The Ratio Of Actual Output To Effective Capacity Is
Breaking News Today
Apr 04, 2025 · 5 min read
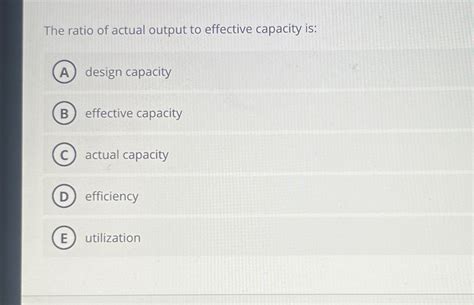
Table of Contents
The Ratio of Actual Output to Effective Capacity: Understanding Utilization and Its Implications
The ratio of actual output to effective capacity is a crucial metric in evaluating the efficiency and productivity of any operation, whether it's a manufacturing plant, a service business, or even a software development team. This ratio, often referred to as utilization, provides a clear picture of how well an organization is leveraging its available resources to achieve its goals. Understanding utilization is paramount for effective resource allocation, cost management, and strategic decision-making. This article delves deep into the concept of utilization, exploring its calculation, interpretation, and practical implications across various sectors.
Defining Actual Output and Effective Capacity
Before diving into the ratio itself, it's crucial to define its core components: actual output and effective capacity.
Actual Output: The Reality Check
Actual output refers to the real-world production achieved within a specific timeframe. This is the tangible result of the operational process, measured in units produced, services rendered, or tasks completed. It's a concrete figure reflecting the current operational performance, taking into account factors like machine downtime, employee absences, material shortages, and unforeseen bottlenecks. For instance, a factory's actual output could be 1000 units produced in a day, while a customer service department's actual output could be 500 calls handled.
Factors Affecting Actual Output:
- Machine breakdowns and maintenance: Unexpected equipment failures significantly reduce production capacity.
- Employee absenteeism and turnover: A shortage of skilled labor impacts productivity.
- Material shortages and supply chain disruptions: Lack of raw materials halts production.
- Process inefficiencies: Ineffective workflows and processes reduce output.
- Unforeseen circumstances: Unexpected events like power outages or natural disasters can cause disruptions.
Effective Capacity: The Potential Achievable
Effective capacity represents the maximum achievable output under ideal operating conditions. It accounts for planned downtime, scheduled maintenance, and other predictable factors that may reduce output. Unlike theoretical capacity (which considers absolute maximum output without any constraints), effective capacity incorporates realistic limitations to provide a more accurate representation of attainable performance. Effective capacity considers factors like planned maintenance, employee breaks, and reasonable production limits. For example, a factory might have an effective capacity of 1200 units per day, factoring in a one-hour lunch break and scheduled maintenance.
Calculating the Utilization Rate
The utilization rate is simply the ratio of actual output to effective capacity, expressed as a percentage:
Utilization Rate = (Actual Output / Effective Capacity) x 100%
For example:
- Actual Output: 1000 units
- Effective Capacity: 1200 units
- Utilization Rate: (1000 / 1200) x 100% = 83.33%
This indicates that the operation is utilizing 83.33% of its effective capacity.
Interpreting the Utilization Rate
The interpretation of the utilization rate depends heavily on the specific context and industry. A high utilization rate (e.g., above 90%) might suggest high efficiency and strong productivity. However, it could also indicate potential problems, such as insufficient capacity to meet future demand or a high risk of equipment breakdowns due to overuse. Conversely, a low utilization rate (e.g., below 70%) might indicate underutilized resources and potentially missed opportunities, inefficient processes, or poor demand forecasting.
Different Industries, Different Interpretations:
The optimal utilization rate varies significantly across industries. Highly capital-intensive industries like manufacturing often strive for higher utilization rates to maximize return on investment. However, in service industries, excessively high utilization rates might compromise service quality and customer satisfaction. Flexibility and responsiveness are often prioritized over maximizing utilization in these sectors.
High Utilization Rate Implications:
- High productivity: Efficient use of resources.
- Cost-effectiveness: Lower unit costs due to high volume.
- Potential for bottlenecks: Strain on resources and risk of breakdowns.
- Limited responsiveness: Difficulty in handling unexpected surges in demand.
Low Utilization Rate Implications:
- Underutilized resources: Wasted capacity and potential revenue loss.
- High unit costs: Increased overhead costs per unit.
- Excess capacity: Potential for cost savings through resource reduction.
- Improved responsiveness: Greater flexibility to handle fluctuations in demand.
Improving Utilization Rate: Strategies and Tactics
Improving the utilization rate requires a multi-pronged approach focusing on both increasing actual output and optimizing effective capacity.
Strategies to Increase Actual Output:
- Process optimization: Streamlining workflows, eliminating bottlenecks, and improving efficiency.
- Employee training and development: Enhancing employee skills and productivity.
- Inventory management: Ensuring timely availability of materials and reducing stockouts.
- Preventive maintenance: Reducing equipment downtime through regular maintenance.
- Technology upgrades: Implementing automation and other technologies to improve efficiency.
- Improved communication and collaboration: Enhancing teamwork and information sharing.
Strategies to Optimize Effective Capacity:
- Capacity planning: Accurately forecasting demand and adjusting capacity accordingly.
- Flexible capacity: Employing flexible working arrangements or outsourcing to adapt to fluctuating demand.
- Resource allocation: Optimizing the allocation of resources based on priorities and demand.
- Shift scheduling: Optimizing work schedules to maximize production during peak hours.
- Lean manufacturing principles: Adopting lean methodologies to eliminate waste and improve efficiency.
Utilizing Technology for Improved Utilization
Technology plays a critical role in monitoring, analyzing, and improving utilization rates. Software solutions can track actual output, predict demand, optimize resource allocation, and provide real-time insights into operational performance. Data analytics tools can identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement, leading to data-driven decision-making.
Utilization Rate and Business Decision-Making
The utilization rate is not merely a performance indicator; it's a crucial factor informing strategic business decisions. Understanding utilization helps businesses:
- Make informed investments: Determining whether to invest in new equipment, expand capacity, or improve existing processes.
- Optimize pricing strategies: Setting prices that reflect the efficient use of resources.
- Negotiate contracts: Establishing realistic timelines and deliverables.
- Plan for future growth: Accurately forecasting demand and ensuring sufficient capacity to meet future needs.
- Evaluate the performance of different departments or teams: Comparing utilization rates across various units to identify areas for improvement.
- Improve efficiency and profitability: Identifying and eliminating bottlenecks leads to cost reduction and higher profit margins.
Conclusion
The ratio of actual output to effective capacity, or utilization rate, is a critical metric for gauging operational efficiency and informing strategic decisions. Understanding and managing utilization requires a comprehensive approach, encompassing process optimization, resource allocation, capacity planning, and the effective use of technology. By consistently monitoring and improving the utilization rate, businesses can enhance productivity, reduce costs, and achieve sustainable growth. Regular analysis and adjustments are essential to maintain optimal utilization and adapt to changing market conditions. The pursuit of an optimal utilization rate should always be balanced with the need to maintain quality, customer satisfaction, and operational flexibility. Ultimately, the goal is not simply to maximize utilization, but to achieve a sustainable balance between efficiency and effectiveness.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Did Many Cubans Resent The Rule Of Fulgencio Batista
Apr 04, 2025
-
Linear Algebra And Its Applications 6th Edition Answers
Apr 04, 2025
-
Optic Nerve And Blood Vessels Enter The Eye At The
Apr 04, 2025
-
Alternating Current Is Normally Produced By A
Apr 04, 2025
-
Any External Force That Acts Against Movement Is Called
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Ratio Of Actual Output To Effective Capacity Is . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
