The Region Of High Hydrogen Ion Concentration Is The
Breaking News Today
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
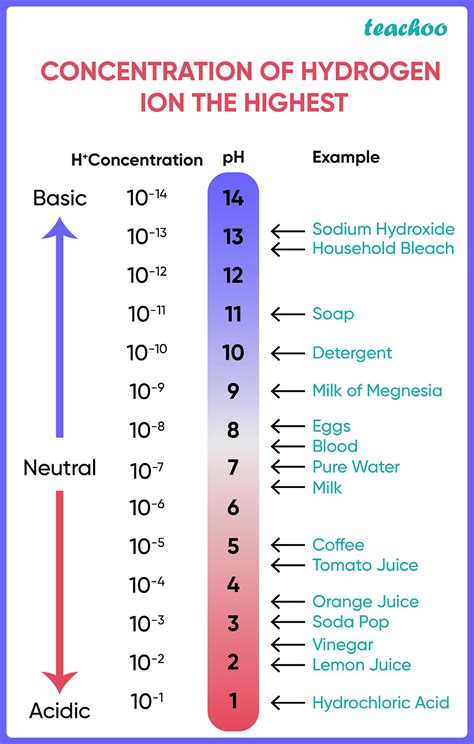
Table of Contents
The Region of High Hydrogen Ion Concentration is the: A Deep Dive into Acidity and its Biological Implications
The question, "The region of high hydrogen ion concentration is the...?" leads us directly to the concept of acidity. A region with a high concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) is, simply put, acidic. This seemingly simple statement, however, opens a door to a vast and complex world of chemical reactions, biological processes, and environmental impacts. Understanding acidity is crucial across multiple scientific disciplines, from chemistry and biology to environmental science and medicine.
Understanding pH and the Hydrogen Ion Concentration
The acidity or alkalinity of a solution is measured using the pH scale. This scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 representing neutrality. A pH less than 7 indicates acidity, while a pH greater than 7 indicates alkalinity (or basicity). The pH scale is logarithmic, meaning that each whole number change represents a tenfold change in hydrogen ion concentration. For instance, a solution with a pH of 3 is ten times more acidic than a solution with a pH of 4, and one hundred times more acidic than a solution with a pH of 5.
pH = -log₁₀[H+]
This equation highlights the inverse relationship between pH and hydrogen ion concentration ([H+]). A higher concentration of H+ ions results in a lower pH value, signifying increased acidity.
The Importance of pH Regulation
Maintaining the correct pH is critical for numerous biological processes. The human body, for example, tightly regulates its pH within a narrow range (around 7.35-7.45). Even slight deviations from this range can have severe consequences, leading to conditions like acidosis (low blood pH) or alkalosis (high blood pH). These conditions can disrupt enzyme function, impair cellular respiration, and ultimately threaten survival.
Many biological systems employ sophisticated buffering mechanisms to maintain a stable pH. Buffers are solutions that resist changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of acid or base. These buffering systems are crucial for protecting cells and tissues from the damaging effects of pH fluctuations.
Acidity in Different Biological Contexts
The significance of hydrogen ion concentration varies dramatically across different biological contexts. Let's explore some key examples:
1. The Stomach: A Highly Acidic Environment
The stomach is a prime example of a region with a high hydrogen ion concentration. The stomach's highly acidic environment, with a pH typically ranging from 1.5 to 3.5, is essential for several reasons:
-
Protein Digestion: The low pH activates pepsin, a crucial enzyme for protein breakdown. Pepsin's optimal activity occurs at low pH values, making the stomach's acidity crucial for efficient protein digestion.
-
Killing Pathogens: The acidic environment effectively kills many harmful bacteria and other pathogens ingested with food, preventing infections.
-
Nutrient Absorption: The acidity helps denature proteins, making them easier to digest and absorb.
2. Lysosomes: Cellular Recycling Centers
Lysosomes are organelles found within cells that act as cellular recycling centers. They contain a variety of hydrolytic enzymes that break down waste materials, cellular debris, and pathogens. The interior of lysosomes is highly acidic (pH around 4.5-5.0), creating an optimal environment for the activity of these enzymes. This acidic environment is essential for the efficient breakdown of waste materials, preventing cellular damage and maintaining cellular homeostasis.
3. Mitochondria: Powerhouses of the Cell
The mitochondria, often called the "powerhouses of the cell", are responsible for generating ATP, the primary energy currency of cells. While not as drastically acidic as the stomach or lysosomes, the mitochondrial matrix maintains a slightly acidic pH (around 7.0-8.0) influencing the efficiency of the electron transport chain and ATP synthesis. Maintaining this specific pH range is crucial for optimal energy production.
4. The Environment: Acid Rain and its Impacts
Acidity also plays a crucial role in environmental contexts. Acid rain, caused by the release of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere, significantly lowers the pH of water bodies like lakes and rivers. This increased acidity has devastating consequences for aquatic ecosystems, harming fish, plants, and other organisms. The increased acidity also impacts soil chemistry, altering nutrient availability and harming terrestrial ecosystems.
5. Industrial Processes: Utilizing Acidity
Acidity is not only significant in biological contexts but also finds widespread applications in industrial processes. Many industrial processes rely on controlling and utilizing acidic conditions to drive specific chemical reactions, improve product quality, or create desired byproducts. Examples include the production of fertilizers, the manufacturing of certain polymers, and various aspects of metal refining.
The Consequences of Imbalance: Acidosis and Alkalosis
As mentioned earlier, maintaining the correct pH is vital for biological systems. Imbalances can lead to serious health problems:
Acidosis: When pH Drops Too Low
Acidosis refers to a condition where the blood pH drops below 7.35. This can result from various causes, including:
-
Metabolic acidosis: This occurs due to an accumulation of acids or a loss of bicarbonate (a base) in the body. Common causes include kidney failure, diabetic ketoacidosis, and severe diarrhea.
-
Respiratory acidosis: This occurs due to impaired breathing, leading to a buildup of carbon dioxide (which forms carbonic acid in the blood). Common causes include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and pneumonia.
Symptoms of acidosis can include shortness of breath, confusion, headache, and fatigue. Severe acidosis can be life-threatening.
Alkalosis: When pH Rises Too High
Alkalosis, on the other hand, is a condition where the blood pH rises above 7.45. Similar to acidosis, this can result from various causes:
-
Metabolic alkalosis: This can occur due to excessive vomiting, excessive intake of antacids, or certain diuretics.
-
Respiratory alkalosis: This occurs due to hyperventilation (rapid breathing), which leads to excessive loss of carbon dioxide from the blood. Common causes include anxiety, high altitude, and certain lung diseases.
Symptoms of alkalosis can include dizziness, tingling in the extremities, muscle cramps, and confusion. Severe alkalosis can also be life-threatening.
Maintaining pH Balance: The Role of Buffers
The body employs sophisticated buffering systems to maintain a stable pH. These buffers act as chemical sponges, absorbing excess hydrogen ions or hydroxide ions (OH-) to prevent drastic pH changes. The primary buffer system in the blood is the bicarbonate buffer system, which involves carbonic acid (H₂CO₃) and bicarbonate ions (HCO₃⁻).
Other important buffer systems include the phosphate buffer system (found within cells) and protein buffer systems. These systems work together to maintain a relatively constant pH, protecting cells and tissues from the damaging effects of pH fluctuations.
Conclusion: The Significance of Hydrogen Ion Concentration
The region of high hydrogen ion concentration, therefore, represents an environment with significant biological and chemical implications. Understanding the complexities of acidity, pH regulation, and the consequences of pH imbalances is crucial in various fields. From understanding digestive processes and cellular function to addressing environmental challenges and developing new medical treatments, the study of hydrogen ion concentration continues to be a vital area of scientific inquiry. The implications span the spectrum from the microscopic world of cellular processes to the macroscopic impacts on global ecosystems. Further research into the intricate roles of acidity in biological systems will continue to unveil critical insights into the functioning of life itself.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not True About Machine Learning
Mar 28, 2025
-
On Net Does A Natural Disaster Create Jobs
Mar 28, 2025
-
The Initial Recording Of Information Into Memory Is Called
Mar 28, 2025
-
Your Meeting Notes Are Unclassified This Means
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Element Of A Story Is Most Clearly A Motif
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Region Of High Hydrogen Ion Concentration Is The . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
