The Core Of The Sun Is Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
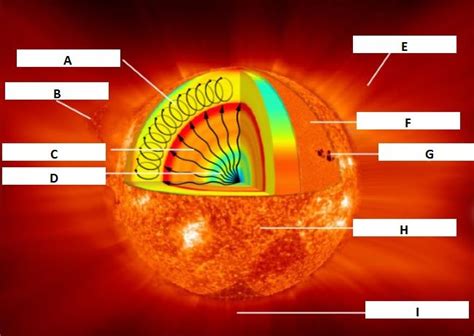
Table of Contents
Delving into the Core of the Sun: A Comprehensive Guide
The Sun, our nearest star, is a captivating celestial body that has fascinated humankind for millennia. Understanding its inner workings, especially the enigmatic core, is crucial to comprehending not only the Sun's behavior but also the formation and evolution of stars in general. This in-depth exploration will delve into the Sun's core, examining its composition, processes, and significance. We’ll go beyond a simple quizlet-style overview, offering a richer, more nuanced understanding of this crucial region.
The Sun's Core: A Furnace of Nuclear Fusion
The Sun's core, occupying the innermost 25% of its radius, is the powerhouse driving all solar activity. It's a region of extreme pressure and temperature, where nuclear fusion converts hydrogen into helium, releasing vast amounts of energy in the process. This energy, generated deep within the core, slowly makes its way to the Sun's surface, ultimately radiating outwards as light and heat that sustains life on Earth.
Temperature and Pressure: The Crucial Ingredients
The core's temperature is estimated to be around 15 million degrees Celsius (27 million degrees Fahrenheit). This extreme heat is necessary to overcome the electrostatic repulsion between hydrogen nuclei (protons), allowing them to get close enough for the strong nuclear force to bind them together. The pressure in the core is equally immense, reaching approximately 250 billion times the Earth's atmospheric pressure. This immense pressure is crucial in confining the plasma and facilitating the nuclear fusion reactions.
Nuclear Fusion: The Engine of the Sun
The dominant process in the Sun's core is the proton-proton chain reaction (pp-chain). This is a series of nuclear reactions where four protons (hydrogen nuclei) fuse to form a helium nucleus (alpha particle), releasing energy in the form of gamma rays, neutrinos, and positrons.
- Step 1: Two protons fuse to form deuterium. One proton transforms into a neutron, emitting a positron (anti-electron) and a neutrino. This step is relatively slow, forming the bottleneck of the pp-chain reaction.
- Step 2: Deuterium fuses with another proton to form helium-3. This step happens much faster than the first.
- Step 3: Two helium-3 nuclei fuse to form helium-4 (alpha particle). This releases two protons, completing the cycle.
While the pp-chain is the primary process, there are also other less dominant fusion reactions occurring, contributing to the overall energy production.
Energy Transport: A Slow Journey to the Surface
The energy generated in the core doesn't escape directly. It's transported outwards through two primary mechanisms:
- Radiative Zone: The energy from the core initially travels through the radiative zone, a vast region where gamma rays are repeatedly absorbed and re-emitted by the plasma. This process is extremely slow, taking hundreds of thousands of years for the energy to traverse this zone.
- Convective Zone: In the outermost layer of the Sun's interior, the convective zone, energy transport switches from radiative to convective. Hot plasma rises to the surface, cools, and sinks back down, creating a churning motion that carries the energy outward much more efficiently.
The Sun's Core and its Impact on the Solar System
The Sun's core is not just a local phenomenon; its activity has profound implications for the entire solar system.
Solar Neutrinos: Messengers from the Core
Neutrinos, nearly massless particles produced during nuclear fusion, stream directly from the core through the Sun and escape into space. Detecting these neutrinos provides invaluable information about the processes occurring deep within the Sun's core, offering a unique "window" into this otherwise inaccessible region. The detection of solar neutrinos has been a cornerstone of verifying our understanding of the Sun's core processes and confirming the pp-chain reaction.
Solar Wind: A Constant Outflow of Particles
The energy generated in the core ultimately drives the solar wind, a continuous stream of charged particles flowing outward from the Sun. The solar wind interacts with planetary magnetospheres, shaping them and creating spectacular auroras near the poles of planets like Earth. Variations in solar activity, rooted in the core's energy production, can influence the intensity and behavior of the solar wind, impacting space weather and potentially affecting technology on Earth.
Solar Flares and Coronal Mass Ejections: Powerful Events
While the core's energy production is relatively stable, it fuels the dynamic activity observed on the Sun's surface, including solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs). These powerful events release enormous amounts of energy and can disrupt Earth's magnetosphere, causing geomagnetic storms that affect satellites, power grids, and communication systems. Although these events originate on the surface, they are ultimately driven by the energy generated in the Sun's core.
Studying the Sun's Core: Challenges and Techniques
Studying the Sun's core presents significant challenges due to its inaccessibility. However, scientists have developed sophisticated techniques to indirectly probe its properties.
Helioseismology: Studying the Sun's Vibrations
Helioseismology is a powerful technique that uses observations of the Sun's surface oscillations to infer the properties of its interior. These oscillations, analogous to seismic waves on Earth, provide information about the Sun's internal structure, composition, and rotation. By analyzing the frequencies and patterns of these waves, scientists can build detailed models of the Sun's core.
Neutrino Detection: A Direct Probe
Neutrino detection provides a direct way to study the Sun's core. Although neutrinos interact very weakly with matter, large detectors have been built to capture a small fraction of the neutrinos streaming from the Sun. The properties of these detected neutrinos provide crucial information about the nuclear reactions occurring in the core.
Computer Modeling: Simulating the Sun's Interior
Sophisticated computer models are used to simulate the Sun's internal structure and processes. These models incorporate our current understanding of physics and are constantly being refined to improve their accuracy and predictive power. These models are vital in testing our theories about the Sun's core and in predicting its future evolution.
The Future of Sun's Core Research
The study of the Sun's core is an ongoing field of research. Future advancements in technology and theoretical understanding are expected to further refine our knowledge of this crucial region.
Advanced Neutrino Detectors: Enhanced Sensitivity
Future generations of neutrino detectors are expected to provide even more precise measurements of solar neutrinos, enhancing our understanding of the nuclear reactions in the Sun's core. These detectors will be larger and more sensitive, allowing for the detection of rarer neutrino events.
Improved Computer Models: Greater Accuracy
Ongoing developments in computational power and numerical techniques will lead to more sophisticated and accurate computer models of the Sun's interior. These models will incorporate more detailed physics and better account for uncertainties in the input parameters.
Space-Based Observatories: Uninterrupted Views
Future space-based observatories will provide uninterrupted views of the Sun, allowing for continuous monitoring of its activity and oscillations. These observations will provide a wealth of data for helioseismology studies and other research efforts.
Conclusion: The Core's Enduring Mystery
The Sun's core remains a subject of intense scientific interest, despite decades of research. Its extreme conditions and inaccessible nature pose considerable challenges to direct observation. However, through innovative techniques like helioseismology, neutrino detection, and sophisticated computer modeling, scientists continue to unravel the mysteries of this celestial powerhouse. A deeper understanding of the Sun's core is not merely an academic pursuit; it is fundamental to our comprehension of stellar evolution, the formation of planetary systems, and the dynamics of our own solar system. The research continues, pushing the boundaries of our knowledge and illuminating the fascinating workings of the Sun’s heart.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Statements Is True Of A Database
Mar 25, 2025
-
A Melodic Line That Moves By Small Intervals Is Called
Mar 25, 2025
-
Drug Abuse Can Often Lead To Suicide Because
Mar 25, 2025
-
Traffic School Final Exam Answers California 2024
Mar 25, 2025
-
The Data Selected To Create A Table Must Include
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Core Of The Sun Is Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
