Sodium 24 Has A Half Life Of 15 Hours
Breaking News Today
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
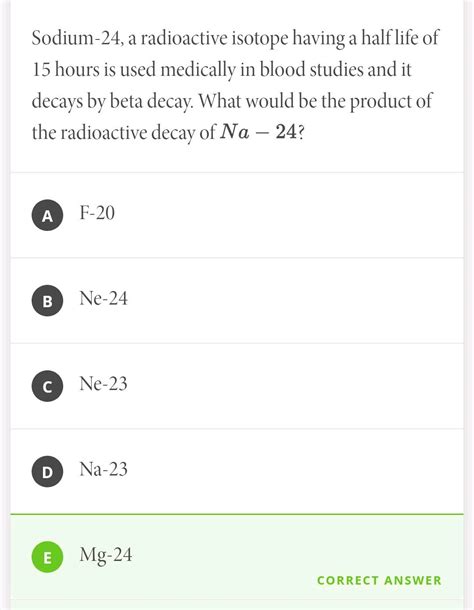
Table of Contents
Sodium-24: A Deep Dive into its 15-Hour Half-Life and Applications
Sodium-24 (²⁴Na), a radioactive isotope of sodium, boasts a relatively short half-life of approximately 15 hours. This characteristic makes it a valuable tool in various scientific and medical applications, but also necessitates careful handling and disposal due to its radioactivity. Understanding its properties, decay mechanisms, and uses is crucial for anyone working with or learning about this important isotope.
Understanding Half-Life and Radioactive Decay
Before delving into the specifics of ²⁴Na, let's clarify the concept of half-life. The half-life of a radioactive isotope is the time it takes for half of the atoms in a given sample to undergo radioactive decay. This decay process involves the unstable atomic nucleus emitting radiation to become more stable. For ²⁴Na, this means that after 15 hours, half of the initial amount of ²⁴Na will have decayed into other isotopes. After another 15 hours (30 hours total), half of the remaining ²⁴Na will decay, and so on. This decay follows an exponential pattern, never reaching zero completely.
Several types of radioactive decay exist. ²⁴Na primarily undergoes beta decay, where a neutron in the nucleus transforms into a proton, emitting a beta particle (an electron) and an antineutrino. This process increases the atomic number by one while the mass number remains unchanged. The resulting nucleus is magnesium-24 (²⁴Mg), a stable isotope. The emitted beta particles are energetic and can be easily detected.
The Significance of the 15-Hour Half-Life
The 15-hour half-life of ²⁴Na is crucial for its applications. It's short enough to allow for relatively quick experiments and procedures, minimizing the long-term exposure to radiation. However, it's long enough to allow for meaningful studies and applications. This intermediate half-life distinguishes it from isotopes with significantly shorter or longer half-lives. Isotopes with shorter half-lives decay too quickly for many applications, while those with longer half-lives pose greater long-term radiation risks.
Production of Sodium-24
²⁴Na is primarily produced through neutron activation of stable sodium-23 (²³Na), the most abundant isotope of sodium. This process involves bombarding ²³Na with neutrons in a nuclear reactor. The neutron absorption leads to the formation of the unstable ²⁴Na isotope. The reaction can be represented as:
²³Na + n → ²⁴Na
The intensity and duration of neutron bombardment control the amount of ²⁴Na produced. After irradiation, the ²⁴Na sample needs careful handling due to its radioactivity.
Detection and Measurement of Sodium-24
The beta particles emitted during the decay of ²⁴Na can be detected using various instruments, such as Geiger counters, scintillation detectors, and beta spectrometers. These instruments measure the radiation emitted by the sample, allowing for the quantification of the remaining ²⁴Na and the determination of its decay rate. The high energy of the beta particles facilitates their detection, even with relatively simple instruments.
Applications of Sodium-24
The unique properties of ²⁴Na, particularly its 15-hour half-life and beta emission, make it suitable for a variety of applications in various fields:
1. Medical Applications:
-
Blood Flow Studies: ²⁴Na is used as a radioactive tracer to study blood flow in the circulatory system. A small, precisely measured amount of ²⁴Na is injected into the bloodstream. Its movement can then be tracked using specialized detectors. This technique helps diagnose vascular diseases and assess the effectiveness of treatments. The short half-life ensures minimal radiation exposure to the patient.
-
Medical Imaging: Although less common than other radioisotopes, ²⁴Na has been used in specific medical imaging techniques. Its beta emission can provide information about the distribution and uptake of sodium ions in the body.
2. Industrial Applications:
-
Flow Rate Measurement: Similar to its use in blood flow studies, ²⁴Na can be used to measure the flow rate of liquids in industrial pipelines and systems. The radioactive tracer is introduced into the liquid stream, and its movement is monitored to determine flow characteristics.
-
Leak Detection: ²⁴Na can be used as a tracer to detect leaks in industrial pipelines and systems. By introducing a small amount of ²⁴Na into the system and monitoring its distribution, leaks can be precisely located.
3. Environmental Studies:
-
Water Tracing: ²⁴Na can be used to trace the movement of water in various environmental systems, such as rivers, aquifers, and soil. This information is valuable for understanding water flow patterns and potential contamination pathways.
-
Sediment Transport Studies: Similar to its use in water tracing, ²⁴Na can track the movement of sediments in rivers and other water bodies, providing insights into sediment transport processes and their impact on the environment.
Safety Precautions and Disposal
Due to its radioactivity, handling ²⁴Na requires strict adherence to safety protocols. These protocols include:
-
Shielding: Using appropriate shielding materials, such as lead, to reduce radiation exposure.
-
Distance: Maintaining a safe distance from the radioactive source to minimize exposure.
-
Time: Minimizing the time spent near the radioactive source. The short half-life helps limit the duration of exposure.
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Utilizing appropriate PPE, including lab coats, gloves, and protective eyewear.
Disposal of ²⁴Na requires careful consideration. The decaying isotope must be handled according to established regulatory guidelines to prevent environmental contamination. The short half-life allows for the decay of most of the radioactivity within a reasonable timeframe, simplifying disposal compared to isotopes with much longer half-lives.
Research and Future Applications
Ongoing research continues to explore the potential applications of ²⁴Na. Advances in detection technologies and the development of new techniques might lead to novel applications in medicine, industry, and environmental science. For example, advancements in tracer technology could make ²⁴Na even more useful for highly-localized studies of processes within smaller systems. The potential for minimally invasive procedures using this short-lived isotope also bears investigation.
Conclusion
Sodium-24, with its 15-hour half-life, is a powerful tool with various applications across diverse scientific and industrial fields. Its short half-life offers advantages in terms of reduced exposure time and simplified disposal, but careful handling and adherence to safety protocols are crucial. Understanding its properties, decay mechanism, and applications is vital for researchers, technicians, and anyone working with or learning about this significant radioactive isotope. Ongoing research will continue to reveal new and innovative applications of this versatile element. The relatively short half-life continues to make it a convenient and relatively safe tool for a range of applications, while minimizing the long-term risks associated with prolonged radiation exposure.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Did Conservatives Oppose The New Deal
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Important Function Do Stream Pools Serve
Mar 22, 2025
-
Explain How Smart Growth Promotes Long Term Sustainable Development
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Is The Second Step Of Direct Observation
Mar 22, 2025
-
Compras Un 1 Of 1 De Ida Y Vuelta
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sodium 24 Has A Half Life Of 15 Hours . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
