The Production Process Is Part Of The
Breaking News Today
Mar 26, 2025 · 6 min read
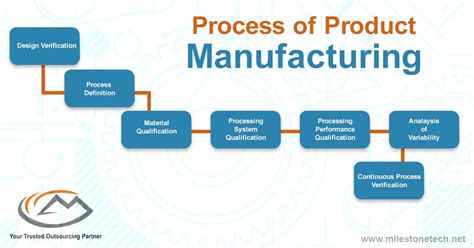
Table of Contents
The Production Process: A Critical Part of the Entire Business Ecosystem
The production process isn't just a series of steps; it's the lifeblood of any business that creates physical goods. From the initial concept to the final delivery, this intricate system directly impacts profitability, customer satisfaction, and overall market competitiveness. Understanding and optimizing this process is crucial for survival and growth in today's dynamic business environment. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the production process, exploring its various stages, key considerations, and the significant role it plays within the broader business ecosystem.
Understanding the Production Process: A Holistic View
The production process encompasses all activities involved in transforming raw materials or inputs into finished goods or services ready for sale. It's far more than just manufacturing; it's a complex interplay of planning, execution, and control, encompassing:
1. Planning and Design: The Foundation of Success
Before a single item is produced, meticulous planning lays the groundwork. This stage includes:
- Product Design and Development: Defining product specifications, features, and functionality. This requires thorough market research to understand customer needs and preferences, and competitor analysis to ensure a competitive advantage. Detailed blueprints, prototypes, and testing are critical elements.
- Process Design: Determining the most efficient and effective sequence of operations to manufacture the product. This involves selecting appropriate machinery, technology, and labor, optimizing workflow, and considering capacity planning to meet anticipated demand. Lean manufacturing principles are frequently applied here to minimize waste and maximize efficiency.
- Material Selection and Sourcing: Identifying and securing the necessary raw materials and components. Factors like cost, quality, availability, and sustainability are carefully evaluated. Establishing reliable supplier relationships is paramount. Supply chain management plays a vital role here.
- Quality Control Planning: Establishing procedures and standards to ensure product quality throughout the entire process. This includes defining acceptable tolerances, implementing inspection protocols, and establishing corrective actions for defects.
2. Production and Manufacturing: Bringing the Plan to Life
This phase involves the actual transformation of raw materials into finished goods. Key aspects include:
- Material Handling and Storage: Efficiently managing the flow of materials through the production process, from storage to workstations and back. Proper inventory management and warehouse optimization are key.
- Manufacturing Operations: Executing the production plan, utilizing the chosen machinery, technology, and labor to transform raw materials according to the design specifications. This might involve various techniques like assembly, machining, casting, molding, etc., depending on the nature of the product.
- Quality Control and Inspection: Implementing the planned quality control measures throughout the production process. This involves regular inspections at various stages to identify and rectify defects early on.
- Production Scheduling and Monitoring: Tracking production progress, ensuring timely completion of orders, and adjusting schedules as needed to meet changing demands or address unforeseen issues. This involves close coordination between different departments and teams.
3. Packaging, Distribution, and Delivery: Reaching the End Customer
Once the product is manufactured, the process continues with:
- Packaging: Preparing the product for transportation and sale. This includes selecting appropriate packaging materials, labeling, and protecting the product from damage during shipping.
- Inventory Management: Effectively managing finished goods inventory, ensuring sufficient stock to meet customer demand without excessive warehousing costs.
- Distribution and Logistics: Coordinating the shipment of goods from the manufacturing facility to warehouses, distributors, and ultimately, the end customer. This involves selecting appropriate transportation modes and managing the logistics effectively.
- Customer Service and Support: Providing after-sales support and addressing customer queries or complaints related to the product. This helps to maintain customer satisfaction and build brand loyalty.
Key Considerations in Optimizing the Production Process
Optimizing the production process involves continuous improvement and adaptation. Several key factors need consideration:
1. Technology and Automation: Embracing Technological Advancements
Integrating advanced technologies like robotics, AI, and IoT can significantly enhance efficiency, accuracy, and productivity. Automation can streamline processes, reduce human error, and increase output. However, the initial investment can be significant, requiring careful evaluation of ROI.
2. Lean Manufacturing Principles: Minimizing Waste and Maximizing Efficiency
Implementing lean manufacturing techniques like Kaizen, 5S, and Six Sigma can significantly reduce waste in all forms—material, time, effort, and cost—leading to improved efficiency and profitability. These principles focus on continuous improvement and eliminating non-value-added activities.
3. Supply Chain Management: Ensuring a Smooth Flow of Materials
Effective supply chain management is crucial for securing reliable sources of raw materials, managing inventory effectively, and ensuring timely delivery. This involves strong relationships with suppliers, robust logistics systems, and risk management strategies.
4. Quality Management Systems: Prioritizing Quality and Consistency
Implementing a robust quality management system (QMS) ensures consistent product quality and customer satisfaction. This includes setting clear quality standards, conducting regular inspections, and implementing corrective actions to address defects. ISO 9001 certification is a widely recognized benchmark for quality management.
5. Workforce Training and Development: Investing in Human Capital
A skilled and well-trained workforce is essential for a successful production process. Investing in employee training and development programs can improve productivity, reduce errors, and enhance overall efficiency.
6. Data Analytics and Business Intelligence: Making Informed Decisions
Utilizing data analytics and business intelligence tools allows for monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs), identifying areas for improvement, and making informed decisions based on data-driven insights. This facilitates continuous improvement and optimization of the production process.
The Production Process and its Impact on the Broader Business Ecosystem
The production process isn't an isolated function; it's deeply interconnected with other aspects of the business, including:
- Marketing and Sales: The production process directly impacts the availability, pricing, and quality of products offered to the market. Effective production planning ensures that products are available when and where they are needed to meet customer demand.
- Finance: Production costs directly affect profitability. Efficient production processes reduce costs and improve margins. Accurate forecasting and inventory management help to optimize cash flow.
- Human Resources: The production process relies heavily on the skills and efficiency of the workforce. Effective HR practices, including recruitment, training, and compensation, are crucial for a successful production process.
- Research and Development (R&D): Continuous innovation and improvement of products and processes require ongoing investment in R&D. This involves exploring new technologies, materials, and production techniques.
- Sustainability: Increasingly, businesses are incorporating sustainability into their production processes. This involves reducing environmental impact, using eco-friendly materials, and implementing sustainable practices throughout the production lifecycle.
Conclusion: A Dynamic and Evolving Process
The production process is a dynamic and constantly evolving system that requires continuous monitoring, optimization, and adaptation to remain competitive. By understanding its various stages, key considerations, and impact on the broader business ecosystem, businesses can build a robust and efficient production system that drives profitability, customer satisfaction, and long-term success. The future of production lies in embracing technological advancements, implementing lean principles, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. Through these strategies, companies can navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape and thrive in an increasingly competitive market. Investing in a well-designed and optimized production process is not just a cost; it’s a strategic investment in the future of the business.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is True Of Psychologically Healthy People
Mar 29, 2025
-
The Ultimate Goal Of Lean Operations Is To Have
Mar 29, 2025
-
La Esposa De Mi Padre Pero No Soy Su Hijo
Mar 29, 2025
-
Informed Consent In Group Counseling Should Include
Mar 29, 2025
-
Middle Adulthood Is Referred To As The Sandwich Generation Because
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Production Process Is Part Of The . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
