The Most Significant Threat To Food Safety Is From
Breaking News Today
Mar 12, 2025 · 5 min read
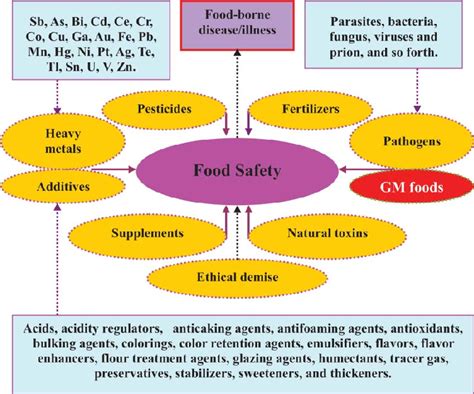
Table of Contents
The Most Significant Threat to Food Safety Is From… Microbial Contamination
Food safety is paramount to public health. A seemingly innocuous meal can quickly turn into a harrowing experience if contaminated. While various factors contribute to foodborne illnesses, microbial contamination remains the most significant threat. This encompasses bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi that can proliferate in food products, leading to a wide range of illnesses, from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions. This comprehensive article will delve into the specifics of this pervasive threat, exploring its various facets and highlighting preventive measures.
The Scope of Microbial Contamination: A Global Concern
Microbial contamination is a global issue affecting both developed and developing nations, transcending geographical boundaries and socioeconomic strata. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates millions of people worldwide suffer from foodborne diseases annually, resulting in substantial economic losses and a significant burden on healthcare systems. The impact extends beyond immediate illness, encompassing long-term health complications and even mortality in severe cases.
The Leading Culprits: Bacteria, Viruses, Parasites, and Fungi
Several microorganisms pose significant risks to food safety. Understanding their characteristics and modes of transmission is crucial for effective prevention:
-
Bacteria: These single-celled organisms are prolific in diverse environments. Examples include Salmonella, E. coli, Listeria monocytogenes, and Campylobacter, each causing unique symptoms and varying levels of severity. These bacteria can contaminate food through various stages, from production to consumption. Improper cooking, inadequate refrigeration, and cross-contamination are major contributing factors.
-
Viruses: Unlike bacteria, viruses are significantly smaller and require a host organism to replicate. Norovirus and Hepatitis A are frequently transmitted through contaminated food and water. These viruses are highly contagious, even in small amounts, leading to widespread outbreaks. Shellfish, particularly oysters, are often implicated in viral contamination.
-
Parasites: These organisms rely on a host for survival and nourishment. Toxoplasma gondii, found in undercooked meat, and various intestinal parasites are significant concerns. Parasites can cause a range of symptoms, some chronic and debilitating. Proper cooking and thorough handwashing are vital preventative measures.
-
Fungi: Molds and yeasts, belonging to the fungal kingdom, can contaminate food and produce toxins called mycotoxins. These toxins can be incredibly harmful, causing various illnesses, including liver damage and cancer. Aflatoxins, produced by certain Aspergillus molds, are particularly dangerous and often found in grains and nuts.
The Stages of Contamination: From Farm to Fork
Microbial contamination can occur at any stage of the food chain, highlighting the need for stringent safety protocols throughout the entire process.
1. Production Stage: On the Farm and in the Field
Contamination can begin at the source – on the farm or during harvesting. Animal feces, contaminated water, and soil can introduce pathogens into produce and livestock. Poor hygienic practices by farm workers, including inadequate handwashing and sanitation, further exacerbate the risk.
2. Processing and Manufacturing: A Critical Control Point
Food processing and manufacturing plants require rigorous hygiene and safety standards. Cross-contamination between different food items is a major concern, as are inadequate cleaning and sanitization procedures. Equipment malfunction or improper maintenance can also lead to contamination.
3. Distribution and Transportation: Maintaining the Cold Chain
Maintaining the cold chain – the uninterrupted refrigeration of perishable foods – is essential to prevent bacterial growth. Breaks in the cold chain during transportation can dramatically increase the risk of contamination and spoilage.
4. Retail and Food Service: Handling and Preparation
Retail establishments and food service operations play a crucial role in maintaining food safety. Proper storage, handling, and preparation are essential to prevent contamination. Cross-contamination between raw and cooked foods is a frequent cause of foodborne illnesses in restaurants and kitchens.
5. Consumption: The Final Hurdle
Even with meticulous care at previous stages, improper handling and preparation at home can compromise food safety. Inadequate cooking, improper reheating, and cross-contamination during food preparation are all potential sources of contamination at the consumption stage.
Factors Influencing Microbial Growth: The Perfect Storm
Several factors contribute to the growth and proliferation of microorganisms in food:
-
Temperature: The "danger zone" – temperatures between 40°F (4°C) and 140°F (60°C) – is ideal for bacterial growth. Maintaining proper refrigeration and cooking temperatures is crucial.
-
Moisture: Microorganisms require moisture to thrive. Reducing water activity (aw) through methods like drying or salting inhibits their growth.
-
pH: The acidity or alkalinity of food influences microbial growth. Low pH (acidic) environments generally inhibit bacterial growth, while high pH (alkaline) environments can promote it.
-
Oxygen: Some microorganisms require oxygen (aerobic) to grow, while others thrive in oxygen-free environments (anaerobic). Packaging techniques can control oxygen levels to inhibit microbial growth.
-
Nutrients: The nutritional content of food provides the energy source for microbial growth. Foods rich in nutrients are more susceptible to contamination.
Preventing Microbial Contamination: A Multifaceted Approach
Preventing microbial contamination requires a comprehensive and integrated approach, involving various stakeholders along the entire food chain:
-
Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs): Implementing GAPs on farms ensures safe production practices, minimizing the risk of contamination at the source.
-
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs): GMPs ensure hygienic manufacturing processes in food processing plants, minimizing cross-contamination and promoting food safety.
-
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP): HACCP is a systematic approach to identifying and controlling hazards throughout the food production process.
-
Proper Food Handling and Storage: Maintaining proper refrigeration temperatures, avoiding cross-contamination, and practicing safe food handling techniques at home are crucial.
-
Effective Sanitation and Hygiene: Thorough cleaning and sanitization of food preparation surfaces and equipment are critical in preventing contamination.
-
Education and Awareness: Educating consumers, food handlers, and food producers about food safety practices is essential to minimize risks.
The Future of Food Safety: Technology and Innovation
Technological advancements are continually improving food safety practices. Rapid detection methods for pathogens, improved packaging techniques, and innovative preservation methods are contributing to safer food supplies. Nanotechnology, genetic engineering, and artificial intelligence are also emerging as potential tools in the fight against microbial contamination.
Conclusion: A Continuous Battle for Safety
Microbial contamination remains the most significant threat to food safety, impacting millions globally. While the challenges are considerable, a multi-pronged approach involving rigorous regulations, technological innovation, and public education is essential to minimize the risks and ensure a safe and secure food supply for all. The fight for food safety is an ongoing battle, requiring continuous vigilance and a commitment to the highest standards of hygiene and sanitation throughout the entire food chain. Only through such concerted efforts can we effectively mitigate this significant threat and protect public health.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Medication Aide Practice Test Questions And Answers
Mar 12, 2025
-
A Policyowners Rights Are Limited Under Which Beneficiary Designation
Mar 12, 2025
-
The Ticketing Area Is More Secure Than The Area Beyond
Mar 12, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Does Not Belong With The Others
Mar 12, 2025
-
Mary I Earned The Nickname Bloody Mary Because She
Mar 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Most Significant Threat To Food Safety Is From . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
