Sister Taxa Are Defined As Those That __________.
Breaking News Today
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
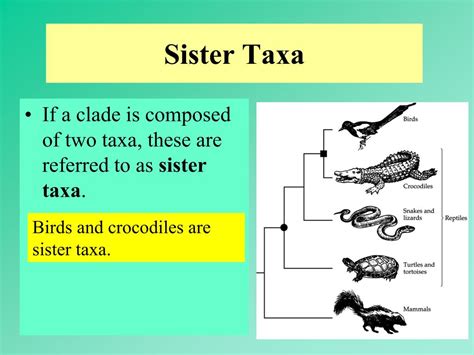
Table of Contents
Sister Taxa: A Deep Dive into Evolutionary Relationships
Sister taxa are defined as those that share an immediate common ancestor. This seemingly simple definition underpins a vast amount of evolutionary biology, informing our understanding of phylogenetic relationships, species diversification, and the history of life on Earth. This article delves into the concept of sister taxa, exploring its implications, the methods used to identify them, and the challenges involved in reconstructing accurate evolutionary trees.
Understanding the Basics: Clades, Nodes, and Branches
Before we delve into the intricacies of sister taxa, let's establish a foundation in phylogenetic terminology. A phylogeny is a visual representation of the evolutionary history of a group of organisms, depicted as a branching diagram called a phylogenetic tree or cladogram.
-
Clade: A clade represents a group of organisms that includes a common ancestor and all of its descendants. It's a monophyletic group, meaning it's a complete branch on the tree of life.
-
Node: A node on a phylogenetic tree represents a common ancestor. This point signifies a speciation event, where a single ancestral lineage splits into two or more descendant lineages.
-
Branch: A branch on a phylogenetic tree represents an evolutionary lineage. The length of the branch can sometimes represent the amount of evolutionary change or the time elapsed since the divergence.
Sister taxa are found at the tips of branches that emerge from the same node. They are, therefore, equally related to each other, sharing a more recent common ancestor than they do with any other taxon on the tree.
Identifying Sister Taxa: Methods and Challenges
Identifying sister taxa involves constructing robust phylogenetic trees. Several methods are employed, each with its strengths and limitations:
1. Morphological Data: Comparing Physical Traits
Historically, phylogenetic analyses heavily relied on morphological data, comparing physical characteristics such as bone structure, leaf shape, or flower morphology. Researchers would identify shared derived characters (synapomorphies) – traits unique to a particular clade – to establish evolutionary relationships. However, this approach has limitations:
- Convergent evolution: Unrelated species may independently evolve similar traits due to similar environmental pressures (e.g., the streamlined bodies of dolphins and sharks). This can lead to inaccurate inferences of evolutionary relationships.
- Homoplasy: This term encompasses both convergent evolution and evolutionary reversals (loss of a trait). Both phenomena can obscure true evolutionary relationships if not carefully considered.
- Incomplete fossil record: The fossil record is incomplete, meaning many extinct lineages are unknown, potentially leading to inaccuracies in reconstructing phylogenetic trees.
2. Molecular Data: Analyzing DNA and Protein Sequences
With the advent of molecular biology, molecular data – DNA and protein sequences – have revolutionized phylogenetic analyses. These data offer several advantages:
- Large datasets: Molecular data provide massive amounts of information, allowing for more robust statistical analyses.
- Directly comparable: DNA and protein sequences are directly comparable across species, providing a more objective measure of relatedness.
- Quantifiable differences: Molecular differences can be quantified, allowing for the construction of more precise phylogenetic trees.
Common molecular techniques include:
- DNA sequencing: Determining the order of nucleotides in DNA.
- Protein sequencing: Determining the order of amino acids in proteins.
- Comparative genomics: Comparing the entire genomes of different species.
However, molecular data also present challenges:
- Horizontal gene transfer: In prokaryotes, and sometimes eukaryotes, genes can be transferred laterally between unrelated species, obscuring true evolutionary relationships.
- Incomplete lineage sorting: During speciation, different gene copies may sort differently into the descendant species, leading to discordant phylogenetic signals.
- Computational demands: Analyzing large molecular datasets requires powerful computational resources.
3. Combining Data: A Powerful Approach
The most robust phylogenetic analyses combine both morphological and molecular data. This integrated approach leverages the strengths of each data type, mitigating the weaknesses. By integrating diverse lines of evidence, researchers can construct more accurate and reliable phylogenetic trees, leading to a more precise identification of sister taxa.
Implications of Sister Taxa Identification
The accurate identification of sister taxa has far-reaching implications in various fields:
1. Understanding Evolutionary History: Tracing the Tree of Life
The identification of sister taxa is crucial for reconstructing the tree of life. By understanding which species share the most recent common ancestor, we can trace the evolutionary pathways leading to the incredible biodiversity we observe today. This helps us understand the patterns and processes of speciation, diversification, and extinction.
2. Conservation Biology: Protecting Evolutionary History
Knowing which species are closely related can be vital for conservation biology. Closely related species often share similar ecological requirements and vulnerabilities, meaning that threats to one species may also affect its sister taxon. This knowledge can inform conservation strategies aimed at protecting both species.
3. Biogeography: Understanding Species Distributions
Sister taxa can provide insights into biogeography, the study of the geographic distribution of species. By comparing the distribution patterns of sister taxa, researchers can infer historical events such as continental drift, dispersal patterns, and vicariance (the splitting of a population into two geographically isolated populations).
4. Studying Adaptation and Diversification: Unraveling Evolutionary Success
Sister taxa are particularly useful for studying adaptation and diversification. By comparing the traits of sister taxa, researchers can identify which traits may have been responsible for their divergence and the success of one lineage over another. This allows us to study adaptation in action.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite significant advancements in phylogenetic methods, several challenges remain:
- Incomplete sampling: Not all species are equally represented in phylogenetic analyses, potentially leading to biased results.
- Rapid speciation: In some cases, speciation occurs so rapidly that phylogenetic signals are weak, making it difficult to identify sister taxa with confidence.
- The role of hybridization: Hybridization, or interbreeding between distinct species, can confound phylogenetic analyses by obscuring evolutionary relationships.
Future directions in phylogenetic research include:
- Developing more sophisticated analytical methods: Advances in computational biology and statistics are leading to the development of more powerful methods for analyzing large and complex datasets.
- Integrating data from diverse sources: Researchers are increasingly integrating data from diverse sources, including genomics, morphology, ecology, and paleontology, to obtain a more holistic view of evolutionary relationships.
- Addressing incomplete lineage sorting: New methods are being developed to address the challenge of incomplete lineage sorting, improving the accuracy of phylogenetic reconstructions.
Conclusion
Sister taxa, defined as those sharing an immediate common ancestor, are fundamental to understanding evolutionary relationships. Their identification, while challenging, is crucial for reconstructing phylogenetic trees and shedding light on the processes that have shaped the biodiversity of our planet. The integration of morphological and molecular data, coupled with continuous advancements in analytical methods, promises to yield ever more accurate and detailed insights into the evolutionary history of life. The ongoing refinement of our understanding of sister taxa relationships continues to enrich fields ranging from conservation biology to the study of adaptive radiation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Emancipation Proclamation Of January 1 1863 Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
These Cards Will Get You Drunk Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Did Quizlet Get Rid Of Q Chat
Mar 18, 2025
-
Myasthenia Gravis Is An Autoimmune Disease In Which Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Fun Sex Questions For Couples Quizlet With Answers
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sister Taxa Are Defined As Those That __________. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
