Select All That Are True Of Glands
Breaking News Today
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
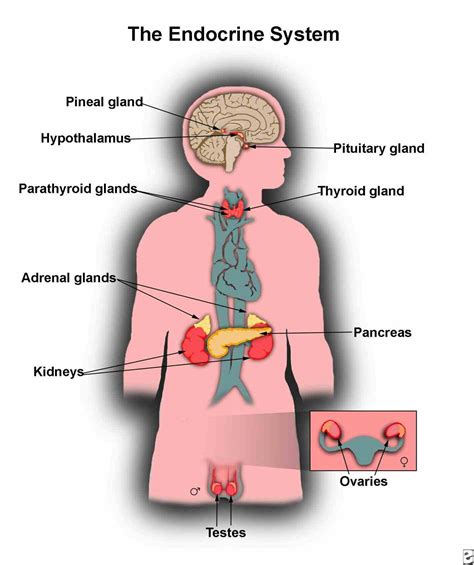
Table of Contents
Select All That Are True of Glands: A Comprehensive Guide to Glandular Function and Classification
Glands are vital organs in the human body, playing a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and enabling various bodily functions. Understanding their diverse roles and classifications is key to comprehending overall health and well-being. This comprehensive guide will delve into the characteristics of glands, exploring what makes them unique and how they contribute to the intricate workings of the human system. We'll examine different types of glands, their secretions, and their impact on various physiological processes. By the end, you'll have a robust understanding of the multifaceted world of glands.
What are Glands?
Glands are specialized epithelial cells or organs that synthesize and secrete substances for use elsewhere in the body or for elimination from the body. This secretion is their defining characteristic. These substances, known as secretions, range from hormones and enzymes to mucus, sweat, and milk. The process of secretion varies depending on the type of gland, but it generally involves the synthesis of a product within the gland cells, its packaging into secretory vesicles, and its release through exocytosis.
The secretion process itself is tightly regulated, often responding to hormonal or neural stimuli. This intricate regulation ensures the appropriate amount of secretion is produced at the right time, crucial for maintaining homeostasis and responding to changes in the body's internal environment.
Classification of Glands: Exocrine vs. Endocrine
Glands are broadly classified into two main categories based on how they release their secretions:
1. Exocrine Glands:
Exocrine glands release their secretions onto an epithelial surface through a duct system. Think of sweat glands releasing sweat onto the skin, salivary glands releasing saliva into the mouth, or sebaceous glands releasing sebum onto hair follicles. These glands maintain a physical connection with the epithelium via ducts. This direct pathway ensures that the secretion reaches its target site efficiently.
Examples of exocrine glands and their secretions:
- Salivary glands: Produce saliva, which aids in digestion and lubrication.
- Sweat glands: Produce sweat, which helps regulate body temperature.
- Sebaceous glands: Produce sebum, an oily substance that lubricates the skin and hair.
- Mammary glands: Produce milk for nourishing offspring.
- Goblet cells: Unicellular exocrine glands found within the lining of various tracts (e.g., respiratory, digestive). They secrete mucus.
- Lacrimal glands: Produce tears, which lubricate and protect the eyes.
- Gastric glands: located in the stomach lining, secrete gastric juices containing hydrochloric acid and pepsinogen crucial for digestion.
- Pancreas (exocrine part): secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum via the pancreatic duct.
Further classification of exocrine glands is based on their structure:
- Simple glands: Have a single, unbranched duct.
- Compound glands: Have a branched duct system.
- Tubular glands: Secretion occurs along a tube-like structure.
- Alveolar (acinar) glands: Secretion occurs within a rounded sac-like structure.
- Tubuloalveolar glands: Combination of tubular and alveolar structures.
2. Endocrine Glands:
Endocrine glands, unlike exocrine glands, are ductless. They release their secretions, known as hormones, directly into the bloodstream. Hormones travel throughout the circulatory system, reaching target cells located in distant parts of the body. This mechanism allows for widespread and coordinated regulation of various bodily functions. The endocrine system is crucial for maintaining homeostasis and regulating processes like growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
Examples of endocrine glands and their hormones:
- Pituitary gland: Releases numerous hormones regulating growth, metabolism, and reproduction. Often referred to as the "master gland."
- Thyroid gland: Produces thyroid hormones, critical for metabolism and growth.
- Parathyroid glands: Regulate calcium and phosphorus levels in the blood.
- Adrenal glands: Produce adrenaline (epinephrine) and cortisol, vital for stress response and metabolism.
- Pancreas (endocrine part): Produces insulin and glucagon, regulating blood sugar levels.
- Ovaries (in females): Produce estrogen and progesterone, crucial for reproductive function.
- Testes (in males): Produce testosterone, vital for male reproductive function and development.
- Pineal gland: Secretes melatonin, involved in regulating sleep-wake cycles.
- Thymus: plays a critical role in the development of the immune system.
The Importance of Glandular Function
The proper functioning of glands is crucial for overall health. Imbalances or dysfunctions in glandular activity can lead to a wide range of health problems. For example:
- Hypothyroidism: Underactive thyroid gland, resulting in slow metabolism and weight gain.
- Hyperthyroidism: Overactive thyroid gland, leading to rapid metabolism and weight loss.
- Diabetes mellitus: Insufficient insulin production by the pancreas, resulting in high blood sugar levels.
- Cushing's syndrome: Excess cortisol production by the adrenal glands, resulting in weight gain, high blood pressure, and other symptoms.
Advanced Considerations: Mixed Glands and Other Secretory Mechanisms
Some organs exhibit both exocrine and endocrine functions, making them mixed glands. The pancreas is a prime example, producing both digestive enzymes (exocrine) and hormones like insulin and glucagon (endocrine). This dual functionality highlights the interconnectedness of different physiological systems.
Furthermore, the mechanisms of secretion are more nuanced than simply exocrine or endocrine. For instance, some glands utilize:
- Merocrine secretion: The product is released via exocytosis without damage to the gland cell. This is a common method for many exocrine glands.
- Apocrine secretion: A portion of the cytoplasm is released along with the secretory product. Mammary glands are a notable example.
- Holocrine secretion: The entire gland cell disintegrates to release its secretion. Sebaceous glands employ this method.
Glandular Disorders and Treatment
Many diseases stem from glandular dysfunction. Diagnosis typically involves blood tests to measure hormone levels, imaging techniques to assess gland size and structure, and other specialized tests depending on the suspected condition. Treatment strategies vary greatly depending on the specific disorder and its severity, ranging from medication to surgery. For example, hypothyroidism can be managed with thyroid hormone replacement therapy, while diabetes may require insulin injections or oral medications. Surgical intervention might be necessary in cases of tumors or severe glandular dysfunction.
The Future of Glandular Research
Ongoing research continues to unravel the complexities of glandular function and its impact on health and disease. Advances in molecular biology, genetics, and imaging techniques are providing new insights into the mechanisms of glandular regulation and the development of glandular disorders. This research holds immense promise for developing more effective diagnostic tools and therapeutic strategies.
Conclusion: A Complex System with Vital Functions
Glands, whether exocrine or endocrine, are indispensable components of the human body, playing critical roles in maintaining homeostasis and facilitating a wide range of vital functions. Their diverse secretions and intricate regulatory mechanisms underscore their importance in overall health and well-being. Understanding the classification, function, and potential disorders associated with glands is essential for appreciating the complexity and sophistication of the human biological system. Further research promises to unveil even more about these fascinating organs and their contributions to human health.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Player Pays 15 To Play A Game
Mar 26, 2025
-
A Product Differentiation Strategy Should Achieve Which Of The Following
Mar 26, 2025
-
Vaccination Against The Hepatitis A Virus Is Unnecessary
Mar 26, 2025
-
Add The Profit Sharing Field To The Pivot Table
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Accurately Describes Follicles In Dry Skin
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Select All That Are True Of Glands . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
