The Usual Starting Point For A Master Budget Is
Breaking News Today
Mar 30, 2025 · 7 min read
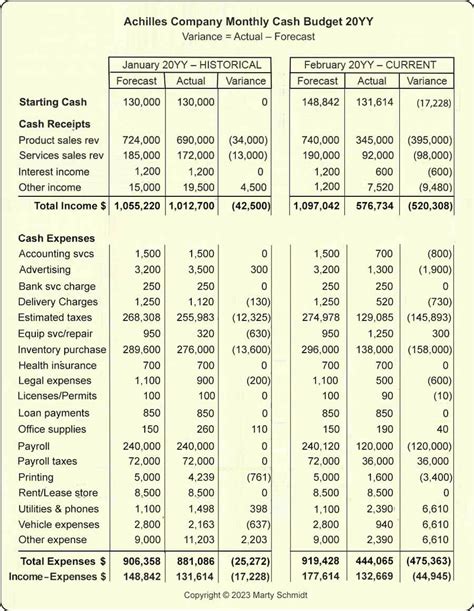
Table of Contents
The Usual Starting Point for a Master Budget: A Comprehensive Guide
Creating a master budget is crucial for any organization, large or small, aiming for financial stability and growth. But where do you begin? This comprehensive guide will delve into the usual starting point for a master budget, exploring the process step-by-step, highlighting key considerations, and offering practical advice to ensure your budget is both accurate and effective.
Understanding the Master Budget: The Big Picture
Before we dive into the starting point, let's clarify what a master budget is. It's not just a single document; it's a comprehensive compilation of all the individual budgets within an organization. Think of it as the overarching financial plan, integrating various departmental budgets into a cohesive whole. This integration allows for a holistic view of the organization's financial health and future projections. A well-structured master budget provides a roadmap for achieving strategic goals, enabling informed decision-making and proactive financial management.
A typical master budget includes, but isn't limited to:
- Sales Budget: Forecasts sales revenue based on market analysis, sales history, and anticipated growth. This is often the foundation upon which the entire master budget is built.
- Production Budget: Determines the quantity of goods to be produced based on the sales budget and desired inventory levels. This budget considers factors such as production capacity and material requirements.
- Direct Materials Budget: Calculates the cost of raw materials needed for production, considering factors such as material costs, waste, and inventory levels.
- Direct Labor Budget: Estimates the labor costs associated with production, including wages, benefits, and overtime.
- Manufacturing Overhead Budget: Includes all indirect manufacturing costs, such as factory rent, utilities, and maintenance.
- Selling and Administrative Expense Budget: Covers all expenses related to selling and administrative functions, such as marketing, sales salaries, and office rent.
- Cash Budget: Projects cash inflows and outflows, ensuring sufficient cash flow to meet operational needs. This is crucial for managing liquidity and avoiding cash shortages.
- Capital Expenditure Budget: Outlines planned investments in fixed assets, such as equipment and property.
- Pro Forma Financial Statements: Projects the company's financial statements (income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement) based on the budgeted figures. These statements provide a clear financial picture of the projected future.
The Usual Starting Point: The Sales Budget – The Foundation of Financial Planning
The usual and most crucial starting point for a master budget is the sales budget. This is because all other budgets are directly or indirectly dependent on the anticipated sales revenue. An inaccurate sales forecast can cascade into errors throughout the entire budgeting process, leading to flawed financial projections and potentially disastrous consequences.
Developing a Realistic Sales Budget: Key Considerations
Creating a robust sales budget requires careful consideration of several key factors:
- Market Research: Thorough market research is essential to understand market trends, competitor activities, and customer demand. This involves analyzing market size, growth potential, and customer segments.
- Sales History: Review past sales data to identify trends, seasonality, and growth patterns. This provides a valuable baseline for forecasting future sales.
- Sales Forecasts: Develop realistic sales forecasts based on market research and historical data. This involves considering various scenarios and potential risks.
- Pricing Strategies: Determine appropriate pricing strategies that balance profitability with market competitiveness.
- Sales Channels: Identify the most effective sales channels to reach target customers, considering online and offline options.
- Sales Team Capabilities: Assess the sales team's capacity to achieve the projected sales targets. This involves considering team size, experience, and training.
Breaking Down the Sales Budget: Detail is Key
The sales budget shouldn't be a single, overarching figure. Instead, it should be broken down into granular detail. This might include:
- Product-Specific Sales: Forecast sales for each individual product or service.
- Geographic Segmentation: Project sales by region or market segment.
- Customer Segmentation: Forecast sales based on different customer groups.
- Time-Based Projections: Develop monthly or quarterly sales forecasts to capture seasonality and fluctuations.
This detailed approach allows for a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of anticipated sales revenue and its impact on other budgets.
From Sales to the Rest: Building the Master Budget
Once the sales budget is finalized, it serves as the foundation for developing other budgets:
1. Production Budget: Meeting Sales Demand
The production budget determines the number of units to be produced to meet the sales forecast. This considers:
- Sales Forecast: The primary driver of the production budget.
- Desired Inventory Levels: Maintaining optimal inventory levels is essential to avoid stockouts and excessive holding costs.
- Production Capacity: Ensure that production capacity is sufficient to meet the planned production volume.
2. Direct Materials, Labor, and Overhead Budgets: Costing the Production
With the production budget in place, the next step is to estimate the costs associated with production:
- Direct Materials Budget: Calculates the cost of raw materials required for production, considering material costs, waste, and inventory levels.
- Direct Labor Budget: Estimates the labor costs based on the production volume and labor rates.
- Manufacturing Overhead Budget: Includes all indirect manufacturing costs, such as rent, utilities, and maintenance. These costs are usually allocated to products based on a predetermined allocation method.
3. Selling and Administrative Expense Budget: Supporting Operations
This budget covers all expenses related to selling and administrative functions:
- Marketing Expenses: Includes advertising, promotions, and sales commissions.
- Sales Salaries: Covers the salaries and benefits of the sales team.
- General and Administrative Expenses: Includes rent, utilities, and other administrative costs.
4. Cash Budget: Maintaining Liquidity
The cash budget is crucial for managing liquidity and ensuring sufficient cash flow to meet operational needs:
- Cash Inflows: Includes cash from sales, collections from accounts receivable, and other sources.
- Cash Outflows: Includes payments for purchases, salaries, rent, and other expenses.
- Net Cash Flow: The difference between cash inflows and outflows. This indicates whether the organization will have sufficient cash on hand to meet its obligations.
5. Capital Expenditure Budget: Investing for the Future
This budget outlines planned investments in fixed assets:
- Equipment Purchases: Includes purchases of new equipment and machinery.
- Building Improvements: Includes renovations, expansions, and other improvements.
- Other Capital Investments: Includes other significant capital investments.
6. Pro Forma Financial Statements: Projecting the Future
Finally, the master budget culminates in the preparation of pro forma financial statements:
- Pro Forma Income Statement: Projects the company's income for the budget period.
- Pro Forma Balance Sheet: Projects the company's assets, liabilities, and equity at the end of the budget period.
- Pro Forma Cash Flow Statement: Projects the company's cash inflows and outflows for the budget period.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Budgeting Techniques and Considerations
While the sales budget serves as the foundation, creating a truly effective master budget requires considering several advanced techniques and factors:
- Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB): This approach requires justifying every expense item from scratch, rather than simply adjusting previous budgets. It encourages efficiency and cost reduction.
- Activity-Based Budgeting (ABB): This method links budget allocations to specific activities and their associated costs, providing a more accurate cost allocation.
- Rolling Forecasts: Instead of a static annual budget, rolling forecasts update the budget on a regular basis (e.g., monthly or quarterly), incorporating the most recent data and market conditions.
- Sensitivity Analysis: This technique evaluates the impact of changes in key assumptions (e.g., sales volume, costs) on the overall budget. This helps identify potential risks and opportunities.
- Variance Analysis: Comparing actual results to budgeted figures to identify variances and investigate their causes. This is crucial for performance monitoring and corrective actions.
Conclusion: Mastering the Master Budget
Creating a master budget is a comprehensive process requiring careful planning, detailed analysis, and effective communication. While the sales budget provides the crucial starting point, its success relies on the accurate and integrated development of all other component budgets. By incorporating advanced techniques and consistently monitoring performance, organizations can leverage the master budget to achieve their financial goals, optimize resource allocation, and ensure long-term sustainability. Remember, a well-crafted master budget is not just a static document; it's a dynamic tool for guiding strategic decision-making and ensuring financial success.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Definition Of Leadership Usually Seen In The Literature Is
Apr 01, 2025
-
Anaphylaxis Is Most Accurately Defined As A N
Apr 01, 2025
-
Why Did California Adopt The Master Plan For Higher Education
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True About Xml
Apr 01, 2025
-
Netflix Launched In The 1990s Offering Customers
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Usual Starting Point For A Master Budget Is . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
