Libertarianism Is A Political Ideology That Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
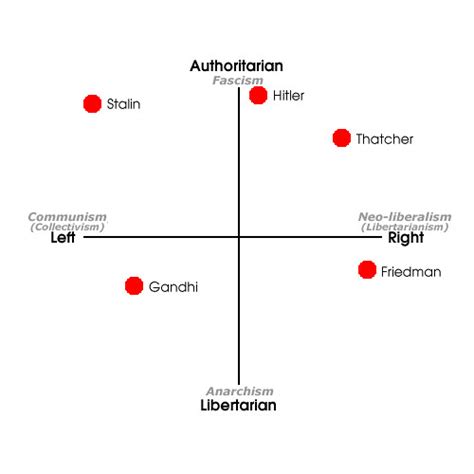
Table of Contents
Libertarianism: A Political Ideology Quizlet-Style Deep Dive
Libertarianism, a political ideology often misunderstood and frequently debated, centers on the core principles of individual liberty and limited government. This deep dive will explore the nuances of libertarianism, examining its key tenets, variations within the philosophy, and its practical applications in the real world. We'll unpack common misconceptions and delve into its strengths and weaknesses, offering a comprehensive understanding far beyond a simple Quizlet definition.
Core Tenets of Libertarianism
At its heart, libertarianism champions individual liberty as paramount. This translates into a belief in:
1. Individual Rights and Freedoms:
- Emphasis on Negative Rights: Libertarians primarily focus on negative rights, which are rights that protect individuals from coercion or interference by others, including the government. These include freedom of speech, religion, assembly, and the right to property. They generally emphasize less on positive rights, which entail a right to receive certain goods or services from others (like healthcare or education).
- Limited Government Intervention: The role of government is strictly limited to protecting individual rights and enforcing contracts. Any intrusion beyond this is considered unjustified infringement on individual liberty. This contrasts sharply with ideologies that advocate for extensive government intervention in social and economic affairs.
- Self-Ownership: A cornerstone of libertarian thought is the concept of self-ownership. Individuals are considered the ultimate authority over their own bodies, minds, and labor. This implies a strong rejection of forced labor, conscription, and other forms of involuntary servitude.
2. Free Markets and Capitalism:
- Minimal Economic Regulation: Libertarians advocate for largely unregulated free markets, believing that competition and individual initiative lead to economic efficiency and prosperity. Government intervention in the economy, such as price controls, subsidies, and regulations, are seen as detrimental to economic growth and individual freedom.
- Property Rights: Strong protection of private property rights is crucial. Individuals are entitled to own, use, and dispose of their property as they see fit, subject only to the non-aggression principle.
- Voluntary Exchange: Economic transactions should be voluntary and based on mutual agreement between individuals. Coercion and force should play no role in economic activity.
3. Non-Aggression Principle (NAP):
- Foundation of Libertarian Ethics: The non-aggression principle is the cornerstone of most libertarian ethical systems. It asserts that the initiation of force or fraud against another individual is morally wrong and should be prohibited. This principle forms the basis for the limited government advocated by libertarians.
- Self-Defense and Punishment: The NAP doesn't preclude self-defense or the use of force in response to aggression. It also allows for the use of force to punish those who violate the principle. However, these actions must be proportionate to the initial aggression and conducted within a framework of due process.
- Implications for Foreign Policy: The NAP also has implications for foreign policy, leading many libertarians to advocate for a non-interventionist approach to international affairs, emphasizing peaceful resolution of disputes and minimizing the use of military force.
Variations Within Libertarianism
While sharing a commitment to individual liberty, different schools of thought exist within libertarianism:
1. Minarchism:
- Minimal State: Minarchists believe in a minimal state, limited to protecting individual rights and enforcing contracts. They generally support a free market economy, with minimal government intervention. They acknowledge the need for a state, albeit a very small one, to maintain order and prevent violence.
2. Anarcho-Capitalism:
- Stateless Society: Anarcho-capitalists advocate for the complete abolition of the state, believing that private entities can provide all necessary services, including law enforcement, defense, and dispute resolution, through voluntary contracts and market mechanisms. This is a far more radical approach than minarchism.
3. Left-Libertarianism:
- Emphasis on Social Justice: Left-libertarians emphasize social justice and economic equality alongside individual liberty. They often advocate for policies like mutual aid and worker cooperatives, while rejecting traditional capitalist approaches to property rights. They aim to reconcile individual autonomy with broader social concerns.
Libertarianism vs. Other Ideologies
Libertarianism contrasts sharply with other major political ideologies:
Libertarianism vs. Conservatism:
While both emphasize individual liberty, conservatism often prioritizes traditional values and institutions, sometimes leading to policies that restrict individual freedom in the name of social order. Libertarians prioritize individual liberty above all else, even when it clashes with traditional values.
Libertarianism vs. Liberalism:
Liberals often support a larger role for government in addressing social and economic inequalities, often advocating for welfare programs and regulations to protect consumers and workers. Libertarians prioritize individual liberty and free markets, believing that government intervention is often counterproductive and infringes on individual rights.
Libertarianism vs. Socialism:
Socialism emphasizes collective ownership of the means of production and a greater degree of economic equality. Libertarians vehemently oppose this, championing private property rights and free markets as essential for individual liberty and economic prosperity.
Common Misconceptions about Libertarianism
Several misconceptions frequently surround libertarianism:
- Libertarians are selfish: This is a common criticism, but it misunderstands the underlying ethics. Libertarians believe that individuals are best positioned to make decisions concerning their own lives and that voluntary cooperation leads to better outcomes than coercion. Helping others should be a matter of choice, not government mandate.
- Libertarianism leads to anarchy: While anarcho-capitalism is a branch of libertarianism, most libertarians support a minimal state to maintain order and enforce contracts. The goal is not chaos, but a society where individual liberty is maximized.
- Libertarians don't care about the poor: While opposing government welfare programs, many libertarians support private charities and voluntary assistance to the less fortunate. They believe that voluntary action is more effective and respectful of individual dignity than government mandates.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Libertarianism
Strengths:
- Emphasis on Individual Liberty: The core principle of individual liberty is highly appealing to many, emphasizing personal autonomy and self-determination.
- Potential for Economic Growth: Free markets and minimal regulation can create an environment conducive to innovation and economic growth.
- Protection Against Government Overreach: The emphasis on limited government helps safeguard against tyranny and government abuse of power.
Weaknesses:
- Potential for Inequality: Unregulated free markets can lead to significant economic inequality, leaving some individuals with limited opportunities.
- Difficulty in Providing Public Goods: Providing public goods such as national defense or infrastructure can be challenging in a system with minimal government intervention.
- Ignoring Social Issues: Critics argue that libertarianism neglects important social issues like environmental protection and healthcare access.
Conclusion: The Enduring Appeal of Libertarianism
Libertarianism, though often simplified and misunderstood, offers a compelling vision of a society based on individual liberty and limited government. Its core tenets, while debated and interpreted differently across its various schools of thought, provide a framework for thinking critically about the relationship between the individual and the state. While challenges and potential downsides exist, its enduring appeal lies in its unwavering commitment to individual freedom and its emphasis on personal responsibility. This deep dive should equip you with a far more nuanced understanding than a simple Quizlet definition can provide, allowing for a more informed and critical engagement with this complex and influential political ideology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
National Voter Registration Act Definition Ap Gov
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Type Of Boating Emergency Causes The Most Fatalities
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Recommended When Docking Your Boat
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Must Be Reported
Mar 18, 2025
-
Typically High Inflation Is A Sign Of
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Libertarianism Is A Political Ideology That Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
