The Area Underneath The Nail Tip Is Called The
Breaking News Today
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
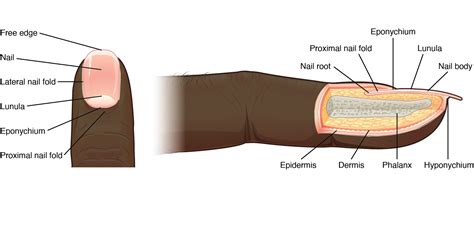
Table of Contents
The Area Underneath the Nail Tip is Called the Hyponychium: A Comprehensive Guide
The area underneath the nail tip, often overlooked, plays a crucial role in nail health and overall well-being. Understanding its anatomy, function, and potential problems is key to maintaining healthy, strong nails. This comprehensive guide delves into the hyponychium, the often-misunderstood area located beneath the free edge of the nail.
What is the Hyponychium?
The hyponychium, also known as the nail bed, is the area of skin underneath the free edge of your fingernail or toenail. It's the slightly thicker, whitish area where the nail plate meets the skin at the tip of your finger or toe. It's a crucial part of the nail unit, connecting the nail plate to the fingertip, acting as a protective barrier, and playing a vital role in nail growth. Many mistakenly refer to this as the cuticle, but the cuticle is actually a separate structure located at the base of the nail.
Key characteristics of the hyponychium include:
- Location: Under the free edge of the nail.
- Appearance: Usually a slightly thicker, whitish or opaque area.
- Function: Provides a seal to protect the nail matrix from infection and injury.
- Composition: Similar in structure to the epidermis (outer layer of skin).
- Significance: Essential for healthy nail growth and preventing infection.
The Hyponychium's Role in Nail Health
The hyponychium's primary function is to act as a protective barrier. It seals the space between the nail plate and the underlying skin, preventing the entry of bacteria, fungi, and other pathogens that can cause nail infections like paronychia. This seal is vital for maintaining nail health and preventing infections that could lead to pain, swelling, and even nail loss.
Furthermore, the hyponychium contributes to healthy nail growth. Its healthy condition is intrinsically linked to the proper growth and development of the nail plate. When the hyponychium is damaged or compromised, it can negatively impact nail growth, potentially leading to weakened, brittle nails, or changes in nail shape and texture.
Conditions Affecting the Hyponychium
Several conditions can affect the hyponychium, leading to various nail problems. Understanding these conditions is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment:
1. Paronychia
Paronychia is a common infection of the skin around the nail, often involving the hyponychium. It's usually caused by bacteria or fungi, and symptoms include pain, swelling, redness, and pus around the nail. This infection can lead to significant discomfort and even nail detachment if left untreated. Good hygiene practices, including keeping the area clean and dry, are crucial in prevention.
2. Onycholysis
Onycholysis refers to the separation of the nail plate from the nail bed. This separation can start at the free edge near the hyponychium, gradually progressing toward the nail root. Several factors contribute to onycholysis, including trauma, fungal infections, psoriasis, and allergic reactions. Treatment depends on the underlying cause.
3. Ingrown Toenails
Although more common in the toenail, an ingrown toenail can also occur in the fingernail. In this condition, the edge of the nail grows into the surrounding skin, often around the hyponychium, causing pain, redness, and inflammation. Improper nail trimming techniques often contribute to ingrown toenails.
4. Trauma and Injury
Direct trauma to the hyponychium, such as a forceful impact or a sharp injury, can lead to pain, bleeding, and potential infection. Proper wound care is necessary to prevent complications.
Maintaining Healthy Hyponychium: Tips and Tricks
Maintaining a healthy hyponychium is crucial for overall nail health. Here's how:
1. Practice Good Hygiene
Keep your nails and the surrounding skin clean and dry. Regularly wash your hands and feet with soap and water, and avoid prolonged exposure to moisture.
2. Proper Nail Trimming
Trim your nails straight across, avoiding rounded edges that can increase the risk of ingrown nails. Use clean nail clippers and avoid cutting too deeply into the skin around the hyponychium.
3. Moisturize Regularly
Moisturizing the skin around the nails, including the hyponychium, can help prevent dryness and cracking. Choose a moisturizer suitable for your skin type.
4. Avoid Harsh Chemicals
Minimize contact with harsh chemicals, detergents, and solvents that can damage the hyponychium. Wear protective gloves when handling such substances.
5. Early Detection and Treatment
If you notice any changes in the hyponychium, such as redness, swelling, pain, or separation of the nail, seek medical attention immediately. Early detection and treatment can prevent serious complications.
6. Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and protein is essential for healthy nail growth. Ensure you're getting enough nutrients to support the growth and repair of your nails.
The Hyponychium and its Connection to Systemic Health
The condition of the hyponychium can sometimes reflect underlying systemic health issues. Changes in nail color, texture, or growth patterns might indicate problems such as:
- Anemia: Pale or brittle nails.
- Fungal infections: Thickened, discolored nails.
- Psoriasis: Pitted or discolored nails.
- Diabetes: Thickened or yellowed nails.
- Respiratory issues: Clubbing of the nails (bulging of the nail bed).
While these are just some examples, it's important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis if you notice any significant changes in your nails.
Differentiating the Hyponychium from the Cuticle and Eponychium
It's essential to differentiate the hyponychium from other nail structures:
-
Cuticle (Eponychium): The cuticle is a fold of skin that covers the base of the nail plate, protecting the nail matrix. It's located at the base of the nail, unlike the hyponychium which is at the tip. Pushing back or removing the cuticle should be done carefully to avoid damaging the nail matrix.
-
Eponychium: This is the technical term for the cuticle. It's the thin layer of skin covering the nail matrix, providing protection and promoting healthy nail growth.
Understanding the difference between these structures is crucial for proper nail care. Mistaking the hyponychium for the cuticle can lead to improper nail care practices, potentially damaging the nail unit.
The Hyponychium and Nail Aesthetics
The hyponychium also plays a role in the overall aesthetics of your nails. A healthy, well-maintained hyponychium contributes to a clean, well-groomed appearance. Conversely, a damaged or infected hyponychium can detract from the appearance of your nails.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Nail Health
The hyponychium, although often overlooked, is a crucial component of the nail unit. Its role in protecting against infection and promoting healthy nail growth cannot be overstated. By understanding its anatomy, function, and potential problems, and by practicing good hygiene and nail care techniques, you can maintain a healthy hyponychium and enjoy strong, beautiful nails for years to come. Remember, if you experience any concerns about your hyponychium or nails, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention is key to preventing serious complications. Taking care of this often-ignored area ensures the health and beauty of your nails.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Group Life Insurance Policies Are Generally Written As Quizlet
Mar 24, 2025
-
Which Action Is The Function Of Antidiuretic Hormone Quizlet
Mar 24, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True Of Compressed Urls Quizlet
Mar 24, 2025
-
What To The Slave Is The Fourth Of July Quizlet
Mar 24, 2025
-
Treatment With Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Quizlet
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Area Underneath The Nail Tip Is Called The . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
