Paget Disease Is Often Associated With Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
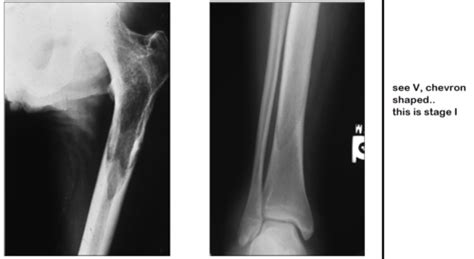
Table of Contents
Paget's Disease: Often Associated With... and Much More
Paget's disease of bone, also known simply as Paget's disease, is a chronic bone disorder that can lead to significant skeletal deformities, pain, and potential complications. While often associated with certain factors and conditions, understanding its full complexity requires a deeper dive into its pathogenesis, symptoms, diagnosis, and management. This article will comprehensively explore Paget's disease, addressing common associations, risk factors, and the latest advancements in its treatment.
What is Paget's Disease of Bone?
Paget's disease is characterized by excessive bone turnover. Instead of the normal, balanced process of bone resorption (breakdown) and bone formation, Paget's disease leads to disorganized and rapid bone remodeling. This results in brittle, enlarged, and weakened bones. The affected bone may become structurally compromised, increasing the risk of fractures and other complications. The exact cause remains unknown, but it's believed to be a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors.
Key Characteristics of Paget's Disease:
- Increased bone resorption: Osteoclasts (bone-resorbing cells) become abnormally active, breaking down bone tissue at an accelerated rate.
- Disordered bone formation: Osteoblasts (bone-forming cells) attempt to compensate, but the new bone formed is disorganized, weaker, and structurally inferior to normal bone.
- Mosaic pattern: Microscopic examination of affected bone reveals a characteristic mosaic pattern reflecting the chaotic bone remodeling process.
- Bone enlargement: The excessive bone formation can lead to bone enlargement, causing deformities in the affected areas.
- Bone pain: The disorganized bone structure and increased bone turnover often lead to pain, which can range from mild to severe.
Paget's Disease: Often Associated With...
The statement "Paget's disease is often associated with..." opens a wide range of possibilities. Several factors and conditions are frequently linked to Paget's disease, increasing the likelihood of its development or influencing its progression.
1. Genetic Predisposition:
A strong family history of Paget's disease significantly increases an individual's risk. While not directly inherited in a simple Mendelian fashion, genetic susceptibility is undeniable. Specific genes, including SQSTM1, have been implicated in the disease's development.
2. Age and Ethnicity:
Paget's disease is predominantly a disease of older adults, with the majority of cases diagnosed after the age of 50. It is also more prevalent in Caucasian populations, particularly those of British and Northern European descent.
3. Geographical Location:
The prevalence of Paget's disease varies geographically. Areas with higher rates include Great Britain, Australia, and New Zealand. These regional differences suggest that environmental factors may play a role in disease development, although the specific factors remain unidentified.
4. Viral Infection:
There's evidence suggesting a possible link between viral infections, particularly paramyxoviruses like measles, and the development of Paget's disease. However, the exact relationship remains unclear and requires further research. This association points to the involvement of the immune system in the disease process.
5. Other Associated Conditions:
Paget's disease can be associated with other conditions, including:
- Osteoarthritis: The bone deformities caused by Paget's disease can lead to secondary osteoarthritis in the affected joints.
- Hearing loss: Paget's disease affecting the skull can damage the auditory nerves, resulting in hearing impairment.
- Osteosarcoma: A rare but serious complication of Paget's disease is the development of osteosarcoma, a type of bone cancer.
- Cardiovascular disease: Individuals with Paget's disease may have an increased risk of cardiovascular problems, possibly due to the increased bone turnover leading to elevated blood calcium levels.
- Hypercalcemia: Although less common, excessive calcium release from affected bone can lead to hypercalcemia (high blood calcium levels), which can have serious health consequences.
- Neurological complications: Depending on the location of the affected bones, Paget's disease may compress nerves, leading to neurological symptoms like nerve pain or paralysis.
Symptoms of Paget's Disease
The symptoms of Paget's disease can vary greatly depending on the location and severity of the bone involvement. Many individuals are asymptomatic, and the disease is only discovered incidentally during routine medical imaging. However, common symptoms include:
- Bone pain: This is often the most prominent symptom, and it can be localized to the affected bone or more generalized. The pain may be aching, throbbing, or sharp.
- Bone deformities: Enlargement of the affected bones can lead to visible deformities, such as bowing of the legs or an increased skull size.
- Fractures: Weakened bones are more susceptible to fractures, even with minimal trauma.
- Joint pain and stiffness: Secondary osteoarthritis can develop due to bone deformities, causing pain and stiffness in the affected joints.
- Hearing loss: If the skull is involved, damage to the auditory nerves can lead to hearing loss.
- Headaches: Paget's disease affecting the skull can cause headaches due to pressure on the brain or blood vessels.
- Visual disturbances: Rarely, Paget's disease can affect the bones surrounding the eyes, potentially causing visual disturbances.
Diagnosis of Paget's Disease
Diagnosis of Paget's disease usually involves a combination of:
- Medical history and physical examination: A thorough assessment of the patient's symptoms, family history, and any relevant medical conditions.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can reveal elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase, a marker of bone turnover, which is often significantly increased in Paget's disease.
- Imaging studies: X-rays, bone scans, and sometimes MRI or CT scans are used to visualize the affected bones and assess the extent of bone involvement. The characteristic changes seen on imaging studies help confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment of Paget's Disease
Treatment for Paget's disease aims to reduce bone turnover, alleviate symptoms, and prevent complications. Treatment options include:
- Bisphosphonates: These are the most commonly used medications for Paget's disease. They inhibit bone resorption, reducing the excessive bone breakdown and alleviating symptoms.
- Calcitonin: This hormone can also help reduce bone resorption and pain.
- Denosumab: A monoclonal antibody that inhibits RANKL, a protein essential for osteoclast activation and bone resorption. It's a relatively new treatment option for Paget's disease showing effectiveness.
- Surgical intervention: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to correct bone deformities, stabilize fractures, or address complications like nerve compression.
Living with Paget's Disease
Managing Paget's disease often involves a multifaceted approach, including:
- Regular medical follow-up: Regular monitoring by a physician is crucial to assess disease progression and adjust treatment as needed.
- Pain management: Pain management strategies, including pain medication and physical therapy, can help control pain and improve quality of life.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help improve mobility, strength, and balance, reducing the risk of falls and fractures.
- Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise (adapted to individual capabilities), and following a balanced diet can help support bone health.
- Fracture prevention: Measures to prevent falls and fractures, such as using assistive devices if needed, are important to prevent complications.
Conclusion
Paget's disease is a complex bone disorder with a wide range of potential associations and complications. While the exact cause remains elusive, a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors likely contributes to its development. Understanding the disease's pathogenesis, recognizing its symptoms, and utilizing appropriate diagnostic tools and treatment strategies are vital for effective management. Early diagnosis and timely intervention can significantly improve the prognosis and quality of life for individuals affected by Paget's disease. Ongoing research continues to shed light on the disease mechanisms and improve therapeutic approaches, offering hope for better treatments and improved outcomes in the future. The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Life Insurance Exam Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Direct Carry Is Used To Transfer A Patient
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Emancipation Proclamation Of January 1 1863 Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
These Cards Will Get You Drunk Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Did Quizlet Get Rid Of Q Chat
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Paget Disease Is Often Associated With Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
