The Actions Of The Internal Obliques Include __________.
Breaking News Today
Mar 30, 2025 · 6 min read
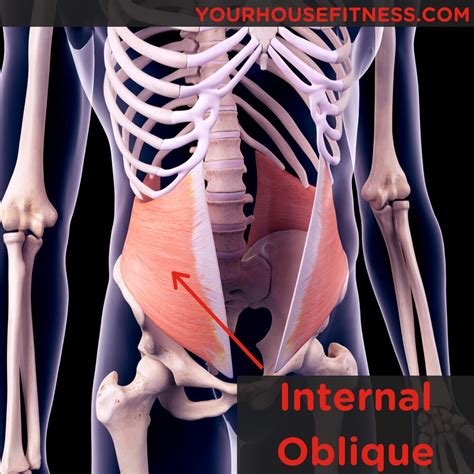
Table of Contents
The Actions of the Internal Obliques Include… A Deep Dive into Core Stability and Movement
The internal oblique muscles, often overlooked in discussions of core strength, play a crucial role in trunk stability, rotation, and flexion. Understanding their multifaceted actions is key to optimizing fitness routines, injury prevention, and overall functional movement. This article delves into the intricacies of internal oblique function, exploring their contributions to various movements and their importance in maintaining a healthy spine.
Understanding the Internal Obliques: Anatomy and Location
Before exploring their actions, let's establish a foundational understanding of the internal obliques' anatomy. Located beneath the external obliques, these muscles are situated on the sides of the abdomen. Their fibers run inferomedially – meaning they slant downwards and towards the midline of the body – in contrast to the superomedial direction of the external obliques. This directional difference is crucial in understanding their unique contributions to movement. Originating from the iliac crest (the superior border of the hip bone), the inguinal ligament (a thickened band of tissue in the groin), and the thoracolumbar fascia (a sheet of connective tissue in the lower back), the internal obliques insert into the linea alba (a fibrous band running down the midline of the abdomen) and the cartilages of the lower ribs.
Primary Actions of the Internal Obliques
The actions of the internal obliques include a range of movements centered around trunk stability and rotation. While often working synergistically with other core muscles, their specific contributions are noteworthy:
1. Trunk Rotation: The Twist and Turn
One of the most prominent actions of the internal obliques includes trunk rotation. When unilaterally activated (one side contracting), the internal oblique on that side causes contralateral rotation, meaning it rotates the trunk towards the opposite side. For instance, contracting the right internal oblique will rotate the torso to the left. This action is essential for activities involving twisting, turning, and throwing.
2. Trunk Flexion: Bending Forward
The internal obliques also contribute to trunk flexion, or bending forward. However, their contribution is less significant than that of the rectus abdominis. They work in conjunction with other core muscles to control the speed and range of motion during flexion, aiding in stability and preventing injury.
3. Lateral Flexion: Bending Sideways
Similar to flexion, the internal obliques contribute to lateral flexion, bending the torso to the side. When the internal obliques on one side contract, they pull the trunk towards that side, leading to lateral flexion. Again, this action is typically coordinated with other muscles for controlled and stable movement.
4. Compression of the Abdominal Cavity: Core Stability
A vital but often underappreciated action of the internal obliques is their role in compressing the abdominal cavity. This compression increases intra-abdominal pressure, which acts like a natural corset, supporting the spine and enhancing overall core stability. This stability is critical for maintaining proper posture, protecting the spine during lifting and exertion, and providing a solid base for limb movements.
Synergistic Actions with Other Core Muscles
The internal obliques rarely act in isolation. They work in concert with other core muscles, including:
1. External Obliques: The Counterbalance
The external obliques work in opposition to the internal obliques during rotation. While the internal obliques cause contralateral rotation, the external obliques facilitate ipsilateral rotation (rotation towards the same side). This interplay allows for controlled and precise rotational movements.
2. Rectus Abdominis: The Six-Pack Muscle
The rectus abdominis, the prominent “six-pack” muscle, works with the internal obliques during trunk flexion. The rectus abdominis provides the primary force for flexion, while the internal obliques contribute to stability and controlled movement.
3. Transverse Abdominis: The Deep Core Stabilizer
The transverse abdominis, the deepest abdominal muscle, plays a significant role in core stability alongside the internal obliques. Both muscles contribute to increasing intra-abdominal pressure, providing a supportive base for the spine.
4. Multifidus and Erector Spinae: Back Support
The muscles of the back, such as the multifidus and erector spinae, work in coordination with the abdominal muscles, including the internal obliques, to maintain balanced posture and control spinal movement.
Importance of Internal Oblique Strength: Benefits and Implications
Strong internal oblique muscles offer numerous benefits, contributing to both athletic performance and overall health:
1. Enhanced Core Stability: The Foundation of Movement
Strong internal obliques are essential for core stability, providing a solid foundation for all movements. This enhanced stability reduces the risk of back pain, improves posture, and facilitates efficient movement patterns.
2. Improved Athletic Performance: Power and Precision
Strong internal obliques are crucial for athletes in various sports, contributing to power generation, rotational movements, and overall athletic performance. Sports such as golf, tennis, baseball, and many others rely heavily on core strength and rotational power.
3. Injury Prevention: Protecting the Spine
Strong core muscles, including the internal obliques, protect the spine from injury by stabilizing the trunk and absorbing forces during movement. This is particularly important for activities involving lifting, twisting, or repetitive movements.
4. Improved Posture: Standing Tall with Confidence
Weak internal obliques can contribute to poor posture. Strong internal obliques help maintain proper spinal alignment, leading to improved posture and a reduction in back pain.
5. Enhanced Balance and Coordination: Moving with Grace
Strong core muscles, including the internal obliques, are vital for balance and coordination. A strong core provides a stable base, allowing for improved balance and coordination during various activities.
Assessing and Strengthening Internal Obliques: Exercises and Considerations
Evaluating and strengthening internal obliques requires a multifaceted approach:
1. Identifying Weaknesses: Recognizing Limitations
Weakness in the internal obliques can manifest as poor posture, decreased rotational strength, increased risk of injury, and difficulty performing certain movements. A qualified healthcare professional can help identify weaknesses.
2. Targeted Exercises: Engaging the Internal Obliques
Numerous exercises effectively target the internal obliques. However, proper form is paramount to ensure effective activation and avoid injury. Some effective exercises include:
- Cable Rotations: Using a cable machine, perform controlled rotations, focusing on controlled movement and feeling the engagement in the internal obliques.
- Russian Twists: While often associated with the external obliques, Russian twists, performed with proper form, also engage the internal obliques for stabilization and controlled rotation.
- Side Plank: This isometric exercise strengthens the entire core, including the internal obliques, by maintaining a stable side plank position.
- Plank Variations: Different plank variations, such as forearm planks and side planks, can effectively target the internal obliques.
- Anti-Rotation Press: Using resistance bands or a cable machine, resist rotation while maintaining a stable core position, engaging the internal obliques to maintain stability.
3. Progressive Overload: Gradual Advancement
Like any muscle group, the internal obliques respond to progressive overload. Gradually increase the intensity and difficulty of exercises over time to continue challenging the muscles and promoting strength gains.
4. Proper Form: Precision over Power
Maintain proper form during all exercises to avoid injury and ensure effective activation of the internal obliques. Focus on controlled movements and feel the muscle engagement.
5. Incorporating into Functional Movements: Real-World Application
Strengthening the internal obliques should not be limited to isolation exercises. Incorporate functional movements, such as lifting, carrying, and rotational activities, into your workout routine to translate strength gains into real-world application.
Conclusion: The Unsung Heroes of Core Stability
The actions of the internal obliques include a complex interplay of trunk rotation, flexion, lateral flexion, and abdominal compression. Understanding these actions is vital for optimizing fitness routines, preventing injuries, and enhancing overall functional movement. By incorporating targeted exercises and focusing on proper form, individuals can strengthen their internal obliques, reaping the benefits of enhanced core stability, improved athletic performance, and a reduced risk of injury. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or certified fitness trainer to create a personalized workout plan that suits your individual needs and goals.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do Phishing Simulations Contribute To Enterprise Security
Apr 01, 2025
-
Accounting And Financial Ratios Expanding The Vintage Lily
Apr 01, 2025
-
Nothing About The Account Changes Even If You Switch Jobs
Apr 01, 2025
-
Hartmans Nursing Assistant Care Workbook Fifth Edition Answer Key Pdf
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Recommended Procedure Regarding Decontamination Is To
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Actions Of The Internal Obliques Include __________. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
