The Following Are Common With Otitis Media Except
Breaking News Today
Mar 27, 2025 · 5 min read
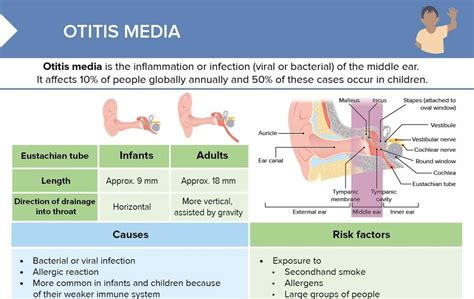
Table of Contents
What is Otitis Media? Understanding the Common Symptoms and Exclusions
Otitis media, commonly known as a middle ear infection, is a prevalent ailment, particularly among young children. It's characterized by inflammation or infection of the middle ear, the air-filled space behind the eardrum. Understanding the common symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment, but equally important is knowing what isn't typically associated with otitis media. This article will delve into the typical symptoms of otitis media, highlighting what conditions are not usually present, ensuring a clear understanding of this common ear infection.
Common Symptoms of Otitis Media
Several key symptoms strongly suggest the presence of otitis media. These are frequently observed in patients of all ages, although the presentation might differ slightly. The symptoms can range in severity from mild discomfort to severe pain and complications.
1. Earache (Otalgia):
This is often the most prominent symptom, presenting as sharp, throbbing pain in the affected ear. The pain can be intense, particularly in acute otitis media, and may worsen at night or when lying down. Infants and young children may exhibit fussiness, pulling at their ears, or difficulty sleeping due to the discomfort.
2. Fever:
Fever is a common systemic response to infection. In otitis media, a fever is frequently observed, particularly in younger children. The fever's severity can vary depending on the severity of the infection, ranging from mild to high fevers. It's essential to monitor the fever closely and seek medical attention if it's persistently high or accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
3. Hearing Loss:
Fluid buildup in the middle ear, a hallmark of otitis media, can temporarily impair hearing. This hearing loss can range from mild to moderate and may cause muffled sounds or difficulty understanding speech. The degree of hearing loss usually correlates with the amount of fluid present. Once the infection resolves and the fluid drains, hearing usually returns to normal.
4. Feeling of Fullness or Pressure in the Ear:
Patients often describe a sensation of fullness or pressure in the affected ear. This is due to the fluid accumulating behind the eardrum. This feeling can be uncomfortable and may be accompanied by a popping or crackling sound in the ear.
5. Drainage from the Ear (Otorrhea):
If the eardrum ruptures (perforates) due to the pressure from the infection, fluid may drain from the ear. This drainage can be clear, yellowish, or even bloody. While drainage indicates a potential complication, it can also signal that the pressure is relieving. It’s crucial to seek medical attention if ear drainage is present.
6. Irritability and Fussiness (especially in infants and young children):
Infants and young children may not be able to verbally express their ear pain. Instead, they might display increased irritability, fussiness, or difficulty sleeping. Changes in behavior should be closely monitored and evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Conditions NOT Usually Associated with Otitis Media
While the above symptoms strongly suggest otitis media, certain conditions are generally not typical findings. These exclusions are important for differential diagnosis and to avoid misinterpretations.
1. Severe Headache:
While discomfort is common, a severe, persistent headache is usually not a characteristic symptom of otitis media. Severe headaches could indicate other underlying conditions requiring different medical attention.
2. Neck Stiffness and Meningism:
Stiffness in the neck, along with other meningeal signs like photophobia (sensitivity to light) and nuchal rigidity (resistance to passive neck flexion), are not typical of otitis media and may signal serious conditions like meningitis, requiring urgent medical intervention.
3. Facial Paralysis (Bell's Palsy):
Facial weakness or paralysis is not a usual presentation of otitis media. Facial paralysis suggests a different neurological problem and necessitates a thorough neurological evaluation.
4. Significant Vertigo or Dizziness:
While some mild dizziness might occasionally be reported, severe, persistent vertigo (a sensation of spinning) is not a typical symptom of otitis media. Vertigo often suggests problems with the inner ear or vestibular system.
5. Severe Vision Changes:
Significant changes in vision are not usually associated with otitis media. Vision problems typically indicate a different underlying condition affecting the eyes.
6. Respiratory Distress:
Difficulty breathing (dyspnea) or respiratory distress is not typically associated with uncomplicated otitis media. These symptoms warrant immediate medical evaluation and could indicate a separate respiratory illness.
7. High Fever lasting for an extended period (>72 hours) without other symptoms:
While fever is common, a prolonged high fever without other associated symptoms of otitis media should prompt a thorough investigation into other potential causes.
Differential Diagnosis: Considering Other Possibilities
It's crucial to remember that several other conditions can mimic the symptoms of otitis media. A proper diagnosis necessitates a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. Some conditions to consider in the differential diagnosis include:
- Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Dysfunction: TMJ problems can cause ear pain that might be mistaken for otitis media.
- Dental Infections: Infections in the teeth or gums can sometimes refer pain to the ear.
- Sinusitis: Sinus infections can also present with ear pain and pressure.
- Neuralgia (e.g., Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia): Certain types of nerve pain can mimic ear pain.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial for otitis media. You should seek medical attention if:
- Your child is less than 6 months old and has symptoms suggesting otitis media.
- The ear pain is severe or persistent.
- The fever is high or persistent (lasting more than 72 hours).
- There is drainage from the ear.
- Your child exhibits significant hearing loss or changes in behavior.
- You notice any of the symptoms described above that are not typically associated with otitis media.
Conclusion: Understanding the Complete Picture of Otitis Media
Otitis media is a common ear infection with characteristic symptoms like earache, fever, and hearing loss. However, it's equally important to be aware of the symptoms not usually associated with this condition. By understanding both the common presentations and the exclusions, individuals can better identify potential otitis media and differentiate it from other conditions requiring alternative medical approaches. Always consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment if you suspect otitis media or experience concerning ear symptoms. Early intervention can prevent potential complications and ensure a swift recovery. Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Match Each Term With The Best Description
Mar 30, 2025
-
Its Recommended That Those With Osteoporosis
Mar 30, 2025
-
Monique Was Highly Regarded By Ther Customer In The Baker
Mar 30, 2025
-
2 1 6 Energy And Matter In The Biosphere Apex
Mar 30, 2025
-
Which Test Helps Id Reproductive Tract Fibroids Tumors And Fistulas
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Following Are Common With Otitis Media Except . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
