Puberty Gender Identity And Sexual Orientation Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
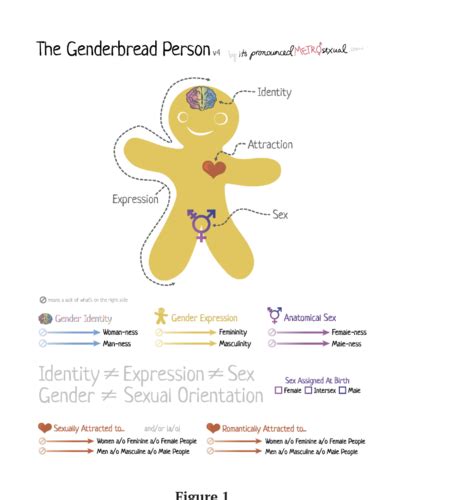
Table of Contents
Puberty, Gender Identity, and Sexual Orientation: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding puberty, gender identity, and sexual orientation is crucial for navigating adolescence and fostering a supportive environment for young people. This guide delves into these complex topics, dispelling common misconceptions and providing a framework for understanding the individual experiences associated with them. While this is not a substitute for professional guidance, it aims to be a valuable resource for individuals, parents, educators, and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of these interconnected aspects of human development.
What is Puberty?
Puberty is a period of rapid physical growth and development that marks the transition from childhood to adulthood. It's triggered by hormonal changes in the body, primarily the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) from the hypothalamus. This hormone stimulates the pituitary gland to release luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which in turn stimulate the gonads (testes in males and ovaries in females) to produce sex hormones like testosterone and estrogen.
Physical Changes During Puberty:
These hormonal changes drive a range of physical changes, including:
-
Primary Sexual Characteristics: These are directly involved in reproduction, such as the development of the testes and penis in males, and the ovaries, uterus, and vagina in females. Menarche (the first menstrual period) is a significant marker in females.
-
Secondary Sexual Characteristics: These are not directly involved in reproduction but are indicative of sexual maturation. Examples include:
- Males: Growth of facial and body hair, deepening of the voice, increased muscle mass.
- Females: Breast development, widening of the hips, growth of pubic and underarm hair.
-
Growth Spurt: A significant increase in height and weight occurs during puberty.
-
Body Composition Changes: The distribution of fat and muscle changes, contributing to the development of adult body shape.
The timing and pace of puberty vary greatly among individuals. Several factors can influence the onset and progression of puberty, including genetics, nutrition, and overall health. Early or delayed puberty can sometimes indicate underlying medical conditions, and professional consultation is advisable if concerns arise.
Understanding Gender Identity
Gender identity is an individual's internal sense of being male, female, both, or neither. It's a deeply personal and complex aspect of self-perception, distinct from biological sex assigned at birth and sexual orientation. Gender identity is formed over time, and individuals may discover their gender identity through self-reflection and exploration.
The Spectrum of Gender Identity:
Gender identity exists on a spectrum, with several possibilities including:
-
Cisgender: An individual whose gender identity aligns with the sex assigned at birth.
-
Transgender: An individual whose gender identity differs from the sex assigned at birth. This encompasses a wide range of experiences and identities.
-
Gender Non-Conforming: Individuals whose gender expression does not conform to societal norms associated with their assigned sex at birth.
-
Gender Fluid: Individuals whose gender identity changes over time.
-
Agender: Individuals who do not identify with any particular gender.
-
Bigender: Individuals who identify with two genders.
It's important to remember that gender identity is not a choice, but rather a fundamental aspect of who a person is. Understanding and respecting an individual's gender identity is crucial for creating inclusive and supportive environments.
Exploring Sexual Orientation
Sexual orientation refers to an individual's enduring physical, romantic, and/or emotional attraction to other people. It's a complex aspect of identity and exists on a spectrum.
The Spectrum of Sexual Orientation:
Some common terms used to describe sexual orientation include:
-
Heterosexual: Attraction to individuals of the opposite sex.
-
Homosexual: Attraction to individuals of the same sex (often further specified as gay for men and lesbian for women).
-
Bisexual: Attraction to individuals of both sexes.
-
Pansexual: Attraction to individuals regardless of their gender identity.
-
Asexual: Lack of sexual attraction to others.
Similar to gender identity, sexual orientation is not a choice and is a significant aspect of an individual's identity. Understanding and respecting diverse sexual orientations is crucial for building inclusive communities.
The Interplay of Puberty, Gender Identity, and Sexual Orientation
Puberty can have a significant impact on individuals' understanding and acceptance of their gender identity and sexual orientation. The physical changes associated with puberty may lead to questioning of one's identity or feelings of discomfort with one's body. For transgender individuals, puberty can be a particularly challenging time as physical changes may not align with their gender identity.
Navigating the Challenges:
-
Body Image Issues: The emphasis on physical appearance during adolescence can exacerbate body image issues, particularly for those whose bodies don't conform to societal expectations.
-
Social Pressure and Stigma: Negative societal attitudes and stigma towards different gender identities and sexual orientations can significantly affect mental health and well-being during puberty.
-
Family Dynamics: Family support plays a crucial role in navigating the challenges of adolescence. Open communication and acceptance are essential for creating a positive and supportive environment.
-
Access to Support: Access to mental health professionals, support groups, and resources specifically tailored to LGBTQ+ youth is critical.
Seeking Professional Guidance
If you or someone you know is struggling with issues related to puberty, gender identity, or sexual orientation, seeking professional guidance is essential. Mental health professionals, including therapists and counselors, can provide support, guidance, and resources to help navigate these complex aspects of development.
Common Misconceptions
Several misconceptions surround puberty, gender identity, and sexual orientation:
-
Puberty is always a straightforward process: The timing and experiences of puberty vary significantly. Early or delayed puberty can be a cause for concern and require medical attention.
-
Gender identity is a choice: Gender identity is not a choice but an intrinsic aspect of a person's identity.
-
Sexual orientation is a choice: Sexual orientation is not a choice but a complex aspect of an individual's identity.
-
Gender identity and sexual orientation are the same: While related, gender identity and sexual orientation are distinct aspects of an individual's identity.
-
Transgender individuals are a recent phenomenon: Transgender identities have existed throughout history, although societal acceptance and understanding have varied.
Creating a Supportive Environment
Creating a supportive and inclusive environment is crucial for individuals navigating puberty, gender identity, and sexual orientation. This involves:
-
Open Communication: Fostering open and honest conversations about these topics helps reduce stigma and promotes understanding.
-
Education: Educating oneself and others about gender identity and sexual orientation can reduce misunderstandings and promote acceptance.
-
Respectful Language: Using inclusive language and respecting an individual's self-identified gender identity and pronouns is essential.
-
Empathy and Understanding: Showing empathy and understanding is critical for fostering a supportive environment.
-
Access to Resources: Providing access to mental health professionals and community resources can provide crucial support.
Conclusion
Puberty, gender identity, and sexual orientation are interwoven aspects of human development. Understanding these topics is essential for fostering supportive environments and promoting the well-being of all individuals. Open communication, education, empathy, and access to resources are vital for navigating the challenges associated with these experiences and creating a more inclusive and accepting society. Remember, seeking professional guidance when needed is crucial for ensuring well-being and mental health support. This guide serves as an introduction to complex topics, and further exploration and research are encouraged to gain a richer understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
When Command Is Transferred The Process Should Include
Mar 25, 2025
-
Compare And Contrast Characteristics Of Healthy Versus Unhealthy Relationships
Mar 25, 2025
-
According To Florida Law What Must Be Aboard A Vessel
Mar 25, 2025
-
Decreasing Term Insurance Is Often Used To
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Do Elephants And Lions Use Carbohydrates
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Puberty Gender Identity And Sexual Orientation Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
