The Body Mass Index Is Defined As ______.
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
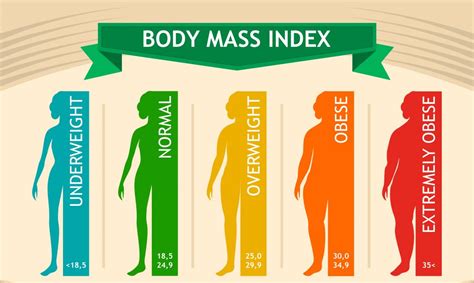
Table of Contents
The Body Mass Index (BMI) is Defined As: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding, Interpreting, and Utilizing This Key Health Metric
The Body Mass Index (BMI) is defined as a person's weight in kilograms divided by the square of their height in meters. While seemingly simple, this seemingly simple calculation provides a valuable, albeit imperfect, tool for assessing weight status and associated health risks. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the definition, interpretation, limitations, and applications of BMI, clarifying its role in maintaining overall well-being.
What is BMI and How is it Calculated?
The fundamental definition of BMI remains consistent: weight (kg) / height (m)². This formula provides a numerical value that categorizes individuals into weight classifications: underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obese. While the calculation itself is straightforward, understanding its implications and limitations is crucial for accurate interpretation.
Several online calculators and apps readily perform this calculation, removing the need for manual computation. However, knowing the formula empowers you to understand the underlying principles and appreciate the nuances of this essential health metric. Remember to use metric units (kilograms and meters) for accurate results.
Understanding BMI Classifications: A Categorical Breakdown
The World Health Organization (WHO) and other leading health organizations use BMI classifications to define weight categories and associated health risks. These categories are typically as follows:
-
Underweight: A BMI below 18.5 kg/m² generally indicates underweight. This can signal malnutrition or underlying health issues, potentially impacting immune function and overall health.
-
Normal Weight: A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 kg/m² falls within the normal weight range, generally associated with lower health risks compared to higher BMI categories.
-
Overweight: A BMI between 25.0 and 29.9 kg/m² indicates overweight. Individuals in this category often have a higher risk of developing weight-related health problems such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer.
-
Obesity: A BMI of 30.0 kg/m² or higher classifies individuals as obese. Obesity significantly increases the risk of numerous serious health complications, making weight management crucial in this category. Obesity is further categorized into Class I (30.0-34.9 kg/m²), Class II (35.0-39.9 kg/m²), and Class III (40.0 kg/m² and above, also known as morbid obesity).
Beyond the Numbers: The Limitations of BMI
While BMI serves as a valuable screening tool, it's crucial to acknowledge its limitations. BMI doesn't directly measure body fat percentage; it's an indirect estimation. This means that highly muscular individuals, athletes for instance, might have a high BMI despite having low body fat. Their elevated BMI is due to muscle mass, not excess fat.
Similarly, individuals with low muscle mass and high body fat might have a BMI that underestimates their true health risk. Older adults, for example, may experience muscle loss with age, resulting in a BMI that may not accurately reflect their body composition. This highlights the need for additional assessments beyond just BMI.
Other limitations of BMI include:
-
It doesn't differentiate between body fat distribution: Abdominal fat (visceral fat) poses a greater health risk than fat stored in other areas. BMI doesn't account for this crucial distinction.
-
It doesn't consider ethnicity or gender differences: Different ethnic groups and genders may have varying BMI thresholds for health risks.
-
It's not suitable for all age groups: BMI is less accurate for children, adolescents, and older adults due to developmental and age-related changes in body composition.
Complementary Assessments: A Holistic Approach to Health
Due to BMI's limitations, health professionals often use complementary assessments to gain a more comprehensive understanding of an individual's health status. These include:
-
Waist Circumference: Measuring waist circumference provides an indication of abdominal fat accumulation, a key indicator of cardiovascular risk.
-
Body Fat Percentage: Methods such as DEXA scans, underwater weighing, and bioelectrical impedance analysis offer more precise measurements of body fat composition.
-
Health History and Lifestyle Factors: A comprehensive assessment also considers factors such as family history, diet, physical activity levels, smoking habits, and overall lifestyle.
Using BMI Effectively: Interpreting Results and Taking Action
While BMI has limitations, understanding its value within a broader context of health assessment is essential. It serves as a screening tool, not a definitive diagnosis. If your BMI falls outside the healthy range, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional.
They can conduct a thorough evaluation, considering your individual factors and using complementary assessments to determine your health risks and recommend appropriate interventions. These interventions might include:
-
Dietary changes: Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
-
Increased physical activity: Incorporating regular exercise into your routine, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.
-
Behavioral therapy: Addressing underlying behavioral patterns that contribute to unhealthy eating habits or sedentary lifestyles.
-
Medication: In some cases, medication might be necessary to address underlying health conditions or assist in weight management.
Conclusion: BMI as a Part of a Broader Picture
The Body Mass Index, defined as weight (kg) / height (m)², remains a widely used metric for assessing weight status. While it provides a valuable initial screening tool, its limitations necessitate a holistic approach to health assessment. BMI should be interpreted in conjunction with other measures, including waist circumference, body fat percentage, and an overall health evaluation. Using BMI responsibly, combined with a thorough health assessment and a commitment to a healthy lifestyle, empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their well-being. Remember, focusing solely on a number doesn't define health; overall well-being involves various contributing factors. Consult a healthcare professional to receive personalized guidance and support in achieving your health goals. Your health journey is unique, and a tailored approach is crucial for sustainable success.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
These Cards Will Get You Drunk Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Did Quizlet Get Rid Of Q Chat
Mar 18, 2025
-
Myasthenia Gravis Is An Autoimmune Disease In Which Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Fun Sex Questions For Couples Quizlet With Answers
Mar 18, 2025
-
Crack Is Regarded As More Addictive Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Body Mass Index Is Defined As ______. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
