The Prime Mover Of Dorsiflexion Is The __________.
Breaking News Today
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
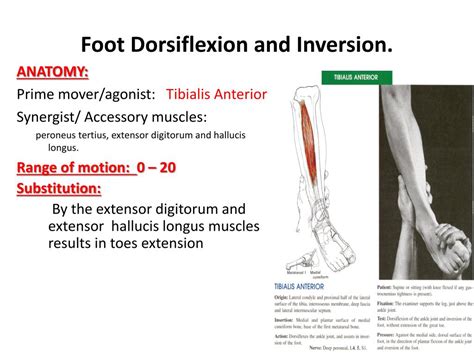
Table of Contents
- The Prime Mover Of Dorsiflexion Is The __________.
- Table of Contents
- The Prime Mover of Dorsiflexion is the Tibialis Anterior: A Deep Dive into Ankle Anatomy and Function
- Understanding Dorsiflexion: More Than Just Pointing Your Toes
- The Role of the Tibialis Anterior: The Prime Mover
- Synergistic Muscles: Supporting the Star Player
- 1. Extensor Hallucis Longus: Focusing on the Big Toe
- 2. Extensor Digitorum Longus: Extending the Toes and Assisting Dorsiflexion
- 3. Peroneus Tertius: A Lesser-Known Contributor
- Antagonistic Muscles: Maintaining Balance
- 1. Gastrocnemius: The Calf Muscle Powerhouse
- 2. Soleus: Deep and Powerful Plantar Flexor
- Clinical Significance and Dysfunction
- Rehabilitation and Strengthening: Restoring Ankle Function
- 1. Rest and Ice: Managing Inflammation
- 2. Physical Therapy: Targeted Exercises
- 3. Orthotics: Supporting the Ankle
- Maintaining Healthy Ankle Function: Prevention is Key
- Conclusion: The Tibialis Anterior - A Crucial Muscle
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Prime Mover of Dorsiflexion is the Tibialis Anterior: A Deep Dive into Ankle Anatomy and Function
The question, "The prime mover of dorsiflexion is the __________," has a straightforward answer: the tibialis anterior. However, understanding this simple statement requires a deeper exploration of the complex anatomy and biomechanics of the ankle joint. This article will delve into the intricacies of dorsiflexion, exploring the role of the tibialis anterior, its synergistic muscles, and the potential consequences of its dysfunction. We'll also touch upon relevant clinical considerations and rehabilitation strategies.
Understanding Dorsiflexion: More Than Just Pointing Your Toes
Dorsiflexion is one of the fundamental movements of the ankle joint. It refers to the movement of the foot upwards towards the shin, decreasing the angle between the foot and the leg. Imagine pulling your toes towards your knee; that's dorsiflexion. This seemingly simple movement is crucial for a range of activities, from walking and running to jumping and balancing. It allows us to adapt to uneven terrain, absorb shock, and maintain proper posture. Without efficient dorsiflexion, even basic locomotion becomes significantly compromised.
The Role of the Tibialis Anterior: The Prime Mover
While several muscles contribute to dorsiflexion, the tibialis anterior muscle reigns supreme as the prime mover. This means it is the muscle primarily responsible for initiating and controlling this movement. Originating on the lateral condyle and upper two-thirds of the tibia, it inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. Its strategic location and powerful structure allow for effective dorsiflexion, particularly against resistance.
Synergistic Muscles: Supporting the Star Player
The tibialis anterior doesn't work in isolation. Other muscles contribute to dorsiflexion, acting as synergists, supporting and enhancing the action of the prime mover. These include:
1. Extensor Hallucis Longus: Focusing on the Big Toe
The extensor hallucis longus primarily extends the big toe, but it also contributes to dorsiflexion of the ankle. Originating on the fibula and interosseous membrane, it inserts into the distal phalanx of the great toe. Its action complements the tibialis anterior, especially in activities requiring precise toe control.
2. Extensor Digitorum Longus: Extending the Toes and Assisting Dorsiflexion
The extensor digitorum longus extends the second to fifth toes, while also assisting in dorsiflexion. Originating on the lateral condyle of the tibia and fibula, it inserts into the distal phalanges of the lateral four toes. Its involvement in dorsiflexion is less significant than the tibialis anterior and extensor hallucis longus but still plays a supportive role.
3. Peroneus Tertius: A Lesser-Known Contributor
The peroneus tertius, a less prominent muscle, also contributes to dorsiflexion. Located in the lateral compartment of the leg, it originates on the distal fibula and inserts into the base of the fifth metatarsal. Its contribution is generally minor compared to the tibialis anterior and its synergistic counterparts.
Antagonistic Muscles: Maintaining Balance
Maintaining proper ankle function requires a delicate balance between agonists (muscles that produce a movement) and antagonists (muscles that oppose a movement). In the case of dorsiflexion, the primary antagonists are the plantar flexors, including the:
1. Gastrocnemius: The Calf Muscle Powerhouse
The gastrocnemius, the prominent calf muscle, is a major plantar flexor. Its powerful contraction pulls the foot downwards, opposing dorsiflexion. A proper balance between gastrocnemius and tibialis anterior is critical for smooth, efficient movement.
2. Soleus: Deep and Powerful Plantar Flexor
The soleus, located deep to the gastrocnemius, is another significant plantar flexor. It contributes significantly to plantar flexion and helps stabilize the ankle joint. Its interaction with the tibialis anterior is vital for maintaining postural stability.
Clinical Significance and Dysfunction
Weakness or injury to the tibialis anterior or its synergistic muscles can lead to significant functional limitations. Conditions such as:
- Tibialis anterior tendinitis: Inflammation of the tibialis anterior tendon, often caused by overuse or repetitive stress.
- Tibialis anterior strain: A muscle tear, ranging in severity from mild to complete rupture.
- Foot drop: A condition characterized by the inability to dorsiflex the foot, often caused by nerve damage or muscle weakness. This can lead to difficulties in walking and balance.
These conditions can significantly impact daily activities, requiring appropriate medical intervention and rehabilitation.
Rehabilitation and Strengthening: Restoring Ankle Function
Rehabilitation protocols for tibialis anterior dysfunction vary depending on the specific injury or condition. However, common strategies include:
1. Rest and Ice: Managing Inflammation
For acute injuries such as strains or tendinitis, rest and ice are crucial to manage inflammation and promote healing. Avoiding activities that aggravate the injury is essential.
2. Physical Therapy: Targeted Exercises
Physical therapy plays a vital role in restoring function and strength. Exercises may include:
- Dorsiflexion stretches: Gentle stretches to improve flexibility and range of motion.
- Tibialis anterior strengthening exercises: Exercises such as resisted dorsiflexion, toe raises, and ankle pumps to strengthen the muscle.
- Proprioceptive exercises: Exercises that improve balance and coordination to enhance ankle stability.
3. Orthotics: Supporting the Ankle
Orthotic devices, such as custom-made shoe inserts or ankle braces, can provide support and reduce stress on the tibialis anterior and other ankle structures.
Maintaining Healthy Ankle Function: Prevention is Key
Maintaining healthy ankle function involves:
- Proper footwear: Wearing supportive shoes that provide adequate cushioning and stability.
- Regular stretching and strengthening: Incorporating exercises that target the ankle muscles into a regular fitness routine.
- Avoiding overuse: Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of activities to avoid overloading the ankle muscles.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight increases stress on the ankle joints and muscles.
Conclusion: The Tibialis Anterior - A Crucial Muscle
The tibialis anterior muscle is unequivocally the prime mover of dorsiflexion. Understanding its role, its interaction with synergistic and antagonistic muscles, and potential consequences of its dysfunction is crucial for healthcare professionals and anyone interested in maintaining healthy ankle function. Through a combination of appropriate exercise, injury prevention, and timely medical intervention, individuals can safeguard the health and performance of this vital muscle, ensuring optimal mobility and quality of life. Remember, while the tibialis anterior is the key player, the entire ankle complex works in harmony to achieve efficient and coordinated movement. Maintaining this harmony is key to preventing injury and maximizing functional capabilities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Select The Right Order Of Enforcement Of Gpos
Mar 22, 2025
-
Letrs Unit 4 Session 7 Check For Understanding
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Did Minor White Desire His Photographs To Be
Mar 22, 2025
-
Intro To Radiologic And Imaging Sciences Chapter 24
Mar 22, 2025
-
A Partial Surrender Is Allowed In What Type Policy
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Prime Mover Of Dorsiflexion Is The __________. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
