The Total Rate Of Photosynthesis In A Given Area.
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
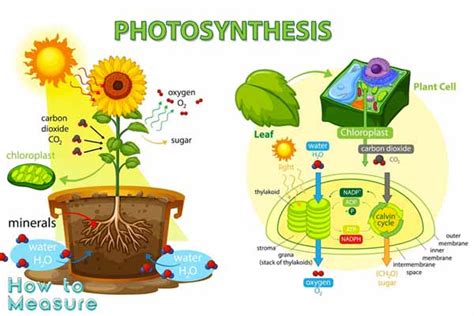
Table of Contents
The Total Rate of Photosynthesis in a Given Area: A Comprehensive Overview
Photosynthesis, the fundamental process by which green plants and other organisms convert light energy into chemical energy, is crucial for life on Earth. Understanding the total rate of photosynthesis within a specific area—a field, a forest, even a vast ocean—is vital for various reasons, from predicting crop yields to modeling climate change effects. This rate, often expressed as the total amount of carbon fixed per unit area per unit time (e.g., grams of carbon per square meter per day), is influenced by a complex interplay of factors. This article delves into the intricacies of measuring and understanding this crucial ecological parameter.
Factors Influencing the Total Rate of Photosynthesis
The total rate of photosynthesis in a given area isn't a static value; it fluctuates constantly depending on a multitude of interacting factors. These factors can be broadly categorized as:
1. Environmental Factors:
-
Light Intensity: This is arguably the most significant factor. Photosynthesis rates generally increase with light intensity up to a saturation point, beyond which further increases in light have little effect. Too much light, however, can lead to photoinhibition, damaging the photosynthetic machinery. The spectral quality of light also matters, with plants showing varying responses to different wavelengths.
-
Temperature: Enzymes involved in photosynthesis have optimal temperature ranges. Temperatures too high or too low can denature enzymes, reducing photosynthetic efficiency. Extreme temperatures can also damage plant tissues.
-
Water Availability: Water is essential for photosynthesis; it's a reactant in the process. Water stress reduces stomatal conductance, limiting CO2 uptake and hindering photosynthesis. Soil moisture content directly impacts plant water status.
-
Carbon Dioxide Concentration: CO2 is another crucial reactant. Increased atmospheric CO2 levels generally boost photosynthesis rates, although other factors like nutrient availability can limit this effect. CO2 diffusion into leaves is influenced by stomatal aperture and boundary layer conductance.
-
Nutrient Availability: Essential nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus are vital components of chlorophyll and other photosynthetic enzymes. Nutrient deficiencies can significantly limit photosynthetic capacity. Soil fertility and nutrient uptake mechanisms are key here.
2. Biological Factors:
-
Plant Species: Different plant species have different photosynthetic capacities. C3, C4, and CAM plants exhibit distinct photosynthetic pathways, each adapted to different environmental conditions. This leads to significant variation in photosynthetic rates across different plant communities.
-
Plant Density and Structure: The density and arrangement of plants within an area affect light interception and therefore overall photosynthetic rates. Canopy structure influences the distribution of light within the plant community, leading to light competition and shading.
-
Plant Age and Health: Young, healthy plants generally exhibit higher photosynthetic rates than older or stressed plants. Disease and pest infestations can severely impair photosynthetic efficiency.
Measuring the Total Rate of Photosynthesis
Accurately measuring the total rate of photosynthesis in a given area is a complex undertaking. Several approaches are used, each with its strengths and limitations:
1. Direct Measurement Techniques:
-
Gas Exchange Systems: These systems measure the uptake of CO2 and release of O2 by plants in a controlled environment (e.g., a cuvette enclosing a leaf or a branch). Data are extrapolated to estimate the total rate for the entire area, but this requires careful sampling and scaling-up procedures. The limitations include the inability to easily measure photosynthesis in large areas and the potential for disturbance of the natural environment during measurement.
-
Remote Sensing: Satellite and airborne sensors can measure vegetation indices like Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), which are correlated with photosynthetic activity. This technique allows for large-scale monitoring, but it relies on indirect measurements and can be affected by atmospheric conditions and sensor limitations. Resolution is a critical factor influencing the accuracy of large-scale estimations.
2. Indirect Measurement Techniques:
-
Biomass Production: Measuring the increase in plant biomass over time provides an estimate of the total amount of carbon fixed through photosynthesis. This is a simple approach, but it only captures net photosynthesis (gross photosynthesis minus respiration). Decomposition and other losses also influence biomass estimations.
-
Stable Isotope Analysis: Analyzing the isotopic ratios of carbon (¹³C/¹²C) in plant tissues can provide information about photosynthetic pathways and potentially, photosynthetic rates. This approach is particularly useful for distinguishing between different plant types and understanding their adaptation to different environmental conditions. However, interpreting the data requires specialized knowledge and assumptions about metabolic pathways.
Applications and Significance
Understanding the total rate of photosynthesis in a given area has broad implications across various scientific disciplines:
1. Agriculture:
Accurate assessment of photosynthesis is crucial for optimizing crop yields. By understanding the limiting factors and improving growing conditions, farmers can increase photosynthetic rates and improve crop productivity. Precision agriculture utilizes remote sensing and other techniques to monitor photosynthetic activity and manage inputs more efficiently.
2. Ecology:
Photosynthesis plays a fundamental role in ecosystem functioning. Measuring photosynthetic rates helps assess the primary productivity of ecosystems, understand carbon cycling, and evaluate the impacts of environmental changes. Conservation efforts rely on understanding the health and productivity of ecosystems, which are directly linked to photosynthetic rates.
3. Climate Change Research:
Photosynthesis is a key process in the global carbon cycle. Changes in photosynthetic rates due to climate change can have profound impacts on atmospheric CO2 levels and global climate. Climate models incorporate photosynthetic rates as a key component to project future climate scenarios. Understanding changes in photosynthetic capacity helps predict the capacity of ecosystems to absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide.
4. Forestry:
Assessing the photosynthetic capacity of forests is vital for forest management and conservation. Measuring photosynthetic rates helps in evaluating forest health, predicting timber yields, and assessing the carbon sequestration potential of forests. Sustainable forest management strategies are informed by monitoring the photosynthetic capacity of forest ecosystems.
Challenges and Future Directions
While significant progress has been made in measuring and understanding photosynthesis, several challenges remain:
-
Scaling up from leaf to ecosystem level: Extrapolating measurements from individual leaves or small plots to entire ecosystems requires sophisticated modelling and careful consideration of spatial heterogeneity.
-
Accounting for environmental variability: Photosynthetic rates are highly dynamic and influenced by numerous interacting factors. Developing accurate models that capture this complexity is challenging.
-
Integrating different measurement techniques: Combining data from different measurement techniques (e.g., gas exchange, remote sensing, biomass production) is crucial for comprehensive understanding but requires careful data integration and validation.
-
Improving remote sensing technologies: Advances in remote sensing technology, including higher spatial and temporal resolution sensors, are needed to improve the accuracy and scalability of large-scale photosynthetic rate assessments.
The development of advanced modelling techniques, coupled with improved measurement technologies, will be crucial for advancing our understanding of the total rate of photosynthesis in given areas. This knowledge is essential for addressing key challenges related to food security, climate change, and ecosystem conservation. Continued research in this field is crucial for a sustainable future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
Life Insurance Exam Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Direct Carry Is Used To Transfer A Patient
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Emancipation Proclamation Of January 1 1863 Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
These Cards Will Get You Drunk Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Total Rate Of Photosynthesis In A Given Area. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
