The Difference Between Respiratory Droplets And Airborne Transmission Is ______.
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
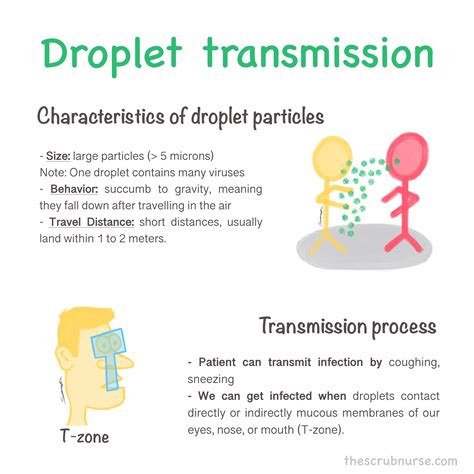
Table of Contents
The Difference Between Respiratory Droplets and Airborne Transmission Is…Complex
The seemingly simple question of how respiratory viruses spread – via droplets or airborne transmission – is actually surprisingly complex. While the terms are often used interchangeably, understanding the key differences is crucial for effective infection control and public health strategies. The difference between respiratory droplets and airborne transmission isn't a simple binary; it's a spectrum of particle sizes and behaviors, influenced by numerous factors.
Understanding Respiratory Droplets
Respiratory droplets are large, relatively heavy particles produced when an infected individual coughs, sneezes, talks, sings, or breathes. These droplets typically range in size from 5 to 10 micrometers (µm) and larger. Due to their size and weight, they generally travel only short distances (typically less than 1 meter) before falling to the ground due to gravity. Think of them like raindrops – they’re visible, and they don't stay suspended in the air for long.
Characteristics of Respiratory Droplets:
- Size: >5 µm
- Travel Distance: Short (generally <1 meter)
- Duration in Air: Brief (seconds to minutes)
- Transmission Mode: Primarily through close contact (within 1-2 meters)
- Examples: Sneezing, coughing forcefully
Understanding Airborne Transmission
Airborne transmission, on the other hand, refers to the spread of respiratory viruses through smaller, lighter particles that can remain suspended in the air for extended periods and travel longer distances. These particles are typically less than 5 µm in diameter, often referred to as droplet nuclei or aerosols. Unlike larger droplets that fall quickly, these tiny particles can remain airborne for hours, circulating in the air and potentially infecting individuals far from the source.
Characteristics of Airborne Transmission:
- Size: <5 µm
- Travel Distance: Long (meters to kilometers, depending on ventilation)
- Duration in Air: Prolonged (hours)
- Transmission Mode: Inhalation of suspended particles
- Examples: Prolonged periods of close contact in poorly ventilated areas, long-range transmission in specific settings
The Overlap and the Spectrum: It's Not Always Black and White
The distinction between droplets and airborne transmission isn't always clear-cut. Many respiratory viruses, including those that cause influenza and COVID-19, exhibit transmission characteristics that fall on a spectrum. Initially released as larger droplets, these droplets can evaporate, leaving behind smaller droplet nuclei that can remain airborne. This process, known as droplet nuclei formation, is influenced by factors such as humidity, temperature, and ventilation.
The initial expulsion might be predominantly through larger droplets, but a significant portion of the virus can then become airborne through this evaporation process. This means that while close-contact transmission is a major factor, airborne transmission can also play a significant role, especially in poorly ventilated indoor spaces.
Factors Influencing Transmission: A Complex Interplay
Several factors influence whether a virus spreads primarily through droplets, airborne transmission, or a combination of both:
- Virus characteristics: The size of the virus itself plays a role. Smaller viruses are more likely to remain airborne for longer periods. The virus's ability to survive outside the host also matters.
- Environmental factors: Humidity, temperature, and ventilation significantly impact droplet evaporation and particle suspension. Dry, poorly ventilated environments favor airborne transmission. Conversely, high humidity can increase the size and weight of droplets, reducing airborne spread.
- Infectious dose: The number of viral particles required to cause infection influences transmission. A virus with a lower infectious dose can spread more readily through airborne transmission, even with a lower concentration of particles in the air.
- Duration and intensity of exposure: Longer exposures, particularly to high concentrations of viral particles (whether droplets or airborne), increase the risk of infection.
- Source control measures: Measures like mask-wearing and hand hygiene primarily mitigate droplet transmission, while improved ventilation and air filtration systems help reduce airborne transmission.
The Significance of Understanding the Difference: Implications for Infection Control
Distinguishing between droplet and airborne transmission is not just an academic exercise. It has significant implications for developing effective infection control strategies.
Droplet precautions:
These focus on preventing the spread of larger droplets through:
- Hand hygiene: Frequent and thorough hand washing.
- Respiratory hygiene: Covering coughs and sneezes.
- Physical distancing: Maintaining a safe distance from infected individuals.
- Environmental cleaning: Regularly disinfecting surfaces.
Airborne precautions:
These are more stringent and involve measures to reduce airborne transmission, including:
- Improved ventilation: Increasing airflow and air exchange in indoor spaces.
- Air filtration: Utilizing HEPA filters to remove airborne particles.
- Negative pressure rooms: Isolating infected individuals in rooms with airflow designed to prevent the spread of airborne contaminants.
- Respiratory protection: Using N95 or higher-level respirators to protect healthcare workers and potentially susceptible individuals.
Case Studies: Illustrating the Spectrum
Many viral outbreaks have highlighted the complex nature of respiratory virus transmission. For instance, the initial understanding of COVID-19 transmission primarily focused on droplet spread, but subsequent research revealed the significant role of airborne transmission, particularly in poorly ventilated indoor settings. This understanding led to significant changes in public health guidelines, including recommendations for improved ventilation, air filtration, and the widespread use of masks.
Similarly, outbreaks of measles, tuberculosis, and chickenpox have demonstrated the importance of airborne transmission in their spread. These viruses produce smaller particles that can remain suspended in the air for extended periods, leading to broader transmission than viruses primarily spread through larger droplets.
The Future of Respiratory Virus Research: Continuous Learning
The field of respiratory virus transmission is constantly evolving. Advanced technologies such as real-time PCR and high-resolution imaging are providing increasingly detailed insights into the size, behavior, and spread of respiratory particles. This research will continue to refine our understanding of the nuanced differences between droplet and airborne transmission and inform the development of more effective infection control measures. This allows for more targeted interventions and a more comprehensive approach to protecting public health. The lines are blurry, and understanding that blurriness is critical.
Conclusion: A Spectrum of Risk
The difference between respiratory droplets and airborne transmission isn't a simple dichotomy. It's a spectrum of particle sizes and behaviors influenced by a multitude of factors. Understanding this spectrum is crucial for developing comprehensive infection control strategies that account for both close-contact and long-range transmission. Effective strategies involve a layered approach, combining droplet and airborne precautions to minimize the risk of infection. Continuous research and a nuanced understanding of transmission dynamics are vital for protecting public health against respiratory viruses.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Is Not A Form Of Maltreatment
Mar 18, 2025
-
If An Individual Is Heterozygous For A Particular Trait
Mar 18, 2025
-
If You Add More Enzyme The Reaction Will
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Purpose Of A Hazcom Program Is To Ensure That
Mar 18, 2025
-
Describe The Continuous Nature Of The Physical Fitness Concept
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Difference Between Respiratory Droplets And Airborne Transmission Is ______. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
