The Gramm-leach-bliley Act Was Passed To Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
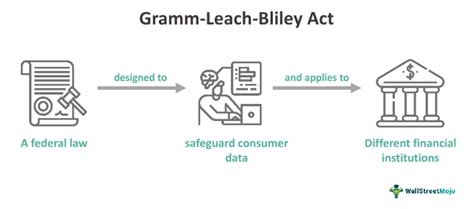
Table of Contents
The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA): A Comprehensive Guide
The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA), also known as the Financial Services Modernization Act of 1999, significantly reshaped the financial services industry in the United States. Its passage marked a pivotal moment, altering the landscape of how financial institutions operate and interact with customer data. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the GLBA, exploring its key provisions, implications, and ongoing relevance in today's digital age.
What is the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act?
The GLBA's primary aim was to modernize the financial services industry by repealing parts of the Glass-Steagall Act of 1933. This earlier legislation had created a strict separation between commercial banks, investment banks, and insurance companies. The GLBA allowed for financial conglomerates, enabling these different entities to merge and offer a wider range of financial products and services under one roof. However, this deregulation came with a crucial caveat: enhanced consumer protection regarding the privacy of financial information.
This dual mandate – deregulation and enhanced privacy – lies at the heart of the GLBA's complexity and enduring importance. The act is not a single, monolithic piece of legislation but rather a collection of interconnected provisions that address different aspects of financial services and data privacy.
Key Provisions of the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act
The GLBA is structured around three main components:
1. The Financial Privacy Rule: This is arguably the most crucial part of the GLBA, focusing directly on protecting consumer financial information. It mandates that financial institutions provide clear and concise privacy notices to their customers, detailing how their nonpublic personal information (NPI) will be collected, used, and shared. This NPI encompasses a wide range of data, including:
- Social Security numbers
- Account balances
- Transaction history
- Credit information
- Address and contact details
Financial institutions must also give customers the opportunity to opt out of sharing their information with non-affiliated third parties for marketing purposes. This opt-out provision is a significant consumer protection mechanism, giving individuals control over how their sensitive data is utilized. The rule also includes stringent requirements for the safeguarding of customer information, emphasizing the importance of security measures to prevent unauthorized access and disclosure.
2. The Pretexting Protection Rule: This provision specifically addresses the illegal practice of "pretexting," which involves obtaining someone's NPI under false pretenses. The GLBA makes it a federal crime to use deceptive means to access someone's financial information. This has proven particularly important in protecting consumers from identity theft and fraud. The penalties for pretexting violations can be substantial, acting as a strong deterrent. This highlights the GLBA's commitment to not only safeguarding data but also prosecuting those who attempt to exploit vulnerabilities.
3. The Safeguards Rule: Recognizing the increasing reliance on technology within the financial services sector, the Safeguards Rule focuses on the security of customer information. It mandates that financial institutions implement reasonable administrative, technical, and physical safeguards to protect customer data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. These safeguards should be appropriate to the size and complexity of the institution and the sensitivity of the data involved. This aspect emphasizes the ongoing responsibility of institutions to adapt their security measures to the ever-evolving threat landscape. It's not a one-time implementation but an ongoing process of review and improvement.
Implications of the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act
The GLBA has had far-reaching implications across the financial services industry, impacting how businesses operate and interact with their customers. Some of the key implications include:
-
Increased regulatory compliance costs: Implementing and maintaining compliance with the GLBA's provisions, particularly the privacy and safeguards rules, has added significant costs for financial institutions. This includes investing in security infrastructure, developing robust data management systems, and training personnel on compliance requirements.
-
Enhanced consumer awareness of data privacy: The GLBA has significantly raised consumer awareness of data privacy issues and their rights regarding financial information. This has led to greater scrutiny of financial institutions' data handling practices and increased expectations for transparency and accountability.
-
Improved data security practices: While compliance costs are high, the GLBA has driven improvements in data security practices across the financial sector. Institutions are now more proactive in implementing and maintaining robust security measures to protect customer information from cyber threats and other vulnerabilities.
-
Shifting industry landscape: The deregulation aspects of the GLBA have resulted in a more consolidated and diversified financial services industry, with larger institutions offering a broader range of products and services.
-
Legal ramifications for non-compliance: The GLBA carries significant penalties for non-compliance, including hefty fines and potential legal action. This underscores the importance of robust compliance programs and ongoing monitoring of regulatory changes. The potential consequences motivate institutions to prioritize compliance.
The GLBA in the Digital Age
The GLBA's relevance has only grown stronger in the digital age, with the increasing use of technology and the rise of cyber threats. The Safeguards Rule, in particular, has taken on heightened significance. The explosion of online banking, mobile payments, and big data analytics necessitates a continuous evaluation and adaptation of security protocols. The ever-evolving nature of cyber threats demands ongoing vigilance and investment in robust security measures.
Moreover, the growing awareness of data privacy concerns among consumers necessitates a transparent and responsible approach to data handling. Institutions need to ensure they are not only meeting the minimum compliance requirements but also exceeding expectations in terms of transparency, accountability, and consumer empowerment. This includes proactively informing customers about data breaches and taking swift action to mitigate potential damage.
Future of the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act
The GLBA remains a cornerstone of financial regulation in the US. While its original intent was to modernize the financial sector, its impact on data privacy has proved enduring and increasingly significant. However, as the technological landscape continues to shift, the need for adaptation and refinement of the GLBA will likely persist. This may involve:
-
Addressing new technologies: The GLBA may need to be updated to encompass emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain, which present both opportunities and challenges in terms of data privacy and security.
-
Enhanced enforcement mechanisms: Strengthening the enforcement mechanisms associated with the GLBA could further deter non-compliance and ensure accountability.
-
Balancing innovation with consumer protection: Maintaining a balance between fostering innovation in the financial sector and ensuring robust consumer protection will remain a key challenge.
-
International harmonization: As financial services become increasingly global, harmonizing data privacy regulations across different jurisdictions could streamline compliance efforts and improve cross-border data flows.
The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, despite its complexity and challenges, remains a vital piece of legislation safeguarding consumer financial data. Its ongoing relevance underscores the importance of data privacy in an increasingly digital world, emphasizing the need for continuous adaptation and a commitment to responsible data handling within the financial services industry. The act is not simply a regulatory framework; it's a testament to the ongoing need to protect consumer interests in the ever-evolving world of finance. Understanding the GLBA is not just a matter of compliance; it is crucial for responsible engagement within the financial landscape.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Periodic Reinvestigation Is Required For Continued Secret Clearance
Mar 24, 2025
-
If High Beam Headlights Are Used Improperly
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is An Effect Of Excessive Ventilation
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is The Relationship Between The Following Compounds
Mar 24, 2025
-
Capitals Of Europe Geography Worksheet Answer Key
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Gramm-leach-bliley Act Was Passed To Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
