The Visceral Pericardium Is The Same As The
Breaking News Today
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
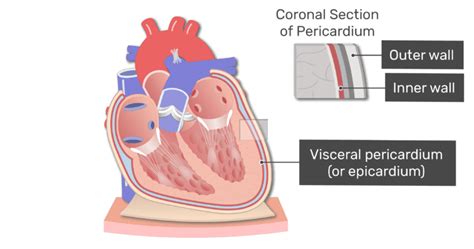
Table of Contents
The Visceral Pericardium: Understanding Its Identity and Relationship to the Heart
The visceral pericardium, also known as the epicardium, isn't "the same as" any other single structure, but rather a crucial part of a larger structure – the pericardium itself. Understanding its unique role requires exploring the pericardium's anatomy and function as a whole. This article will delve deep into the visceral pericardium, clarifying its identity, function, and its intimate relationship with the heart.
Understanding the Pericardium: A Protective Sac
The pericardium is a double-walled sac that encloses the heart and the roots of the great vessels (the aorta, pulmonary artery, venae cavae, and pulmonary veins). Its primary function is to protect the heart, providing a lubricated environment to minimize friction during its constant contractions. This protective sac is composed of two main layers:
1. The Parietal Pericardium: The Outer Layer
The parietal pericardium is the tough, fibrous outer layer of the pericardium. It's a strong, inelastic sac that provides structural support and anchors the heart within the mediastinum (the central compartment of the thoracic cavity). This layer helps prevent overdistension of the heart.
2. The Visceral Pericardium (Epicardium): The Inner Layer
This is where we focus our attention. The visceral pericardium, also known as the epicardium, is the innermost layer of the pericardium. It's not merely a separate sac; it's actually the outermost layer of the heart wall itself. This crucial distinction clarifies its identity. It's not the same as the parietal pericardium; rather, it's the part of the pericardium directly fused with the heart. Think of it as the heart's outermost protective covering, intimately integrated with its structure.
The Epicardium: More Than Just a Layer
The epicardium isn't just a passive protective layer. It's a dynamic structure with several important functions:
1. Protection: The First Line of Defense
As the outermost layer of the heart, it provides a physical barrier against infection and injury. This protective role is crucial in safeguarding the delicate cardiac muscle underneath.
2. Coronary Arteries and Veins: The Heart's Lifeline
The epicardium houses the coronary arteries and veins, which are responsible for supplying the heart muscle with oxygenated blood and removing waste products. These vessels are embedded within the epicardial fat, a layer of adipose tissue that cushions the heart and helps regulate its temperature. Damage to the epicardium can compromise the integrity of these vital blood vessels.
3. Nervous Innervation: Controlling the Heartbeat
The epicardium also contains a significant component of the heart's nervous system, including nerve fibers and ganglia. These structures play a critical role in regulating the heart rate and contractility. This neural network ensures the heart functions smoothly and efficiently.
4. Role in Cardiac Regeneration: Ongoing Research
Recent research is exploring the epicardium's role in cardiac regeneration. Studies suggest that epicardial cells can contribute to the formation of new cardiac muscle cells, potentially offering new avenues for treating heart damage and disease. This exciting area of research highlights the dynamic nature of this often-overlooked layer.
The Pericardial Cavity: A Lubricated Space
Between the parietal and visceral pericardia lies the pericardial cavity, a potential space filled with a small amount of pericardial fluid. This fluid acts as a lubricant, minimizing friction between the heart and the surrounding pericardium during each heartbeat. This lubrication is crucial for preventing damage from the constant movement of the heart. The integrity of both the parietal and visceral pericardium is essential to maintaining this vital lubrication.
Clinical Significance: Pericardial Diseases
Disorders affecting the pericardium, including the visceral pericardium, can have serious consequences. These include:
1. Pericarditis: Inflammation of the Pericardium
Pericarditis is an inflammation of the pericardium, potentially impacting both the parietal and visceral layers. The inflammation causes pain and can lead to fluid buildup in the pericardial cavity (pericardial effusion). Severe cases can result in cardiac tamponade, a life-threatening condition where the fluid accumulation compresses the heart, hindering its ability to pump effectively.
2. Pericardial Effusion: Fluid Buildup
Pericardial effusion refers to an abnormal accumulation of fluid within the pericardial cavity. This can result from various underlying conditions, including infection, inflammation, or cancer. As mentioned above, large effusions can lead to cardiac tamponade.
3. Cardiac Tamponade: A Life-Threatening Condition
Cardiac tamponade is a medical emergency caused by excessive fluid accumulation within the pericardial cavity. The compression of the heart impairs its ability to fill with blood, leading to a dramatic drop in cardiac output and potentially death. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial.
Differentiating the Visceral Pericardium from Other Structures
It's important to reiterate that the visceral pericardium (epicardium) is not interchangeable with other structures. While it's part of the pericardium, it's fundamentally different from the parietal pericardium. It's also distinct from the other layers of the heart wall: the myocardium (cardiac muscle) and the endocardium (inner lining of the heart chambers). Understanding these distinctions is critical for accurate anatomical and clinical interpretation.
The Visceral Pericardium: An Integral Part of Cardiac Health
The visceral pericardium, or epicardium, isn't just a passive protective layer; it's an active participant in cardiac function. Its role in protecting the heart, housing coronary vessels and nerves, and potentially contributing to cardiac regeneration highlights its crucial significance. Understanding its unique identity and function is essential for comprehending the overall health and well-being of the heart. Disorders affecting the pericardium can have serious consequences, emphasizing the importance of early detection and treatment. Further research into the epicardium’s potential role in cardiac repair holds exciting promise for future advancements in cardiovascular medicine. This detailed exploration should provide a comprehensive understanding of the visceral pericardium and its vital role in maintaining a healthy heart.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Food Safety Policy Is A Statement That Lists
Mar 16, 2025
-
Which Is An Example Of An Expressed Power Congress Holds
Mar 16, 2025
-
Which Medication May Cause Photophobia As An Adverse Effect
Mar 16, 2025
-
Which Of These Organelles Produces H2o2 As A By Product
Mar 16, 2025
-
Which Statement Is An Example Of Personification
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Visceral Pericardium Is The Same As The . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
