- Chromosome Doubling During Mitosis: Errors during mitotic cell division can result in the failure of cytokinesis, leading to a cell with a doubled chromosome number. This can occur in somatic cells, leading to sectors of polyploid tissue within a diploid organism, or in germline cells, resulting in polyploid gametes.
- Chromosome Doubling During Meiosis: Errors during meiosis, such as the failure of chromosome segregation, can produce diploid gametes (2n). Fertilization of a diploid gamete by a haploid (n) gamete results in a triploid (3n) offspring, while fertilization of two diploid gametes yields a tetraploid (4n) offspring.
- Unreduced Gamete Formation: Sometimes, meiosis fails to reduce the chromosome number, leading to the production of unreduced gametes (2n) that carry a diploid chromosome complement. These can fuse with haploid gametes or other unreduced gametes to produce polyploids.
Evaluating Statements About Autopolyploid Individuals
Now, let's analyze some common statements regarding autopolyploid individuals and determine their validity:
Statement 1: Autopolyploids exhibit increased vigor and larger size compared to their diploid progenitors (heterosis).
Truth Value: Generally True. This statement reflects the phenomenon of heterosis, also known as hybrid vigor. Autopolyploids often display increased size, biomass, and overall vigor. This is attributed to several factors including:
- Increased gene dosage: The presence of multiple copies of genes can lead to increased expression of beneficial traits.
- Gene masking: Multiple gene copies can mask the effect of deleterious recessive alleles.
- Improved metabolic efficiency: The increased number of chromosomes can lead to enhanced metabolic activity and resource utilization.
However, it's important to note that not all autopolyploids show increased vigor. The degree of heterosis depends on several factors including the specific species, the genetic background, and environmental conditions. Some autopolyploids may exhibit reduced fertility or other negative consequences.
Statement 2: Autopolyploids generally exhibit reduced fertility compared to their diploid counterparts.
Truth Value: Often True. This statement highlights a significant challenge associated with autopolyploidy. The presence of multiple sets of homologous chromosomes leads to complications during meiosis. The pairing and segregation of homologous chromosomes become irregular, resulting in the production of unbalanced gametes with varying chromosome numbers. This often leads to reduced seed set, sterility, or the production of aneuploid offspring with abnormal chromosome numbers. The degree of fertility reduction varies depending on the ploidy level and the species. Tetraploids generally exhibit more reduced fertility than triploids.
Statement 3: Autopolyploids are always sterile.
Truth Value: False. While many autopolyploids exhibit reduced fertility, they are not always sterile. Some autopolyploids can maintain relatively high levels of fertility through mechanisms such as:
- Autotetraploid Pairing: In autotetraploids, homologous chromosomes can pair in various configurations during meiosis, leading to some viable gametes.
- Somatic Doubling: A subsequent round of somatic doubling in a triploid can lead to a fertile hexaploid.
- Apomixis: Some autopolyploids can reproduce asexually through apomixis, a form of asexual reproduction producing seeds without fertilization.
Therefore, while reduced fertility is common, sterility is not an inevitable consequence of autopolyploidy.
Statement 4: Autopolyploids are easily identifiable through cytogenetic analysis.
Truth Value: True. Cytogenetic analysis, which involves examining chromosomes under a microscope, is a powerful tool for identifying autopolyploids. Autopolyploids show a clear increase in chromosome number compared to their diploid progenitors. Moreover, the morphology of the chromosomes in autopolyploids is typically identical to the diploid parent species, distinguishing them from allopolyploids which show distinct chromosome morphologies. Techniques like chromosome counting and karyotyping provide conclusive evidence of autopolyploidy.
Statement 5: Autopolyploidy plays a minor role in plant evolution.
Truth Value: False. Autopolyploidy has played a significant role in plant evolution, particularly in some lineages and environments. It can lead to:
- Rapid speciation: The reproductive isolation created by polyploidy can lead to the formation of new species.
- Adaptation to new environments: Polyploids may have altered phenotypes that enable them to thrive in diverse environments.
- Increased genetic variation: Autopolyploidy increases genetic diversity within a species, providing raw material for natural selection.
- Evolutionary Novelties: The combined gene action in polyploids can create phenotypes previously unseen in the diploid progenitors.
Autopolyploidy in Agriculture and Horticulture
Autopolyploidy has been exploited in agriculture and horticulture to enhance crop production. Many commercially important crops are polyploids, often artificially induced through techniques such as colchicine treatment. The advantages of polyploidy in agriculture include:
- Increased yield: Larger fruits, seeds, or vegetative structures.
- Improved quality: Enhanced nutritional value or desirable traits.
- Disease resistance: Enhanced tolerance to pests or pathogens.
However, the challenges associated with polyploidy, such as reduced fertility, must be carefully considered when using polyploidization for crop improvement.
Conclusion
In summary, while many statements about autopolyploids hold true in many cases, it is essential to remember that the characteristics of autopolyploids vary depending on the species, ploidy level, and environment. Understanding the complexities of autopolyploidy is vital for comprehending plant evolution, speciation, and the development of improved crops. The statements analyzing the effects of autopolyploidy highlighted the often-observed increased vigor and size, the frequently seen reduced fertility, and the critical roles of cytogenetic analysis and its significant contributions to plant evolution. It's vital to embrace the nuances within this fascinating area of biology to continue advancing our knowledge. The interplay of genetic changes, reproductive strategies, and environmental pressures shapes the evolutionary trajectory of autopolyploid species, making them an endlessly captivating subject of scientific inquiry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Determine An Appropriate Use Of The Emergency Access Procedure
Mar 25, 2025
-
Dejo Viudo A Su Esposo El 28 De Junio
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not True About Deep Learning
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Records Select All That Apply
Mar 25, 2025
-
Compare And Contrast A Casual Friendship With A Close Friendship
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Statements About Autopolyploid Individuals Is True . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
