Production Units Have An Optimal Rate Of Output Where
Breaking News Today
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
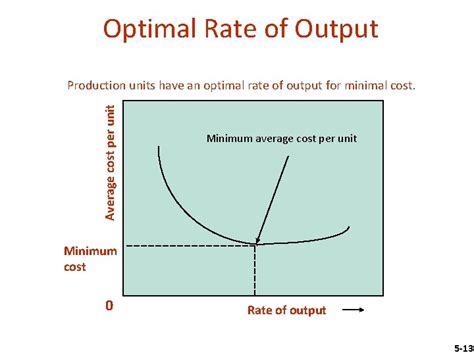
Table of Contents
Production Units: Finding the Sweet Spot – The Optimal Rate of Output
Every production unit, regardless of size or industry, strives for efficiency and profitability. A crucial element in achieving these goals lies in understanding and achieving the optimal rate of output. This isn't simply about producing as much as possible; it's about finding the sweet spot where production costs are minimized, and profits are maximized. This article delves deep into the concept of optimal output, exploring the factors that influence it, the methods used to determine it, and the implications of operating above or below this crucial point.
Understanding the Concept of Optimal Output
The optimal rate of output represents the production level at which a firm minimizes its average cost of production per unit. This point is often depicted graphically as the minimum point on the average cost curve (AC). Achieving this optimal rate isn't merely about maximizing production; it’s a delicate balance between several key factors. Producing too little leads to underutilization of resources and potentially higher per-unit costs. Producing too much can lead to increased costs due to factors like overtime pay, equipment wear and tear, and potentially diminishing returns.
The Role of Economies and Diseconomies of Scale
Understanding optimal output requires a firm grasp of economies and diseconomies of scale.
Economies of Scale: These refer to the cost advantages experienced by firms as their output expands. As production volume increases, the average cost per unit tends to decrease. This is because fixed costs (like rent and machinery) are spread over a larger number of units, leading to lower per-unit costs. Examples include bulk purchasing of raw materials and specialization of labor.
Diseconomies of Scale: Conversely, diseconomies of scale occur when increasing production leads to rising average costs. This typically happens beyond a certain point, where the challenges of managing a larger operation outweigh the benefits of increased volume. Reasons for diseconomies of scale include communication difficulties, coordination problems, and increased managerial complexity.
Factors Influencing the Optimal Rate of Output
Numerous factors contribute to determining the optimal output level for a production unit. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective management and strategic decision-making.
1. Production Function:
The production function describes the relationship between inputs (labor, capital, raw materials) and output. A well-defined production function is essential for predicting the output at various input levels. Understanding the marginal productivity of each input (the additional output generated by adding one more unit of input) is critical in determining the optimal combination of inputs for a given output level.
2. Cost Structure:
The cost structure of a production unit heavily influences the optimal output. This includes fixed costs (rent, salaries, machinery depreciation) and variable costs (raw materials, labor directly involved in production, energy). The optimal output will be where the total cost is minimized relative to the output. Analyzing cost curves (average total cost, average variable cost, marginal cost) is vital for this determination.
3. Demand Conditions:
The market demand for the product significantly influences the optimal output. If demand is high, a higher optimal output might be justified, even if it leads to slightly higher average costs. Conversely, low demand may necessitate a lower output level to avoid excess inventory and associated costs. Market research and forecasting are essential for accurately assessing demand conditions.
4. Technological Advancements:
Technological improvements can significantly impact the optimal output. New technologies can enhance productivity, reduce waste, and improve efficiency, potentially shifting the optimal output to a higher level. Automation, improved machinery, and streamlined processes are all examples of how technology can influence optimal output.
5. Competition:
The competitive landscape also plays a role. In highly competitive markets, firms might need to produce at a higher output level to achieve economies of scale and remain price-competitive. Conversely, in less competitive markets, firms might be able to operate at a lower output level with higher profit margins.
6. Government Regulations:
Government regulations, including environmental regulations, labor laws, and safety standards, can influence the optimal output. Compliance with these regulations often incurs additional costs, potentially altering the optimal production level.
Determining the Optimal Rate of Output
Several methods can be employed to determine the optimal rate of output. These methods often involve a combination of quantitative analysis and managerial judgment.
1. Break-Even Analysis:
Break-even analysis determines the point where total revenue equals total costs. While it doesn't directly pinpoint the optimal output (which aims for maximum profit, not just covering costs), it provides a crucial benchmark. Operating below the break-even point leads to losses, while operating above it generates profit.
2. Marginal Analysis:
Marginal analysis focuses on the change in total revenue and total cost resulting from producing one additional unit. The optimal output is achieved when marginal revenue (MR) equals marginal cost (MC). This is because producing beyond this point would lead to diminishing returns, with each additional unit costing more to produce than it generates in revenue.
3. Cost Minimization:
This approach involves finding the combination of inputs that minimizes the cost of producing a given output level. This often requires sophisticated mathematical modeling and optimization techniques, taking into account the specific production function and input prices.
4. Simulation and Modeling:
Advanced simulation models can help analyze the impact of various factors on output and cost. These models can incorporate complex relationships between inputs, outputs, and market conditions, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the optimal output under different scenarios.
5. Data Analytics:
Modern data analytics techniques, including machine learning, can be applied to historical production data to identify patterns and predict optimal output levels under changing conditions. This approach relies on the availability of accurate and reliable production data.
Implications of Operating Above or Below Optimal Output
Operating at a production level different from the optimal rate carries significant implications:
Operating Below Optimal Output: This can lead to underutilization of resources, higher average costs per unit due to fixed cost spreading over fewer units, and potentially lost opportunities for increased profits. It might suggest inefficiencies in the production process or inadequate demand forecasting.
Operating Above Optimal Output: Producing beyond the optimal level can lead to several problems: diminishing returns (where each additional unit produced costs more than the previous one), increased strain on resources (leading to equipment breakdowns and higher maintenance costs), potential quality issues, and worker burnout due to overtime. This can also lead to excess inventory, storage costs, and potential price reductions to offload surplus stock.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Pursuit of Optimal Output
Determining and maintaining the optimal rate of output is an ongoing challenge for any production unit. It requires a continuous monitoring of various factors, from production costs and market demand to technological advancements and competitive pressures. By employing appropriate analytical techniques and adapting to changing circumstances, businesses can strive to achieve this crucial balance between efficiency, profitability, and sustainable growth. The pursuit of optimal output is not a one-time event but an ongoing process of refinement and adaptation, crucial for long-term success in any industry. Regular reviews, data analysis, and a proactive approach to operational efficiency are essential components of this crucial endeavor. Ignoring the importance of optimal output can lead to significant financial losses and hinder a company's ability to compete effectively. Therefore, understanding and actively managing towards optimal output is paramount for sustained business success.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Definition Of Distracted Driving
Apr 02, 2025
-
Which Factor Is A Component Of Mental Health
Apr 02, 2025
-
If A Technical Rescue Team Is Required
Apr 02, 2025
-
The Concept Of Structural Social Mobility Refers To
Apr 02, 2025
-
A Flexible Budget Performance Report Combines The
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Production Units Have An Optimal Rate Of Output Where . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
